
Francesco I Sforza was an Italian condottiero who founded the Sforza dynasty in the duchy of Milan, ruling as its (fourth) duke from 1450 until his death.

Federico da Montefeltro, also known as Federico III da Montefeltro KG, was one of the most successful mercenary captains (condottieri) of the Italian Renaissance, and lord of Urbino from 1444 until his death. A renowned intellectual humanist and civil leader in Urbino on top of his impeccable reputation for martial skill and honour, he commissioned the construction of a great library, perhaps the largest of Italy after the Vatican, with his own team of scribes in his scriptorium, and assembled around him a large humanistic court in the Ducal Palace, Urbino, designed by Luciano Laurana and Francesco di Giorgio Martini.

The Duchy of Milan was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277.

Filippo Maria Visconti was the duke of Milan from 1412 to 1447. Reports stated that he was "paranoid", but "shrewd as a ruler." He went to war in the 1420s with Romagna, Florence, and Venice in the Wars in Lombardy but was eventually forced to surrender under Pope Martin V. He would return to war again, where another peace agreement was required to stop the war. He married twice. Her second wife was Marie, from which he married in 1448. She was the daughter of his ally Amadeus VIII. When he died, Fillippo was the last of the Visconti male line and was succeeded by Francesco Sforza, husband to his daughter.

Niccolò Piccinino was an Italian condottiero.
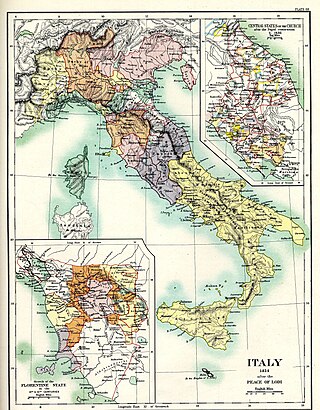
The Treaty of Lodi, or Peace of Lodi, was a peace agreement to put an end to the Wars in Lombardy between the Venetian Republic and the Duchy of Milan, signed in the city of Lodi on 9 April 1454.

Ghedi is a town and comune in the province of Brescia, in Lombardy, Italy. It received the honorary title of city with a presidential decree on November 24, 2001.

The Golden Ambrosian Republic was a short-lived republic founded in Milan by members of the University of Pavia with popular support, during the first phase of the Milanese War of Succession. With the aid of Francesco Sforza they held out against the forces of the Republic of Venice, but after a betrayal Sforza defected and captured Milan to become Duke himself, abolishing the Republic.

The Italian Wars of 1499–1504 are divided into two connected, but distinct phases: the Second Italian War (1499–1501), sometimes known as Louis XII's Italian War, and the Third Italian War (1502–1504) or War over Naples. The first phase was fought for control of the Duchy of Milan by an alliance of Louis XII of France and the Republic of Venice against Ludovico Sforza, the second between Louis and Ferdinand II of Aragon for possession of the Kingdom of Naples.

Bianca Maria Visconti also known as Bianca Maria Sforza or Blanca Maria was Duchess of Milan from 1450 to 1468 by marriage to Francesco I Sforza. She was regent of Marche during the absence of her spouse in 1448. She served as Regent of the Duchy of Milan during the illness of her spouse in 1462, as well as in 1466, between the death of her spouse and until her son, the new Duke, who was absent, was able to return to Milan to assume power.

The Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy. They lasted from 1423 until the signing of the Treaty of Lodi in 1454. During their course, the political structure of Italy was transformed: out of a competitive congeries of communes and city-states emerged the five major Italian territorial powers that would make up the map of Italy for the remainder of the 15th century and the beginning of the Italian Wars at the turn of the 16th century. They were Venice, Milan, Florence, the Papal States and Naples. Important cultural centers of Tuscany and Northern Italy—Siena, Pisa, Urbino, Mantua, Ferrara—became politically marginalized.

Alessandro Sforza was an Italian condottiero and lord of Pesaro, the first of the Pesaro line of the Sforza family.

Micheletto Attendolo, also called Micheletto da Cotignola, was an Italian condottiero. He was seigneur of Acquapendente, Potenza, Alianello, Castelfranco Veneto and Pozzolo Formigaro.

Francesco Piccinino was an Italian condottiero.
The War of L'Aquila was a conflict in 15th-century Italy. It started in 1423 as a personal conflict against the condottiero Braccio da Montone and the city of L'Aquila in Abruzzo, but later turned into a national conflict when the forces of the Duchy of Milan, the Republic of Florence, the Papal States, and the Kingdom of Naples were also involved. Braccio da Montone was killed in the final battle near L'Aquila.
The Milanese War of Succession was a war of succession over the Duchy of Milan from the death of duke Filippo Maria Visconti on 13 August 1447 to the Treaty of Lodi on 9 April 1454.
The first siege of Pontevico was fought between 6 and 8 June 1452 at Pontevico (Lombardy) between the armies of the Duchy of Milan and that of Republic of Venice, an episode of the Wars in Lombardy.
The second siege of Pontevico was fought between 25 and 29 may 1453 at Pontevico (Lombardy) between the armies of the Duchy of Milan and that of Republic of Venice, an episode of the Wars in Lombardy.
The third siege of Pontevico was fought between 16 and 19 October 1453 at Pontevico (Lombardy) between the armies of the Duchy of Milan and that of Republic of Venice, an episode of the Wars in Lombardy.












