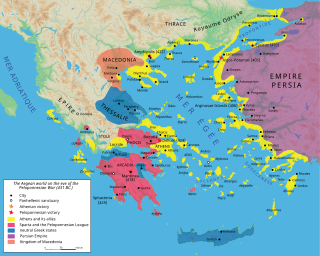
The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (symmachia) of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies".

Aegina is one of the Saronic Islands of Greece in the Saronic Gulf, 27 km (17 mi) from Athens. Tradition derives the name from Aegina, the mother of the mythological hero Aeacus, who was born on the island and became its king.

The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaphernes. The battle was the culmination of the first attempt by Persia under King Darius I, to subjugate Greece. The Greek army inflicted a crushing defeat on the more numerous Persians, marking a turning point in the Greco-Persian Wars.

The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

Themistocles was an Athenian politician and general. He was one of a new breed of non-aristocratic politicians who rose to prominence in the early years of the Athenian democracy. As a politician, Themistocles was a populist, having the support of lower-class Athenians, and generally being at odds with the Athenian nobility. Elected archon in 493 BC, he convinced the polis to increase the naval power of Athens, a recurring theme in his political career. During the first Persian invasion of Greece, he fought at the Battle of Marathon, and may have been one of the ten Athenian strategoi (generals) in that battle.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
This article concerns the period 379 BC – 370 BC.

Lysander was a Spartan military and political leader. He destroyed the Athenian fleet at the Battle of Aegospotami in 405 BC, forcing Athens to capitulate and bringing the Peloponnesian War to an end. He then played a key role in Sparta's domination of Greece for the next decade until his death at the Battle of Haliartus.
Year 376 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Tribunate of Mugillanus, Lanatus, Cornelius and Praetextatus. The denomination 376 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Cyzicus was an ancient Greek town in Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula, a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic times either by artificial means or an earthquake.
Cleon was an Athenian general during the Peloponnesian War. He was an early representative of the commercial class in Athenian politics; which during the early Peloponnesian war was coming into prominence – although he was an aristocrat himself. He strongly advocated for an offensive war strategy and is remembered for being ruthless in carrying out his policies. He was often depicted in a negative way, predominantly by Thucydides and the comedic playwright Aristophanes, who both represent him as an unscrupulous, warmongering demagogue. Cleon was the son of Cleaenetus.

Classical antiquity, also known as the classical era, classical period, classical age, or simply antiquity, is the period of cultural European history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD comprising the interwoven civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome known together as the Greco-Roman world, centered on the Mediterranean Basin. It is the period during which ancient Greece and ancient Rome flourished and had major influence throughout much of Europe, North Africa, and West Asia.

Aristides was an ancient Athenian statesman. Nicknamed "the Just", he flourished at the beginning of Athens' Classical period and is remembered for his generalship in the Persian War. The ancient historian Herodotus cited him as "the best and most honourable man in Athens", and he received similarly reverent treatment in Plato's Socratic dialogues.
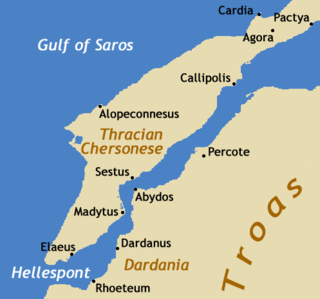
Sestos was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
Archelaus was a prominent Greek general who served under King Mithridates VI of Pontus in northern Anatolia and was also his favorite general.

The idea of the Common Peace was one of the most influential concepts of 4th century BC Greek political thought, along with the idea of Panhellenism. The term described both the concept of a desirable, permanent peace between the Greek city-states (poleis) and a sort of peace treaty which fulfilled the three fundamental criteria of this concept: it had to include all the Greek city-states, it had to recognise the autonomy and equality of all city states without regard for their military power, and it had to be intended to remain in force permanently.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining mathematics, science, artistic thought, theatre, literature, philosophy, and politics of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.

Achilleion was an ancient Greek city in the south-west of the Troad region of Anatolia. It has been located on a promontory known as Beşika Burnu about 8 km south of Sigeion. Beşika Burnu is 2 km south of the modern village of Yeniköy in the Ezine district of Çanakkale Province, Turkey. The site considered in classical antiquity to be the tomb of Achilles is a short distance inland at a tumulus known as Beşiktepe. Achilleion in the Troad is not to be confused with Achilleion near Smyrna and Achilleion in the territory of Tanagra.
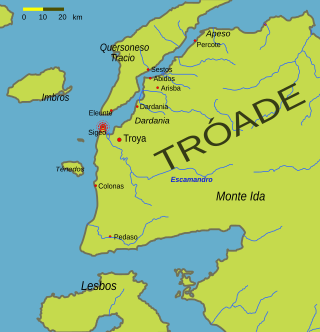
Sigeion was an ancient Greek city in the north-west of the Troad region of Anatolia located at the mouth of the Scamander. Sigeion commanded a ridge between the Aegean Sea and the Scamander which is now known as Yenişehir and is a part of the Çanakkale district in Çanakkale province, Turkey. The surrounding region was referred to as the Sigean Promonotory, which was frequently used as a point of reference by ancient geographers since it marked the mouth of the Hellespont. The outline of this promontory is no longer visible due to the alluvial activity of the Karamenderes which has filled in the embayment east of Yenişehir. The name 'Sigeion' means 'silent place' and is derived from Ancient Greek σιγή (sigē), 'silence'; in Classical Antiquity, the name was assumed to be antiphrastic, i.e. indicating a characteristic of the place contrary to reality, since the seas in this region are known for their fierce storms.

Archeptolis, also Archepolis, was a Governor of Magnesia on the Maeander in Ionia for the Achaemenid Empire circa 459 BCE to possibly around 412 BCE, and a son and successor of the former Athenian general Themistocles.

















