
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the west almost by the Morocco–Spain border. The Mediterranean Sea covers an area of about 2,500,000 km2 (970,000 sq mi), representing 0.7% of the global ocean surface, but its connection to the Atlantic via the Strait of Gibraltar—the narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates the Iberian Peninsula in Europe from Morocco in Africa—is only 14 km (9 mi) wide.

The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Europe from Africa. The two continents are separated by 7.7 nautical miles at its narrowest point. Ferries cross between the two continents every day in as little as 35 minutes. The Strait's depth ranges between 300 and 900 metres.

The Tethys Ocean, also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean during much of the Mesozoic Era and early-mid Cenozoic Era. It was the predecessor to the modern Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Eurasian inland marine basins.

The Rock of Gibraltar is a monolithic limestone mountain 426 m (1,398 ft) high dominating the western entrance to the Mediterranean Sea. It is situated near the end of a narrow 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) long promontory stretching due south into the Mediterranean Sea and is located within the British territory of Gibraltar, and is 27 km north-east of Tarifa, Spain, the southwestern tip of Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. The rock serves as an impregnable fortress and contains a labyrinthine network of man-made tunnels known as the Tunnels of Gibraltar. Most of the Rock's upper area comprises a nature reserve which is home to about 300 Barbary macaques. It is a major tourist attraction.

A cay, also spelled caye or key, is a small, low-elevation, sandy island on the surface of a coral reef. Cays occur in tropical environments throughout the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, including in the Caribbean and on the Great Barrier Reef and Belize Barrier Reef.

The Alboran Sea is the westernmost portion of the Mediterranean Sea, lying between the Iberian Peninsula and the north of Africa. The Strait of Gibraltar, which lies at the west end of the Alboran Sea, connects the Mediterranean with the Atlantic Ocean.
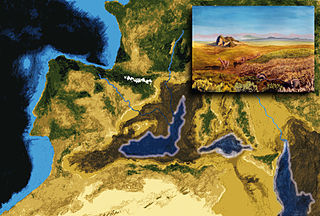
In the Messinian salinity crisis the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (drying-up) throughout the latter part of the Messinian age of the Miocene epoch, from 5.96 to 5.33 Ma. It ended with the Zanclean flood, when the Atlantic reclaimed the basin.

The Zanclean is the lowest stage or earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene. It spans the time between 5.332 ± 0.005 Ma and 3.6 ± 0.005 Ma. It is preceded by the Messinian Age of the Miocene Epoch, and followed by the Piacenzian Age.

Bioclasts are skeletal fossil fragments of once living marine or land organisms that are found in sedimentary rocks laid down in a marine environment—especially limestone varieties around the globe, some of which take on distinct textures and coloration from their predominate bioclasts—that geologists, archaeologists and paleontologists use to date a rock strata to a particular geological era.

The geology of the Iberian Peninsula consists of the study of the rock formations on the Iberian Peninsula, connected to the rest of the European landmass by the Pyrenees. The peninsula contains rocks from every geological period from the Ediacaran to the Quaternary, and many types of rock are represented. World-class mineral deposits are also found there.

The Gibraltar Arc is a geological region corresponding to an arcuate orogen surrounding the Alboran Sea, between the Iberian Peninsula and Africa. It consists of the Betic Cordillera, and the Rif. The Gibraltar Arc is located at the western end of the Mediterranean Alpine belt and formed during the Neogene due to convergence of the Eurasian and African plates.

Afro-Eurasia is a landmass comprising the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia. The terms are compound words of the names of its constituent parts. Afro-Eurasia has also been called the "Old World", in contrast to the "New World" referring to the Americas.

The Iberian plate is a microplate typically grouped with the Eurasian plate that includes the microcontinent Iberia, Corsica, Sardinia, the Balearic Islands, the Briançonnais zone of the Penninic nappes of the Alps, and the portion of Morocco north of the High Atlas Mountains. The Iberian plate is a part of the Eurasian plate.
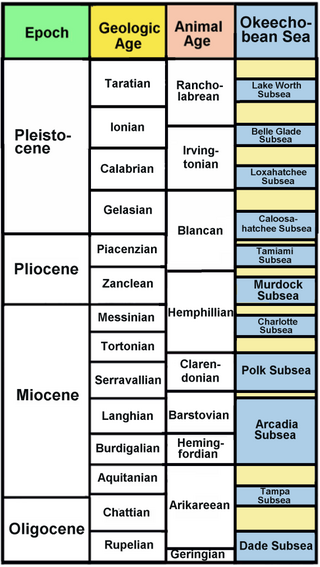
The Okeechobean Sea was a Cenozoic eutropical subsea, which along with the Choctaw Sea, occupied the eastern Gulf of Mexico basin system bounding Florida.
The Lexington Limestone is a prominent geologic formation that constitutes a large part of the late Ordovician bedrock of the inner Bluegrass region in Kentucky. Named after the city of Lexington, the geologic formation has heavily influenced both the surface topography and economy of the region.

The offshore Indus Basin is one of the two basins in offshore Pakistan, the other one being the offshore Makran Basin. The Murray Ridge separates the two basins. The offshore Indus basin is approximately 120 to 140 kilometers wide and has an areal extent of ~20,000 square km.
The geology of Sicily records the collision of the Eurasian and the African plates during westward-dipping subduction of the African slab since late Oligocene. Major tectonic units are the Hyblean foreland, the Gela foredeep, the Apenninic-Maghrebian orogen, and the Calabrian Arc. The orogen represents a fold-thrust belt that folds Mesozoic carbonates, while a major volcanic unit is found in an eastern portion of the island. The collision of Africa and Eurasia is a retreating subduction system, such that the descending Africa is falling away from Eurasia, and Eurasia extends and fills the space as the African plate falls into the mantle, resulting in volcanic activity in Sicily and the formation of Tyrrhenian slab to the north.

The Zanclean flood or Zanclean deluge is theorized to have refilled the Mediterranean Sea 5.33 million years ago. This flooding ended the Messinian salinity crisis and reconnected the Mediterranean Sea to the Atlantic Ocean, although it is possible that even before the flood there were partial connections to the Atlantic Ocean. The re-connection marks the beginning of the Zanclean age which is the name given to the earliest age on the geologic time scale of the Pliocene.
The Aksu Basin is a sedimentary basin in southwestern Turkey, around the present-day Aksu River. Located at the intersection of several major tectonic systems, in the Isparta Angle, the Aksu Basin covers an area of some 2000 square kilometers. Together with the Köprü Çay Basin and the Manavgat Basin, the Aksu Basin forms part of the broader Antalya Basin. It forms a graben relative to the surrounding Anatolian plateau.

Il-Blata tal-Melħ is a landmark in the north-western region of the island of Malta, close to Rabat and Mġarr. The name Il-Blata tal-Melħ can be translated as the Salt Rock, named after a series of salt deposits in the limestone at this location.

















