
The Oromo Liberation Front is an Oromo nationalist political party formed in 1973 to promote self-determination for the Oromo people inhabiting today's Oromia Region and Oromia Zone in the Amhara Region of Ethiopia. The OLF has offices in Addis Ababa, Washington, D.C., and Berlin, from which it operates radio stations that broadcast in Amharic and Oromo.
Ahmad Taqi "Hundee" Sheikh Mohammed Rashid was an Ethiopian Oromo nationalist, known, along with his comrade Elemo Qiltu, as the "first true fighters and martyrs of the Oromo causes". It was these two persons and their few colleagues who founded an organization with a fighting unit that bears the name of the Oromo people, although before them, many nationalists had fought and died for the Oromo causes. In addition, these men are credited with reviving and popularizing usage of the name Oromo in early 1970s.
Galamso, is a town in West Haraghe of Oromia Region, Ethiopia, Gelemso is located eastern Ethiopian is far from country capital 301 km and second way 413 km in the western periphery of the highly networked mountain chain referred to by the natives as Fugug and by geographers as the Ahmar Mountains most people say that city
Umar Bakkalcha (1953?–1980) was an Ethiopian nationalist and one of the early Oromo nationalists and martyrs well-remembered in the Chercher highlands of Harerghe especially for the heroic speeches he made at his death spot. His name had been Umar Sheikh Mohammed Rabi, but the people usually refer to him as “Umar Bakkalcha” or simply “Bakkalcha”.

Tadesse Birru was an Ethiopian general of the Imperial Ethiopian Army and civil rights activist. Initially a strong proponent of Ethiopian unity, Tadesse eventually became an activist for the empowerment of the Oromo people in the 1960s. His advocacy turned into repeated attempts to overthrow the government through a coup and later through a military rebellion. He was eventually captured and executed by the Derg regime. He is considered to be the father of modern Oromo nationalism.

The Oromo Liberation Army is an armed opposition group active in the Oromia Region of Ethiopia. The OLA consist primarily of former armed members of the pre-peace deal Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) who refused to disarm out of skepticism of the peace deal, and former youth protestors who grew disillusioned with nonviolent resistance.

Hassan Ibrahim, more commonly known by his nom de guerreElemo Qiltu, was an Ethiopian guerilla commander and businessman, a prominent member of the Oromo nationalist movement and one of the first leaders of the Oromo Liberation Army.
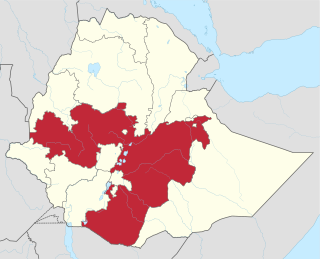
The Oromo conflict is a protracted conflict between the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) and the Ethiopian government. The Oromo Liberation Front formed to fight the Ethiopian Empire to liberate the Oromo people and establish an independent state of Oromia. The conflict began in 1973, when Oromo nationalists established the OLF and its armed wing, the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA). These groups formed in response to prejudice against the Oromo people during the Haile Selassie and Derg era, when their language was banned from public administration, courts, church and schools, and the stereotype of Oromo people as a hindrance to expanding Ethiopian national identity.
This timeline of the Tigray War is part of a chronology of the military engagements of the Tigray War, a civil war that began in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia in early November 2020.

Fano is an ethno-nationalist Amhara militia. It has engaged in violent clashes throughout Ethiopia in the name of neutralizing perceived threats to the Amhara people. Fano has absorbed many units and personnel of the Amhara Regional Special Forces that did not integrate into the Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF). Fano militias are have been involved in armed conflicts with the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA), and the ENDF. They have also clashed with the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) on the border of Ethiopia and Sudan.
The Tigray Defense Forces, colloquially called the Tigray Army is a paramilitary group located in the Tigray region of Ethiopia. It was founded by former generals of the Ethiopian Military in 2020 to combat federal forces enforcing national government mandates in the Tigray region, culminating in 2020 with the outbreak of the Tigray War. The TDF has made use of guerilla tactics and strategies. Human rights groups including Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch have reported that the TDF has committed war crimes against civilians including gang rape and extrajudicial killing during their occupation of both the Afar and Amhara regions. According to the Ethiopian Ministry of Justice, TDF combatants have been found liable for upwards of 540 civilians casualties. as of 28 December 2021.
Following the 2018 dissolution of the ethnic federalist, dominant party political coalition, the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front, there was an increase in tensions within the country, with newly resurgent regional and ethnically based factions carrying out armed attacks on military and civilians in multiple conflicts throughout Ethiopia.

The OLA insurgency is an armed conflict between the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA), which split from the Oromo Liberation Front (OLF) in 2018, and the Ethiopian National Defense Force (ENDF), continuing in the context of the long-term Oromo conflict, typically dated to have started with the formation of the Oromo Liberation Front in 1973.

The United Front of Ethiopian Federalist and Confederalist Forces (UFEFCF) is an apparent coalition of six Ethiopian rebel groups, including the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF) before 2022 and the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA), created in November 2021 during the Tigray War.

The TDF–OLA joint offensive was a series of military battles starting in late October 2021 opposing a coalition of the Tigray Defense Forces (TDF) and Oromo Liberation Army (OLA) against the Ethiopian National Defense Forces (ENDF) in the context of the Tigray War and the OLA insurgency. The TDF and OLA took control of several towns south of Tigray Region in the direction of the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa in late October and early November. Claims of war crimes included that of the TDF extrajudicially executing 100 youths in Kombolcha, according to federal authorities.

Since the 1990s, the Amhara people of Ethiopia have been subject to ethnic violence, including massacres by Tigrayan, Oromo and Gumuz ethnic groups among others, which some have characterized as a genocide. Large-scale killings and grave human rights violations followed the implementation of the ethnic-federalist system in the country. In most of the cases, the mass murders were silent with perpetrators from various ethno-militant groups— from TPLF/TDF, OLF–OLA, and Gumuz armed groups.
The 1995 Ethiopian Federal Constitution formalizes an ethnic federalism law aimed at undermining long-standing ethnic imperial rule, reducing ethnic tensions, promoting regional autonomy, and upholding unqualified rights to self-determination and secession in a state with more than 80 different ethnic groups. But the constitution is divisive, both among Ethiopian nationalists who believe it undermines centralized authority and fuels interethnic conflict, and among ethnic federalists who fear that the development of its vague components could lead to authoritarian centralization or even the maintenance of minority ethnic hegemony. Parliamentary elections since 1995 have taken place every five years since enactment. All but one of these have resulted in government by members of the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) political coalition, under three prime ministers. The EPRDF was under the effective control of the Tigray People's Liberation Front (TPLF), which represents a small ethnic minority. In 2019 the EPRDF, under Abiy, was dissolved and he inaugurated the pan-ethnic Prosperity Party which won the 2021 Ethiopian Election, returning him as prime minister. But both political entities were different kinds of responses to the ongoing tension between constitutional ethnic federalism and the Ethiopian state's authority. Over the same period, and all administrations, a range of major conflicts with ethnic roots have occurred or continued, and the press and availability of information have been controlled. There has also been dramatic economic growth and liberalization, which has itself been attributed to, and used to justify, authoritarian state policy.
On 18 June 2022, the Oromo Liberation Army (OLA) was accused of massacring over 500 Amhara civilians in the Gimbi county of Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Witnesses said that the OLA intentionally targeted ethnic Amhara people. This attack is part of a series of Amhara massacres that occurred in 2022.
On July 4, 2022, alleged Oromo Liberation Army militants killed hundreds of civilians in Kelam Welega Zone, Oromia in Ethiopia. The massacre sparked condemnation from Ethiopian prime minister Abiy Ahmed, and was the second mass killing in Oromia region after the Gimbi massacre just a week prior. Qelem is also known as Kellem.
The 2022 North Shewaclashes were a series of clashes that broke out between ethnic Amhara Fano militiamen, the Oromo Liberation Army, and the Ethiopian National Defence Forces in the North Shewa zone in the Oromia region and the Oromia Zone in the Amhara region, which resulted in dozens of people killed and thousands displaced.










