The Bavarian Oberland (German : Bayerisches Oberland) is a region in Upper Bavaria north of and including the Bavarian Pre-alps between the rivers Lech and Inn.
Contents

The Bavarian Oberland (German : Bayerisches Oberland) is a region in Upper Bavaria north of and including the Bavarian Pre-alps between the rivers Lech and Inn.

Originally the region, which roughly corresponds to the county of Miesbach, was called the Oberland.
In 1705, during the War of the Spanish Succession the first rebellion against its Austrian occupiers broke out. This Bavarian People's Uprising soon met a tragic end in the Sendling night of murder.
Since the creation in the 1970s of the Oberland Planning Region, the term has changed.
The planning region extends over the four counties of Miesbach, Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen, Garmisch-Partenkirchen and Weilheim-Schongau. Sometimes areas to the north (Munich, Starnberg, Landsberg am Lech) or to the east (Chiemgau) are incorrectly considered part of the Bavarian Oberland.
The Bavarian Oberland is a region that is still largely rural and that continues to play a major role in its culture and customs. The region is one of the strongest economically in Germany today. Tourism is of great significance as well as agriculture and forestry. Today (2006) around 432,000 people live in the region on an area of 3,953 km2. In a 2006 Germany-wide survey into how content people were with where they lived the Bavarian Oberland achieved first place. [1]

The Baiuvarii, Bavarii, sometimes simply called Bavarians were a Germanic people who lived in or near present day southern Bavaria, which is named after them.

Vorarlberg is the westernmost state of Austria. It has the second-smallest geographical area after Vienna and, although it also has the second-smallest population, it is the state with the second-highest population density. Two thirds of the country are situated above 1,000m. It borders three countries: Germany, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. The only Austrian state that shares a border with Vorarlberg is Tyrol, to the east.
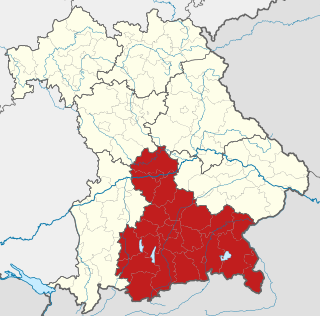
Upper Bavaria is one of the seven administrative regions of Bavaria, Germany.
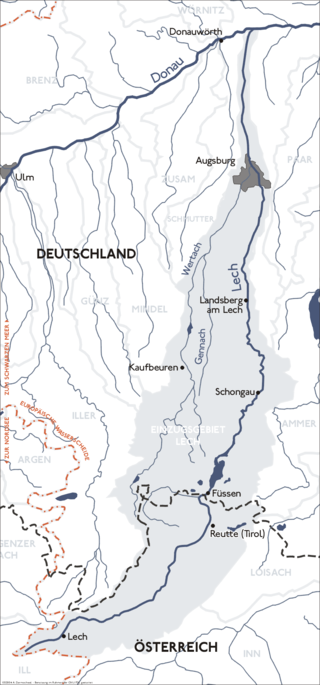
The Lech is a river in Austria and Germany. It is a right tributary of the Danube 255 kilometres (158 mi) in length with a drainage basin of 3,919 square kilometres (1,513 sq mi). Its average discharge at the mouth is 115 m3/s (4,100 cu ft/s). Its source is located in the Austrian state of Vorarlberg, where the river rises from lake Formarinsee in the Alps at an altitude of 1,870 metres (6,120 ft). It flows in a north-north-easterly direction and crosses the German border, forming the Lechfall, a 12-metre-high (39 ft) waterfall; afterwards the river enters a narrow gorge. Leaving the Alps, it enters the plains of the Allgäu at Füssen at an elevation of 790 metres (2,580 ft) in the German state of Bavaria, where it used to be the location of the boundary with Swabia. The river runs through the city of Füssen and through the Forggensee, a man-made lake which is drained in winter. Here, it forms rapids and a waterfall.

The canton of Bern, or Berne, is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. Its capital city, Bern, is also the de facto capital of Switzerland. The bear is the heraldic symbol of the canton, displayed on a red-yellow background.
Landsberg am Lech is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Aichach-Friedberg, Fürstenfeldbruck, Starnberg, Weilheim-Schongau, Ostallgäu and Augsburg.
Miesbach is a Landkreis (district) in Bavaria, Germany. It is bounded by the districts of Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen, Munich and Rosenheim, and by the Austrian state of Tyrol.
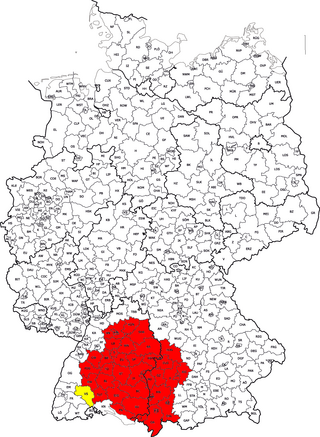
Swabia is a cultural, historic and linguistic region in southwestern Germany. The name is ultimately derived from the medieval Duchy of Swabia, one of the German stem duchies, representing the historic settlement area of the Germanic tribe alliances named Alemanni and Suebi.
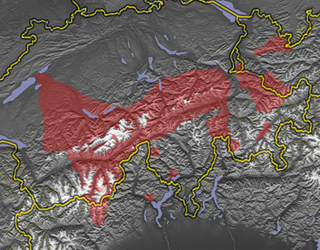
The Walser people are the speakers of the Walser German dialects, a variety of Highest Alemannic. They inhabit the region of the Alps of Switzerland and Liechtenstein, as well as the fringes of Italy and Austria. The Walser people are named after the Wallis (Valais), the uppermost Rhône valley, where they settled from roughly the 10th century in the late phase of the migration of the Alamanni, crossing from the Bernese Oberland; because of linguistic differences among the Walser dialects, it is supposed that there were two independent immigration routes.

The Bernese Oberland, sometimes also known as the Bernese Highlands, is the highest and southernmost part of the canton of Bern. It is one of the canton's five administrative regions. It constitutes the Alpine region of the canton and the northern side of the Bernese Alps, including many of its highest peaks, among which the Finsteraarhorn, the highest in both range and canton.

The Bayerische Oberlandbahn GmbH (BOB) is a private railway company based in Holzkirchen, Germany, and owned by Transdev Germany. Since June 2020 its services are operated under the brand Bayerische Regiobahn (BRB) of its sister company.

Zürs is one of the most renowned winter sports resorts in the Alps. Located in the westernmost Austrian state of Vorarlberg, almost directly on the border to North Tyrol, near the Flexenpass, Zürs is part of the Arlberg region, which also includes Lech, Oberlech, Zug, and Stubenbach. This region offers 87 ski-lifts, 200 kilometers of deep snow slopes and 305 km of ski runs. It has several hotels and guest houses, with a total of over 1,700 beds. It is popular for its downhill skiing, but also for its backcountry skiing and its Olympic ski championships. About four kilometers north of Zürs is Lech am Arlberg, another ski resort which is linked to Zürs not only via road, but also via ski lifts and pistes.

Tegernsee is a town in the Miesbach district of Bavaria, Germany. It is located on the shore of Lake Tegernsee, which is 747 m (2,451 ft) above sea level. A spa town, it is surrounded by an alpine landscape of Upper Bavaria, and has an economy mainly based on tourism.

Schwabmünchen is a town in Bavaria, Germany in the administrative region of Swabia south of Augsburg in the Augsburg district.

Upper Swabia is a region in Germany in the federal states of Baden-Württemberg and Bavaria. The name refers to the area between the Swabian Jura, Lake Constance and the Lech. Its counterpart is Lower Swabia (Niederschwaben), the region around Heilbronn.

The Großer Arber ; Czech: Velký Javor, "Great Maple") or Great Arber, is the highest peak of the Bavarian/Bohemian Forest mountain range and in Lower Bavaria, with an elevation of 1,455.5 metres (4,775 ft). As a result, it is known in the Lower Bavarian county of Regen and the Upper Palatine county of Cham as the "King of the Bavarian Forest". Its summit region consists of paragneiss.

Schliersee is a small town (Markt) and a municipality in the district of Miesbach in Bavaria in Germany. It is named after the nearby Lake Schliersee. It comprises the districts Schliersee (town), Westenhofen, Neuhaus, Fischhausen, Josefsthal and Spitzingsee.

The Bavarian uprising of 1705–1706 was a revolt against the occupation of the Electorate of Bavaria by the Imperial Army of the Habsburg Monarchy during the War of the Spanish Succession (1701–1714). It lasted from early November 1705 to 18 January 1706, approximately 75 days. Henric L. Wuermeling speaks of this as "the first revolution of modern history."

The Mangfall Mountains, or sometimes Mangfall Alps, are the easternmost part of the Bavarian Prealps that, in turn, belong to the Northern Limestone Alps. The name comes from the river Mangfall, whose tributaries, the Rottach, Weißach, Schlierach and Leitzach, drain large parts of the area and form an important drinking water reservoir for the city of Munich.

The Forggensee, also called the Roßhaupten Reservoir, is a reservoir located north of Füssen in the county of Ostallgäu in Bavaria, Germany and one of many lakes in the region around Hohenschwangau and Neuschwanstein castles. With a surface area of 15.2 km2, it is the fifth-largest lake in Bavaria and the largest reservoir in Germany by area. The River Lech flows through it. The Forggensee is known primarily as a tourist destination for aquatic sports and recreation. Besides Füssen, other settlements on the lake include Halblech, Rieden am Forggensee and Roßhaupten. The lake takes its name from the former hamlet of Forggen which has been submerged by the reservoir.