The 450s decade ran from January 1, 450, to December 31, 459.
The 460s decade ran from January 1, 460, to December 31, 469.

Year 456 (CDLVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Avitus without colleague. The denomination 456 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.

Ricimer was a Romanized Germanic general who effectively ruled the remaining territory of the Western Roman Empire from 456 after defeating Avitus, until his death in 472, with a brief interlude in which he contested power with Anthemius. Deriving his power from his position as magister militum of the Western Empire, Ricimer exercised political control through a series of puppet emperors. Ricimer's death led to unrest across Italy and the establishment of a Germanic kingdom on the Italian Peninsula.

Majorian was the Western Roman emperor from 457 to 461. A prominent commander in the Western military, Majorian deposed Avitus in 457 with the aid of his ally Ricimer at the Battle of Placentia. Possessing little more than Italy and Dalmatia, as well as some territory in Hispania and northern Gaul, Majorian campaigned rigorously for three years against the Empire's enemies. In 461, he was murdered at Dertona in a conspiracy, and his successors until the Fall of the Empire in 476 were puppets either of barbarian generals or the Eastern Roman court.

Procopius Anthemius was the Western Roman emperor from 467 to 472. Born in the Eastern Roman Empire, Anthemius quickly worked his way up the ranks. He married into the Theodosian dynasty through Marcia Euphemia, daughter of Eastern emperor Marcian. He soon received a significant number of promotions to various posts, and was presumed to be Marcian's planned successor. However, Marcian's sudden death in 457, together with that of Western emperor Avitus, left the imperial succession in the hands of Aspar, who instead appointed Leo, a low-ranking officer, to the Eastern throne, probably out of fear that Anthemius would be too independent. Eventually, this same Leo designated Anthemius as Western emperor in 467, following a two-year interregnum that started in November 465.

Eparchius Avitus was Roman emperor of the Western Empire from July 455 to October 456. He was a senator of Gallic extraction and a high-ranking officer both in the civil and military administration, as well as Bishop of Piacenza.

In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. Particularly during the period from AD 395 to 476, there were separate, coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire into the Western provinces and the Eastern provinces with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were de facto independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts for administrative expediency. The Western Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna disappeared by AD 554, at the end of Justinian's Gothic War.

The Sack of Rome in 455 AD was carried out by the Vandals led by their king Genseric.

Marcellinus was a Roman general and patrician who ruled over the region of Dalmatia in the Western Roman Empire and held sway with the army there from 454 until his death. Governing Dalmatia both independently from, and under, six Emperors during the twilight of the Western Empire, Marcellinus proved to be an able administrator and military personality with sources making reference that he ruled justly and well and kept Dalmatia independent of the emperor and of barbarian rulers.
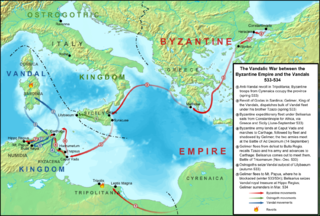
The Vandalic War was a conflict fought in North Africa between the forces of the Eastern Roman Empire and the Vandalic Kingdom of Carthage in 533–534. It was the first of Justinian I's wars of the reconquest of the Western Roman Empire.
Gaiseric, also known as Geiseric or Genseric was king of the Vandals and Alans from 428 to 477. He ruled over a kingdom and played a key role in the decline of the Western Roman Empire during the 5th century.

The Battle of Cape Bon was an engagement during a joint military expedition of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires led by Basiliscus against the Vandal capital of Carthage in 468. The invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals was one of the largest amphibious operations in antiquity, with 1,113 ships and over 50,000 personnel.
The Battle of Agrigentum was fought in 456 A.D. at Agrigentum, now Agrigento in modern-day Sicily. An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the general Ricimer, drove off an invading force, a fleet of sixty ships, sent by the Vandal king Gaiseric to raid Sicily. Ricimer then led the Roman fleet against the Vandals and defeated them in a naval battle off the coast of Corsica. The victory gave the Romans only temporary relief from Vandal raids.
The Battle of Campi Canini was fought between the Alemanni and the Western Roman Empire in 457. Taking advantage of the confusion after the defeat of Emperor Avitus at Placentia on 16 October 456, an Alemannic army crossed the Rhaetian Alps through Switzerland into Italy, reaching Lake Maggiore. At nearby Campi Cannini, the Alemanni were defeated by the Roman officer Burco, in the name of the usurper Majorian.

The Gothic War of 457-458 was a military conflict between the Visigoths of Theoderic II against the Western Roman Empire of Emperor Majorian. The war began in 457 with a revolt of the Goths in Aquitania that pushed aside Roman authority, followed by an aggressive conquest in the adjacent Septimania aimed at area expansion. The war ended with a Roman victory over the Goths in the Battle of Arles in 458.

The Roman Civil War of 456 was a civil war fought in the Western Roman Empire during the second half of 456 AD.

The Vandal War (461–468) was a long-term conflict between the two halves of the Roman Empire on the one hand and the Vandals in North Africa on the other. This war revolved around hegemony in the Mediterranean and the empire of the west. The Vandals as a rising power posed an enormous threat to the stability of the Roman Empire. Piracy and plunder were a scourge, threatening trade throughout the Mediterranean. The Roman war effort from 466 onwards was aimed at the destruction of the Vandal Kingdom in order to restore the empire to its original territory. Armed conflicts alternated with peace talks and the two parts of the Roman Empire did not always act in unison.













