Sources
- Guillotel, Hubert. "Une autre marche de Neustrie." in Christian Settipani and Katharine S. B. Keats-Rohan, Onomastique et Parenté dans l'Occident médiéval. 2000.
Berengar I was a 9th-century nobleman of East Francia, a son of Gebhard, Count of Lahngau, and younger brother of Udo. He and his brother were created Margraves of Neustria by Charles the Bald in 861.
He was possibly a Conradine, a relative for sure of Adalard the Seneschal, a Girardid. Berengar was probably the namesake of Berengar II of Neustria, who was probably the son of Berengar I's successor, Henry of Franconia. He is believed to be the same person as Bérenger I, Count of Ivois.
With his brothers, Udo and Waldo the Abbot, he took part in the 861 revolt of Carloman of Bavaria, possible his cousin-in-law, against Louis the German. The revolt was crushed and the three brothers fled with their relative Adalard to the court of the West Frankish king, Charles the Bald, who granted them wardship of the march against the Vikings while the march against the Bretons was granted to Robert the Strong.
Charles' patronage of the family provoked the jealousy of the Rorgonids, the most powerful family local to Neustria and then controlling the ducatus Cenomannicus (Maine). In 865, they allied with Saloman of Brittany and attacked the brothers. Charles, to attain peace, took the march back and gave it to Gauzfrid, a Rorgonid.
A charter of 879 mentions Berengar and his brothers taking part in the foundation of the college of Gemünden. Evidently, the death of Louis the German in 876 had allowed them to return to the court of Carloman.
His daughter Ota became wife of Arnulf of Carinthia.

Arnulf of Carinthia was Duke of Carinthia who overthrew his uncle, Emperor Charles the Fat, became the Carolingian king of East Francia from 887, the disputed King of Italy from 894 and the disputed Holy Roman Emperor from February 22, 896 until his death at Regensburg, Bavaria.

Year 862 (DCCCLXII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar.
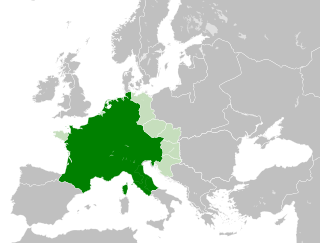
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the Lombards in Italy from 774. In 800, the Frankish king Charlemagne was crowned emperor in Rome by Pope Leo III in an effort to transfer the Roman Empire from east to west. The Carolingian Empire is considered the first phase in the history of the Holy Roman Empire, which lasted until 1806.

Carloman was a Frankish king of the Carolingian dynasty. He was the eldest son of Louis the German, king of East Francia, and Hemma, daughter of a Bavarian count. His father appointed him governor of Carantania in 856, and commander of southeastern frontier marches in 864. Upon his father's death in 876 he became King of Bavaria. He was appointed by King Louis II of Italy as his successor, but the Kingdom of Italy was taken by his uncle Charles the Bald in 875. Carloman only conquered it in 877. In 879 he was incapacitated, perhaps by a stroke, and abdicated his domains in favour of his younger brothers: Bavaria to Louis the Younger and Italy to Charles the Fat.

Neustria was the western part of the Kingdom of the Franks.

Louis III was King of West Francia from 879 until his death in 882. He succeeded his father and ruled over West Francia in tandem with his brother Carloman II. Louis controlled the northern part of West Francia (Neustria), including the capital of Paris, while Carloman controlled the southern portion (Aquitania). Louis ruled from March 880 to 5 August 882, when he died and left the rest of West Francia to his brother. His short reign was profoundly influenced by his military success, including his defeating Northern Vikings in August 881.

Charles III, also known as Charles the Fat, was the emperor of the Carolingian Empire from 881 to 888. A member of the Carolingian dynasty, Charles was the youngest son of Louis the German and Hemma, and a great-grandson of Charlemagne. He was the last Carolingian emperor of legitimate birth and the last to rule over all the realms of the Franks.

Robert the Strong was the father of two kings of West Francia: Odo and Robert I of France. His family is named after him and called the Robertians. In 853, he was named missus dominicus by Charles the Bald, King of West Francia. Robert the Strong was the great-grandfather of Hugh Capet and thus the ancestor of all the Capetians.

Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks, Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire, was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. After the Treaty of Verdun in 843, West Francia became the predecessor of France, and East Francia became that of Germany. Francia was among the last surviving Germanic kingdoms from the Migration Period era before its partition in 843.
Bernardof Septimania (795–844), son of William of Gellone, was the Frankish Duke of Septimania and Count of Barcelona from 826 to 832 and again from 835 to his execution. He was also count of Carcassonne from 837. He was appointed to succeed his fellow Frank Rampon. During his career, he was one of the closest counsellors of the Emperor Louis the Pious, a leading proponent of the war against the Moors, and opponent of the interests of the local Visigothic nobility.

Berengar I was the king of Italy from 887. He was Holy Roman Emperor between 915 and his death in 924. He is usually known as Berengar of Friuli, since he ruled the March of Friuli from 874 until at least 890, but he had lost control of the region by 896.
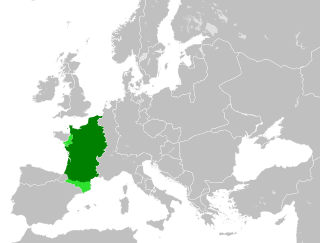
In medieval history, West Francia or the Kingdom of the West Franks refers to the western part of the Frankish Empire established by Charlemagne. It represents the earliest stage of the Kingdom of France, lasting from about 840 until 987. West Francia emerged from the partition of the Carolingian Empire in 843 under the Treaty of Verdun following the death of Charlemagne's son, Louis the Pious.
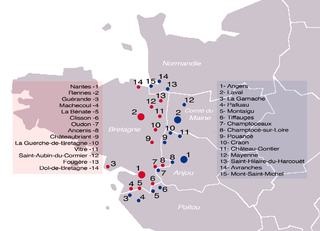
The Marches of Neustria were two marches created in 861 by the Carolingian king of West Francia Charles the Bald that were ruled by officials appointed by the Crown, known as wardens, prefects or margraves. Originally, one March was created as a buffer against the Bretons and the other against the Norsemen, often called the Breton March and Norman March respectively.
Gauzfrid of Maine was both Count of Maine and Margrave of the Norman March from 865 until his death. He was a son of Rorgon of Maine by his wife Bilechilde.
Adalard, also known as Adalhard or Alard, and called the Seneschal, was a Frankish nobleman of the 9th century. He served as warden of the Norman march from 861 to 865, and was Lord Chancellor of France under Louis the Pious.
Udo was a 9th-century nobleman of East Francia, a son of Gebhard, Count of Lahngau, and older brother of Berengar I of Neustria. He and his brother were afforded their position in the March of Neustria both by kinship to Adalard the Seneschal and the favour of Charles the Bald.
The Conradines or Conradiner were a dynasty of Franconian counts and dukes in the 8th to 11th Century, named after Duke Conrad the Elder and his son King Conrad I of Germany.
Louis the Younger, sometimes Louis the Saxon or Louis III, was the second eldest of the three sons of Louis the German and Emma. He succeeded his father as the King of Saxony on 28 August 876 and his elder brother Carloman as King of Bavaria from 876 to 882. He died in 882 and was succeeded in all his territories, which encompassed most of East Francia, by his younger brother, Charles the Fat, already king of Italy and emperor.
Wilfred or Wifred, called the Hairy, was Count of Urgell, Cerdanya, Barcelona, Girona, Besalú and Ausona. On his death in 897, his son, Wilfred Borrell, inherited these Catalan counties.
Bérenger I was the first known Count of Ivois. It is conjectured that Bérenger is the same person as Berengar I of Neustria, son of Gebhard, Count of Lahngau.