The Battle of Almonacid was fought on 11 August 1809 during the Peninsular War between Sébastiani's IV Corps of the French Peninsular Army, which King Joseph of Spain had withdrawn from the Battle of Talavera to defend Madrid, and the Spanish Army of La Mancha under General Venegas. After the decisive charges of Polish uhlans, the battle resulted in a French victory.

The Battle of Monterey, at Monterey, California, occurred on 7 July 1846, during the Mexican–American War. The United States captured the town unopposed.

The Argentine War of Independence was a secessionist civil war fought from 1810 to 1818 by Argentine patriotic forces under Manuel Belgrano, Juan José Castelli, Martin Miguel de Guemes and José de San Martín against royalist forces loyal to the Spanish crown. On July 9, 1816, an assembly met in San Miguel de Tucumán, declaring independence with provisions for a national constitution.

The Battle of Cancha Rayada, was fought in Chile between South American patriots and Spanish royalists, during the Osorio's campaign in the South American wars of independence. The result was a defeat for the patriot forces, weeks later the patriots take their rematch at the Battle of Maipú.

The Battle of Arica, also known as Assault and Capture of Cape Arica, was a battle in the War of the Pacific. It was fought on 7 June 1880, between the forces of Chile and Peru.
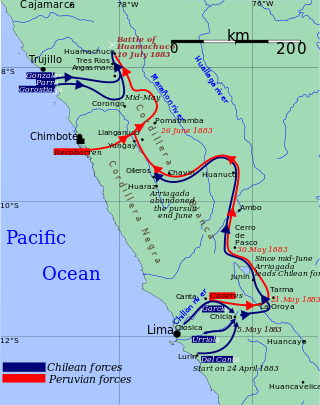
The Battle of Huamachuco was fought on the 10 July 1883, and it was the last major battle of the War of the Pacific. The Chilean soldiers, led by Colonel Alejandro Gorostiaga, decisively defeated the Peruvian army commanded by General Andrés Avelino Cáceres near the town of Huamachuco. This Chilean victory effectively eliminated Cáceres' Ejército de la Breña, ending any real threat or resistance in the Peruvian Andes. The Peruvian defeat paved the way for the Treaty of Ancón that finally put an end to the war. Also, one of Peru's greatest heroes, Colonel Leoncio Prado, died as a consequence of this battle.

Yerbas Buenas is a Chilean town and commune in Linares Province, Maule Region. It lies in the geographical center of the country, on the fertile central plain, some 300 km (186 mi) south of the national capital of Santiago, 50 km (31 mi) south of Talca, the regional capital and 12 km (7 mi) north of Linares, the provincial capital.

Colonel Luis Florentino Juan Manuel Silvestre de los Dolores de la Carrera y Verdugo was a Chilean military officer who fought in the Chilean War of Independence. Together with his brothers José Miguel and Juan José, they were some of most important leaders of Chilean struggle for independence during the period of the Patria Vieja. The Carrera family is of Basque origin.

Brigadier José Antonio de Pareja y Mariscal was a Spanish Navy officer. He captained the Argonauta during the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805 and in 1812 commanded Royalist troops during the Chilean War of Independence.
Clemente de Lantaño Pino was a royalist military officer during the Chilean War of Independence. Later, during the Spanish reconquest, he changed sides and fought for independence against the royalist forces.

Yerba Buena was the name of an anchorage spot and later a town that grew into the city of San Francisco, California. The settlement, built in an area known earlier as El Paraje de Yerba Buena and named for an herb that grew abundantly there, was founded in 1834 and was located near the northeastern end of the San Francisco Peninsula, on the shores of Yerba Buena Cove. Yerba Buena was the first civilian pueblo in San Francisco, which had previously only had indigenous, missionary, and military settlements, and was originally intended as a trading post for ships visiting San Francisco Bay. The settlement was arranged in the Spanish style around a plaza that remains as the present day Portsmouth Square. The area that was the Yerba Buena settlement is now in the Financial District and Chinatown neighborhoods of San Francisco.

The Battle of El Toro was fought near Maullín, Chile between Chilean patriots and Spanish royalists, during the Chilean War of Independence.

The Army of the North, contemporaneously called Army of Peru, was one of the armies deployed by the United Provinces of the Río de la Plata in the Spanish American wars of independence. Its objective was freeing the Argentine Northwest and the Upper Peru from the royalist troops of the Spanish Empire. It was headed by Hipólito Vieytes (1810), Juan José Castelli (1810–1811), Juan Martín de Pueyrredón (1811–1812), Manuel Belgrano (1812–1814), José de San Martín (1814), José Rondeau (1814–1816), Manuel Belgrano (1816–1819) and Francisco Fernández de la Cruz (1819–1820).
The Battle of Curapalihue fought in Chile, was a minor encounter between South American rebels and Spanish royalists, during the South American wars of independence. The result was a defeat for the royalists.
The Battle of Portada de Guías, also known as the Battle of Guía or Battle of Piñonate, took place between the Chilean Army and the secessionist Peruvian Republic in 1838, during the War of the Confederation.
The Mapuche uprising of 1655 was a series of coordinated Mapuche attacks against Spanish settlements and forts in colonial Chile. It was the worst military crisis in Chile in decades, and contemporaries even considered the possibility of a civil war among the Spanish. The uprising marks the beginning of a ten-year period of warfare between the Spanish and the Mapuche.

The Lima campaign is the third land campaign of the War of the Pacific, carried out by Chile between December 1880 and January 1881. The campaign ended with the Chilean occupation of the Peruvian capital and the establishment of the Chilean authority in it and other surrounding territories, which would extend until 1883, with the end of the war.

The Battle of Peralejo was a military confrontation between Cuban independence rebels, under the command of Major General Antonio Maceo against the forces of the Spanish Army, under the command of Captain General Arsenio Martínez Campos, which was part of Maceo's First Eastern Campaign during the Cuban War of Independence.

The October 9 Revolution was a successful revolt against the Spanish Empire in Guayaquil on October 9, 1820. It was led by the General Antonio José de Sucre and directed by Simón Bolívar. The revolt established a revolutionary junta and created the Free Province of Guayaquil, an independent state. The independence of Guayaquil revived the war of independence of the Real Audiencia de Quito as part of the Spanish American wars of independence. Prominent events in the revolution include the uprising of the Spanish garrison in the city of Guayaquil and the control of the Pacific by the Liberating Expedition of Peru, under the command of José de San Martín.

The Peruvian resistance movement was composed of the Peruvian militias and guerrillas commanded by local, civilian or military leaders, who confronted the Chilean Army and Navy during the period of occupation that took place during the War of the Pacific.
















