
In mathematics, the absolute value or modulus|x| of a real number x is the non-negative value of x without regard to its sign. Namely, |x| = x for a positive x, |x| = −x for a negative x, and |0| = 0. For example, the absolute value of 3 is 3, and the absolute value of −3 is also 3. The absolute value of a number may be thought of as its distance from zero.
In mathematics, the Laplace transform is an integral transform named after its inventor Pierre-Simon Laplace. It takes a function of a real variable t to a function of a complex variable s.
In mathematics, a product is the result of multiplying, or an expression that identifies factors to be multiplied. Thus, for instance, 6 is the product of 2 and 3, and is the product of and .
In mathematics and in particular measure theory, a measurable function is a function between two measurable spaces such that the preimage of any measurable set is measurable, analogously to the definition that a function between topological spaces is continuous if the preimage of each open set is open. In real analysis, measurable functions are used in the definition of the Lebesgue integral. In probability theory, a measurable function on a probability space is known as a random variable.
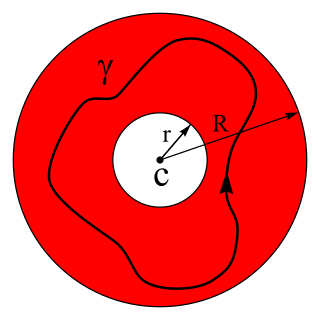
In mathematics, the Laurent series of a complex function f(z) is a representation of that function as a power series which includes terms of negative degree. It may be used to express complex functions in cases where a Taylor series expansion cannot be applied. The Laurent series was named after and first published by Pierre Alphonse Laurent in 1843. Karl Weierstrass may have discovered it first in a paper written in 1841, but it was not published until after his death.
In mathematics, a self-adjoint operator on a finite-dimensional complex vector space V with inner product is a linear map A that is its own adjoint: for all vectors v and w. If V is finite-dimensional with a given orthonormal basis, this is equivalent to the condition that the matrix of A is a Hermitian matrix, i.e., equal to its conjugate transpose A∗. By the finite-dimensional spectral theorem, V has an orthonormal basis such that the matrix of A relative to this basis is a diagonal matrix with entries in the real numbers. In this article, we consider generalizations of this concept to operators on Hilbert spaces of arbitrary dimension.
In complex analysis, the Hardy spacesHp are certain spaces of holomorphic functions on the unit disk or upper half plane. They were introduced by Frigyes Riesz, who named them after G. H. Hardy, because of the paper. In real analysis Hardy spaces are certain spaces of distributions on the real line, which are boundary values of the holomorphic functions of the complex Hardy spaces, and are related to the Lp spaces of functional analysis. For 1 ≤ p ≤ ∞ these real Hardy spaces Hp are certain subsets of Lp, while for p < 1 the Lp spaces have some undesirable properties, and the Hardy spaces are much better behaved.
The Laplace–Stieltjes transform, named for Pierre-Simon Laplace and Thomas Joannes Stieltjes, is an integral transform similar to the Laplace transform. For real-valued functions, it is the Laplace transform of a Stieltjes measure, however it is often defined for functions with values in a Banach space. It is useful in a number of areas of mathematics, including functional analysis, and certain areas of theoretical and applied probability.
In the physical sciences, the Airy functionAi(x) is a special function named after the British astronomer George Biddell Airy (1801–92). The function Ai(x) and the related function Bi(x), are linearly independent solutions to the differential equation
In mathematics, the Cauchy principal value, named after Augustin Louis Cauchy, is a method for assigning values to certain improper integrals which would otherwise be undefined.
In mathematics and its applications, a classical Sturm–Liouville theory, named after Jacques Charles François Sturm (1803–1855) and Joseph Liouville (1809–1882), is the theory of a real second-order linear differential equation of the form
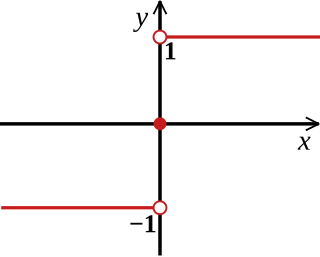
In mathematics, the sign function or signum function is an odd mathematical function that extracts the sign of a real number. In mathematical expressions the sign function is often represented as sgn.
In mathematics, the Hartley transform (HT) is an integral transform closely related to the Fourier transform (FT), but which transforms real-valued functions to real-valued functions. It was proposed as an alternative to the Fourier transform by Ralph V. L. Hartley in 1942, and is one of many known Fourier-related transforms. Compared to the Fourier transform, the Hartley transform has the advantages of transforming real functions to real functions and of being its own inverse.

The Voigt profile is a probability distribution given by a convolution of a Cauchy-Lorentz distribution and a Gaussian distribution. It is often used in analyzing data from spectroscopy or diffraction.

The rectangular function is defined as

A stochastic differential equation (SDE) is a differential equation in which one or more of the terms is a stochastic process, resulting in a solution which is also a stochastic process. SDEs are used to model various phenomena such as unstable stock prices or physical systems subject to thermal fluctuations. Typically, SDEs contain a variable which represents random white noise calculated as the derivative of Brownian motion or the Wiener process. However, other types of random behaviour are possible, such as jump processes.
In mathematics, the metaplectic group Mp2n is a double cover of the symplectic group Sp2n. It can be defined over either real or p-adic numbers. The construction covers more generally the case of an arbitrary local or finite field, and even the ring of adeles.
In mathematics, applying the Schwarz reflection principle is a way to extend the domain of definition of an analytic function of a complex variable, F, which is defined on the upper half-plane and has well-defined and real number boundary values on the real axis. In that case, the putative extension of F to the rest of the complex plane is

The mathematical concept of a Hilbert space, named after David Hilbert, generalizes the notion of Euclidean space. It extends the methods of vector algebra and calculus from the two-dimensional Euclidean plane and three-dimensional space to spaces with any finite or infinite number of dimensions. A Hilbert space is an abstract vector space possessing the structure of an inner product that allows length and angle to be measured. Furthermore, Hilbert spaces are complete: there are enough limits in the space to allow the techniques of calculus to be used.
In mathematics, singular integral operators on closed curves arise in problems in analysis, in particular complex analysis and harmonic analysis. The two main singular integral operators, the Hilbert transform and the Cauchy transform, can be defined for any smooth Jordan curve in the complex plane and are related by a simple algebraic formula. The Hilbert transform is an involution and the Cauchy transform an idempotent. The range of the Cauchy transform is the Hardy space of the bounded region enclosed by the Jordan curve. The theory for the original curve can be deduced from that on the unit circle, where, because of rotational symmetry, both operators are classical singular integral operators of convolution type. The Hilbert transform satisfies the jump relations of Plemelj and Sokhotski, which express the original function as the difference between the boundary values of holomorphic functions on the region and its complement. Singular integral operators have been studied on various classes of functions, including Hőlder spaces, Lp spaces and Sobolev spaces. In the case of L2 spaces—the case treated in detail below—other operators associated with the closed curve, such as the Szegő projection onto Hardy space and the Neumann–Poincaré operator, can be expressed in terms of the Cauchy transform and its adjoint.














