
Benito Pablo Juárez García was a Mexican politician, military commander, and lawyer who served as the 26th president of Mexico from 1858 until his death in office in 1872. A Zapotec, he was the first Indigenous president of Mexico and the first democratically elected Indigenous president in the postcolonial Americas. A member of the Liberal Party, he previously held a number of offices, including the governorship of Oaxaca and the presidency of the Supreme Court. During his presidency, he led the Liberals to victory in the Reform War and in the Second French intervention in Mexico.

Ignacio Zaragoza Seguín was a Mexican Army officer and politician. He is best known for leading a Mexican army of 3,791 men which defeated a 5,730-strong force of French troops at the battle of Puebla on May 5, 1862 during the second French intervention in Mexico. The Mexican victory is celebrated annually as Cinco de Mayo.

Miguel Gregorio de la Luz Atenógenes Miramón y Tarelo, known as Miguel Miramón, was a Mexican conservative general who disputed the Mexican presidency with Benito Juarez at the age of twenty seven during the Reform War, serving between February 1859 and December 1860. He was the first Mexican president to be born after the Mexican War of Independence.

The Home Squadron was part of the United States Navy in the mid-19th century. Organized as early as 1838, ships were assigned to protect coastal commerce, aid ships in distress, suppress piracy and the Atlantic slave trade, make coastal surveys, and train ships to relieve others on distant stations. It was discontinued in 1861 after the outbreak of the American Civil War, when the Union blockade forced a reassignment of ships to close off Southern ports.

Félix María Zuloaga Trillo (1813–1898) was a Mexican conservative general and politician who played a key role in the outbreak of the Reform War in early 1860, a war which would see him elevated to the presidency of the nation. President Zuloaga was unrecognized by and fought against the liberals supporters of President Benito Juarez.

Manuel Robles Pezuela was a military engineer, military commander, and eventually interim president of Mexico during a civil war, the War of Reform, being waged between conservatives and liberals, in which he served as president of the Conservatives, in opposition to President Benito Juarez, head of the Liberals.

José Tomás de la Luz Mejía Camacho, better known as Tomás Mejía, was a Mexican soldier of Otomi background, who consistently sided with the Conservative Party throughout its nineteenth century conflicts with the Liberals.
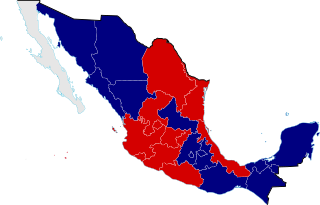
The Reform War, or War of Reform, also known as the Three Years' War, and the Mexican Civil War, was a complex civil conflict in Mexico fought between Mexican liberals and conservatives with regional variations over the promulgation of Constitution of 1857. It has been called the "worst civil war to hit Mexico between the War of Independence of 1810–21 and the Revolution of 1910–20". Following the liberals' overthrow of the dictatorship of conservative Antonio López de Santa Anna, liberals passed a series of laws codifying their political program. These laws were incorporated into the new constitution. It aimed to limit the political power of the executive branch, as well as the political, economic, and cultural power of the Catholic Church. Specific measures were the expropriation of Church property; separation of church and state; reduction of the power of the Mexican Army by elimination of their special privileges; strengthening the secular state through public education; and measures to develop the nation economically.

The Federal War — also known as the Great War or the 5 Year War — was a civil war in Venezuela between the Conservative Party and the Liberal Party over the monopoly the Conservatives held over government positions and land ownership, and their intransigence in granting any reforms. This drove the Liberals – known as the Federalists – to look for greater autonomy for the provinces: a new federalism for Venezuela, as it were. It was the biggest and bloodiest civil war that Venezuela had since its independence from Spain on 5 July 1811. Around a hundred thousand people died in the violence of the war, or from hunger or disease, in a country with a population of just over a million people.

Jocotitlán is a municipality located in the northwestern part of the State of Mexico on the central highlands of the country of Mexico. The municipal seat is the town of Jocotitlán and is located at the foot of the Jocotitlán or Xocotépetl volcano, while most of the rest of the municipality is in the Ixtlahuaca Valley. The area has culturally been Mazahua since the pre-Hispanic period, with this indigenous group's traditions strongest in a number of smaller communities in the municipality. Jocotitlán is also home to the Pasteje Industrial Park, which was established in the 1960s, and began the industrialization of the economy. Today, about half of the municipality is employed in industry.
Ixtlahuaca de Rayón is the municipal seat and 5th largest city in the municipality of Ixtlahuaca north of Toluca in the northwest part of the State of Mexico, in Mexico. The distance between Mexico City and Ixtlahuaca is 32 km. The name Ixthahuaca comes from Náhuatl and means plains without trees. The city and municipality were officially established by decree on November 14, 1816 by the Congress of the State of Mexico.

The Second Federal Republic of Mexico refers to the period of Mexican history involving a second attempt to establish a federal government in Mexico after the fall of the unitary Centralist Republic of Mexico in 1846 at the start of the Mexican-American War. It would last up until the Second French Intervention in Mexico led to the proclamation of the Second Mexican Empire in 1863.

The Battle of Silao took place on 10 August 1860 in the vicinity of Silao in Guanajuato state, Mexico, between elements of the liberal army, under the command of General Jesús González Ortega and Ignacio Zaragoza with a force of 8,000 men and elements of the conservative army commanded General Miguel Miramón by commanding an army of 3,282 during the War of Reform. The battle was a liberal victory. General Miramón was almost captured, but escaped in the disorder caused by the Republican artillery, abandoning artillery, ammunition and weapons.
The Battle of Celaya took place on 8 and 9 March 1858 in Celaya, an early battle of the Reform War. Fought between elements of the liberal army, under General Anastasio Parrodi, governor of Jalisco, and elements of the conservative army, commanded by General Luis G. Osollo. The victory was won by the conservative side and corresponded to the first liberal defeat. The defeat made General Parrodi fell back to Salamanca, where the next battle was fought and won by the conservatives.
The Battle of Ahualulco took place on 29 September 1858 during the War of Reform, near the town of Ahualulco in the state of San Luis Potosí, Mexico, between elements of the liberal army, commanded by the Generals Santiago Vidaurri, Juan Zuazua and Francisco Naranjo and conservative army troops commanded by General Miguel Miramón and Leonardo Márquez. Vidaurri's army was defeated and the conservatives won the battle as the result. The liberals suffered 672 casualties and 91 prisoners. It is considered by some to be one of the most brilliant triumphs of Miramón.
The Battle of San Joaquín in the War of Reform took place on 26 December 1858 in the municipality of Cuauhtémoc, between elements of the liberal army, under General Santos Degollado, and elements of the conservative army, commanded by General Miguel Miramón.

The Battle of Calpulalpan took place on December 22, 1860 during the War of Reform in the vicinity of the community of San Miguel de la Victoria in the municipality of Jilotepec de Abasolo in the State of Mexico, Mexico. It would be the last battle of the War of Reform (1858-1860).
The Battle of Salamanca took place between 9 and 10 March 1858 in Salamanca, during Mexico's War of Reform (1858-1860). Elements of the liberal army, under General Anastasio Parrodi, governor of the Jalisco, fought with Generals Leandro Valle, Santos Degollado, and Mariano Moret, against conservatives, commanded by General Luis G. Osollo. Osollo's army had some 5,000 men, including Generals Miguel Miramón and Tomás Mejía, Francisco García Casanova. The conservatives won, handed the liberals a second liberal defeat, and forced them to retreat to Guadalajara from Guanajuato.
The Battle of La Albarrada took place in the year 1858 in La Albarrada, at the time a colony of the city of Colima, between elements of the liberal army during the War of Reform. The victory went to the conservative side that won the Juarist (liberal) defeat.
The Battle of Guadalajara (1858) took place on 14 December 1858 in the vicinity of La Hacienda de Atequiza, near the city of Guadalajara in the state of Jalisco, Mexico, during Reform War. Between elements of the liberal army, under General Santos Degollado, and elements of the conservative army commanded by Generals Miguel Miramón, Leonardo Márquez, Marcelino Cobos, the victory went to the conservative side. The conservatives attacked the ranch of San Miguel, near Poncitlán, Jalisco, where the battle took place. By the end of the battle, the conservatives had gained great quantities of weapons and other war materials. Afterwards, Miramón sent orders to shoot the captured liberal officers.












