Berkelium fluoride may refer to:
- Berkelium(III) fluoride (Berkelium trifluoride), BkF3
- Berkelium(IV) fluoride (Berkelium tetrafluoride), BkF4
Berkelium fluoride may refer to:
Berkelium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Bk and atomic number 97. It is a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949. Berkelium was the fifth transuranium element discovered after neptunium, plutonium, curium and americium.

Einsteinium is a synthetic chemical element; it has symbol Es and atomic number 99. Einsteinium is a member of the actinide series and it is the seventh transuranium element. It was named in honor of Albert Einstein.

Radon difluoride is a compound of radon, a radioactive noble gas. Radon reacts readily with fluorine to form a solid compound, but this decomposes on attempted vaporization and its exact composition is uncertain. Calculations suggest that it may be ionic, unlike all other known binary noble gas compounds. The usefulness of radon compounds is limited because of the radioactivity of radon. The longest-lived isotope, radon-222, has a half-life of only 3.82 days, which decays by α-emission to yield polonium-218.
BK or Bk may refer to:
Fluorosis may refer to:
Berkelium (97Bk) is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic weight cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 243Bk in 1949. There are 20 known radioisotopes, from 230Bk and 233Bk to 253Bk, and 6 nuclear isomers. The longest-lived isotope is 247Bk with a half-life of 1,380 years.

Plutonium(IV) fluoride is a chemical compound with the formula (PuF4). This salt is generally a brown solid but can appear a variety of colors depending on the grain size, purity, moisture content, lighting, and presence of contaminants. Its primary use in the United States has been as an intermediary product in the production of plutonium metal for nuclear weapons usage.
97 may refer to:
Silver fluoride can refer to:
Berkeley most often refers to:
Bismuth fluoride may refer to:

Few compounds of californium have been made and studied. The only californium ion that is stable in aqueous solutions is the californium(III) cation. The other two oxidation states are IV (strong oxidizing agents) and II (strong reducing agents). The element forms a water-soluble chloride, nitrate, perchlorate, and sulfate and is precipitated as a fluoride, oxalate or hydroxide. If problems of availability of the element could be overcome, then CfBr2 and CfI2 would likely be stable.
Berkelium forms a number of chemical compounds, where it normally exists in an oxidation state of +3 or +4, and behaves similarly to its lanthanide analogue, terbium. Like all actinides, berkelium easily dissolves in various aqueous inorganic acids, liberating gaseous hydrogen and converting into the trivalent oxidation state. This trivalent state is the most stable, especially in aqueous solutions, but tetravalent berkelium compounds are also known. The existence of divalent berkelium salts is uncertain and has only been reported in mixed lanthanum chloride-strontium chloride melts. Aqueous solutions of Bk3+ ions are green in most acids. The color of the Bk4+ ions is yellow in hydrochloric acid and orange-yellow in sulfuric acid. Berkelium does not react rapidly with oxygen at room temperature, possibly due to the formation of a protective oxide surface layer; however, it reacts with molten metals, hydrogen, halogens, chalcogens and pnictogens to form various binary compounds. Berkelium can also form several organometallic compounds.

Californium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound, a salt with a chemical formula CfBr3. Like in californium oxide (Cf2O3) and other californium halides, including californium(III) fluoride (CfF3), californium(III) chloride, and californium(III) iodide (CfI3), the californium atom has an oxidation state of +3.

Berkelium(IV) oxide, also known as berkelium dioxide, is a chemical compound with the formula BkO2. This compound slowly decays to californium(IV) oxide. It can be converted to berkelium(III) oxide by hydrogen reduction at 600 °C.

Berkelium(III) nitrate is the berkelium salt of nitric acid with the formula Bk(NO3)3. It commonly forms the tetrahydrate, Bk(NO3)3·4H2O, which is a light green solid. If heated to 450 °C, it decomposes to berkelium(IV) oxide and 22 milligrams of the solution of this compound is reported to cost one million dollars.
Einsteinium compounds are compounds that contain the element einsteinium (Es). These compounds largely have einsteinium in the +3 oxidation state, or in some cases in the +2 and +4 oxidation states. Although einsteinium is relatively stable, with half-lives ranging from 20 days upwards, these compounds have not been studied in great detail.

Berkelium(III) chloride also known as berkelium trichloride, is a chemical compound with the formula BkCl3. It is a water-soluble green salt with a melting point of 603 °C. This compound forms the hexahydrate, BkCl3·6H2O.

Berkelium tetrafluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula BkF4.
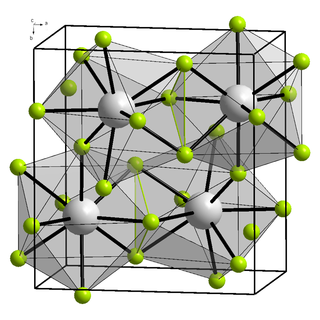
Berkelium(III) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of berkelium and fluorine with the chemical formula BkF
3.