
Pharnaces II of Pontus was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithridates VI of Pontus from his first wife, his sister Queen Laodice. He was born and raised in the Kingdom of Pontus and was the namesake of his late double great grandfather Pharnaces I of Pontus. After his father was defeated by the Romans in the Third Mithridatic War and died in 63 BC, the Romans annexed the western part of Pontus, merged it with the former Kingdom of Bithynia and formed the Roman province of Bithynia and Pontus. The eastern part of Pontus remained under the rule of Pharnaces as a client kingdom until his death.

The Mithridatic Wars were three conflicts fought by the Roman Republic against the Kingdom of Pontus and its allies between 88 – 63 BCE. They are named after Mithridates VI, the King of Pontus during the course of the wars who initiated the hostilities with Rome. Mithridates led the Pontic forces in every war. The Romans were led by various generals and consuls throughout the wars, namely Lucius Cornelius Sulla, Lucius Licinius Lucullus, and Gnaeus Pompey Magnus.
The Battle of Chaeronea was fought by the Roman forces of Lucius Cornelius Sulla and Mithridates' general, Archelaus, near Chaeronea, in Boeotia, in 86 BC during the First Mithridatic War. The battle ended with a complete rout of the Pontic army and a decisive victory for the Romans.

The First Mithridatic War was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates VI of Pontus against Rome and the allied Kingdom of Bithynia. The war lasted five years and ended in a Roman victory, which forced Mithridates to abandon all of his conquests and return to Pontus. The conflict with Mithridates VI later resumed in two further Mithridatic Wars.

The Third Mithridatic War, the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies, dragging the entire east of the Mediterranean and large parts of Asia into the war. The conflict ended in defeat for Mithridates; it ended the Pontic Kingdom and the Seleucid Empire, and also resulted in the Kingdom of Armenia becoming an allied client state of Rome.
Archelaus was a prominent Greek general who served under King Mithridates VI of Pontus in northern Anatolia and was also his favorite general.
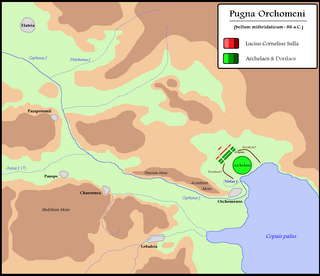
The Battle of Orchomenus was fought in 85 BC between Rome and the forces of Mithridates VI of Pontus. The Roman army was led by Lucius Cornelius Sulla, while Mithridates' army was led by Archelaus. The Roman force was victorious, and Archelaus later defected to Rome. The battle ended the Mithridatic invasion of Europe. Information on the battle is included in Plutarch's Life of Sulla, chapters 20–21.

The siege of Cyzicus took place in 73 BC between the armies of Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman-allied citizens of Cyzicus in Mysia and Roman Republican forces under Lucius Licinius Lucullus. It was in fact a siege and a counter-siege. It ended in a decisive Roman victory.
The Battle of Cabira was fought in 72 or 71 BC between forces of the Roman Republic under proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus and those of the Kingdom of Pontus under Mithridates the Great. It was a decisive Roman victory.
The Battle of Lemnos was fought on the island of Lemnos in 73 BC between a Roman fleet and a Mithridatic fleet; it was a decisive event during the Third Mithridatic War. The primary chroniclers of the battle are Appian, Cicero and Memnon, but there remain debates about the specifics in these different accounts.
Taxiles was a general in the service of Mithridates VI of Pontus, and one of those in whom he reposed the highest confidence. He is first mentioned in 86 BC, when he was sent by Mithridates, with an army of not less than 110,000 men, to make his way through Thrace and Macedonia to provide support to Archelaus in Greece. This task he successfully accomplished. He reduced Amphipolis, which had at first defied his arms, and having thus struck terror into the Macedonians, advanced, without further opposition, through that country and Thessaly into Phocis. Here he at first laid siege to Elateia, but was foiled in his attacks, and relinquished the enterprise, in order to meet up with Archelaus in Boeotia. The two Pontic generals now found themselves at the head of a formidable host, but their combined forces were defeated in 86 BC by Sulla near Chaeronea, with great slaughter.

Pontus was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus in modern-day Turkey, and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty of Persian origin, which may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. The kingdom was proclaimed by Mithridates I in 281 BC and lasted until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 63 BC. The Kingdom of Pontus reached its largest extent under Mithridates VI the Great, who conquered Colchis, Cappadocia, Bithynia, the Greek colonies of the Tauric Chersonesos, and for a brief time the Roman province of Asia. After a long struggle with Rome in the Mithridatic Wars, Pontus was defeated.

Cappadocia was a province of the Roman Empire in Anatolia, with its capital at Caesarea. It was established in 17 AD by the Emperor Tiberius, following the death of Cappadocia's last king, Archelaus.
The Battle of Zela, not to be confused with the more famous battle in 47 BC, was fought in 67 BC near Zela in the Kingdom of Pontus. The battle resulted in a stunning Pontic victory and King Mithridates' successful reclamation of his kingdom. Mithridates' victory was short-lived however, as within a few years he would be completely defeated by Pompey the Great.

The Battle of Chalcedon was a land and naval battle between the Roman Republic and King Mithridates VI of Pontus near the city of Chalcedon in 74 BC. It was the first major clash of the Third Mithridatic War. The Roman forces were led by Marcus Aurelius Cotta, one of the consuls for 74 BC, while Mithridates had the overall command of the Pontic forces. The Mithridatic forces were victorious on both land and sea.
Neoptolemus was a distinguished general of King Mithridates VI of Pontus. He was the brother of Archelaus, another general of Mithridates VI and the paternal uncle of Archelaus’ sons: Archelaus and Diogenes.
The Battle of the Rhyndacus occurred in 73 BC between a Roman Republican force under the command of the proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus and a division of the army of Mithridates VI of Pontus as part of the Third Mithridatic War. The Romans were victorious.

The siege of Athens and Piraeus was a siege of the First Mithridatic War that took place from autumn of 87 BC to the spring of 86 BC. The battle was fought between the forces of the Roman Republic, commanded by Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix on the one hand, and the forces of the Kingdom of Pontus and the Athenian City-State on the other. The Greek Pontian forces were commanded by Aristion and Archelaus.
Arcathias was a Pontic prince of Persian and Greek Macedonian ancestry, and figure in the First Mithridatic War. Arcathias was a son of Mithridates VI of Pontus and his sister-wife Laodice.

The Battle of Protopachium was fought in 89 BC at the start of the First Mithridatic War, between the Roman Republic and the Pontic Empire. The battle ended in a Roman defeat and their expulsion from Asia Minor.










