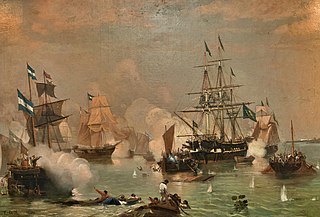The Argentine Confederation was the last predecessor state of modern Argentina; its name is still one of the official names of the country according to the Argentine Constitution, Article 35. It was the name of the country from 1831 to 1852, when the provinces were organized as a confederation without a head of state. The governor of Buenos Aires Province managed foreign relations during this time. Under his rule, the Argentine Confederation engaged in conflicts with Brazil, Bolivia, Uruguay, France and the United Kingdom, as well as other Argentine factions during the Argentine Civil Wars.

The Battle of Caseros was fought near the town of El Palomar, Argentina, on 3 February 1852, between forces of the Argentine Confederation, commanded by Juan Manuel de Rosas, and a coalition consisting of the Argentine provinces of Entre Ríos and Corrientes, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay.

In the Paraguayan War, the Battle of Yatay was fought on August 17, 1865, between the troops of the Triple Alliance and the soldiers of Paraguay near Paso de los Libres, Corrientes, Argentina.

José Lins do Rego Cavalcanti was a Brazilian novelist most known for his semi-autobiographical "sugarcane cycle." These novels were the basis of films that had distribution in the English-speaking world.

The Battle of Ituzaingó, also known as the Battle of Passo do Rosário, was a pitched battle fought in the vicinity of the Santa Maria River, in a valley of small hills where a stream divided the valley into two.
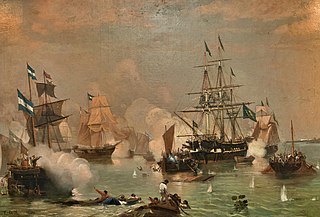
The naval Battle of Monte Santiago was fought on 7–8 April 1827, between the Argentine Navy and the Imperial Brazilian Navy, during the Cisplatine War. It was a decisive Brazilian victory, with the allied forces losing its best ships. The battle is highlighted by Argentine historians as one of the most courageous and ferocious naval encounters in the country's history. On that day, Captain Francis Drummond died on deck, firing his marooned ship's cannons instead of retreating.

The Battle of Estero Bellaco was one of the bloodiest battles of the Paraguayan War. The battle was fought on 2 May 1866 with the Paraguayan Army suffering 2,000 casualties among the dead and wounded. Likewise, 300 of their men were taken prisoner by the troops belonging to the Triple Alliance: Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay. The allies lost nearly 2,000 men, mostly wounded, and the Uruguayan troops of General Venancio Flores - commanded by León de Pallejas - were severely decimated, accounting for the vast majority of allied deaths.
The Battle of Pirajá was fought as part of the Independence of Bahia and more broadly, as part of the War of Independence of Brazil. It was fought in Pirajá, now a neighborhood of the city of Salvador, Bahia on November 8, 1822. The Battle of Pirajá was the largest engagement in the fight for the independence of Bahia, involving approximately 10,000 troops.
The Battle of Catalán was fought between the Luso-Brazilian forces under the command of Luís Teles da Silva Caminha e Meneses, the Marquis of Alegrete, and the artiguistas commanded by Andrés Latorre in Arroyo Catalán, present-day Uruguay.

The Battle of Sarandí was fought on 12 October 1825, in the vicinity of the Arroyo Sarandí in Uruguay, between troops of the Banda Oriental and the Empire of Brazil. It resulted in a decisive victory for the Orientals.
The Iguape War occurred during 1534-1536, in the region of São Vicente, São Paulo. Due to the interpretation of the Treaty of Tordesilhas, some Spaniards, led by Ruy Garcia de Moschera, established themselves around Vicentina. They were allied with indigenous Carijós, founded a village and won several battles against French corsairs.

The Battle of Paso de Cuevas was fought on 12 August 1865 during the Paraguayan invasion of the Argentine province of Corrientes.
The Battle of Passo Fundo was a military engagement fought between forces of the First Brazilian Republic and various military units affiliated with the Federalist Revolution. The battle, which was fought on 27 June 1894 along the Passo Fundo River, was the largest battle of the Federalist Revolution. It ended in a victory for the Brazilian Republic.

The Battle of Butuí took place on June 26, 1865 in the Butuí or M'Butuí stream between the municipalities of São Borja and Itaqui in Rio Grande do Sul during the Paraguayan War.

The Battle of Perecué, also known as Battle of Tayí Island, was an armed action that occurred during the Paraguayan War. Paraguayan general Bernardino Caballero's troops launched guerrilla-style raids on the Allied encampment in the Tayí area, near the Humaitá Fortress. The Marquis of Caxias, Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, who had replaced Bartolomé Mitre in the supreme command of allied troops, learned of the Paraguayan presence in the area and prepared a counterattack on his enemies, failing in this action that resulted in a pyrrhic victory of the Paraguayans.

The naval Battle of Quilmes took place between a fleet of the Imperial Brazilian Navy, commanded by British admiral James Norton and a fleet of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata under the command of William Brown. The confrontations began at dawn on July 30, 1826 and lasted for three hours.
The Battle of Vacacai, also known as the Battle of Bacacay or Vacacay, was a small skirmish fought on 13 February 1827 between a small militia cavalry force of the Imperial Brazilian Army and an Argentine detachment in the context of the Cisplatine War.

The Battle of Azenha Bridge was the first battle of the Ragamuffin War, which took place on the night of the 19th to the 20th of September 1835. It gave way to the capture of Porto Alegre by the rebels on the following day.

The naval Battle of Punta Colares, also known as the Battle of Corales, was the first major naval engagement of the Cisplatine War. It took place between a fleet of the Empire of Brazil, commanded by admiral Rodrigo José Ferreira Lobo, and a squadron of the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata under the command of admiral William Brown. The confrontations began at around 10 o'clock on 9 February 1826 and lasted for seven hours.

The battle of Colonia del Sacramento consisted of a series of failed attempts made by admiral William Brown of capturing the town of Colonia del Sacramento, which was under Brazilian control and being sieged on land by insurgent Uruguayan forces, in the context of the Cisplatine War between the Empire of Brazil and the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata. The confrontations began in the morning of 26 February 1826 and ended on 14 March 1826.