Related Research Articles

Kannauj is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is an evolved form of the classical name Kanyakubja. In Ancient Vedic period, it was famous city of Panchala Mahajanpada and also its capital during Panchala king Vajrayudha.

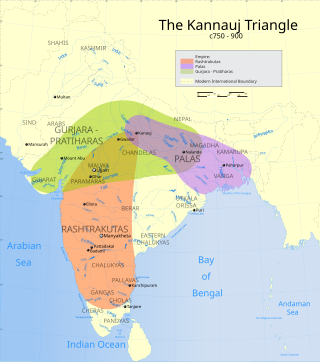
The Pratihara dynasty, also called the Gurjara-Pratiharas, the Pratiharas of Kannauj or the Imperial Pratiharas, was a prominent medieval Indian dynasty. It initially ruled the Gurjaradesa till 816 and from then onwards, the Kingdom of Kannauj until 1036 when the kingdom collapsed due the Ghaznavid invasions. Cadet branches of the dynasty ruled other minor states in the subcontinent.
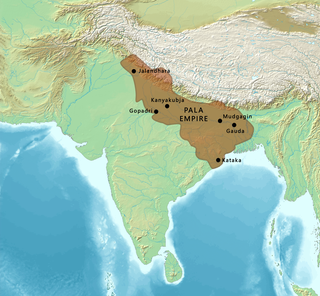
The Pāla Empire was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffix Pāla. The empire was founded with the election of Gopāla as the emperor of Gauda in late eighth century CE. The Pala stronghold was located in Bengal and eastern Bihar, which included the major cities of Gauḍa, Vikramapura, Pāṭaliputra, Monghyr, Somapura, Ramavati (Varendra), Tāmralipta and Jagaddala.
Yasovarman I was an Angkorian king who reigned in 889–910 CE. He was called "Leper King".

Bhoja was the Paramara Rajput ruler of the Kingdom of Malwa in central India, where his capital Dhara-nagara was located. Bhoja fought wars with nearly all his neighbours in attempts to extend his kingdom, with varying degrees of success. At its zenith, his empire extended from Chittor in the north to upper Konkan in the south, and from the Sabarmati River in the west to Vidisha in the east.

Mihira Bhoja or Bhoja I was the Pratiharan Emperor from 836 to 885 CE. He inherited a weakened realm in an adverse situation from his father, Ramabhadra. However, his capable reign transformed it into a large and prosperous empire. Bhoja was a devotee of Vishnu and adopted the title of Ādivarāha, which is inscribed on some of his coins.. One of the outstanding political figures of India in the ninth century, he ranks with Dhruva Dharavarsha and Dharmapala as a great general and empire builder.
Nagabhata II was an Indian Emperor from Pratihara dynasty. He ascended the throne of Pratihara dynasty after his father Vatsraja. His mother was queen Sundari-Devi. He was designated with imperial titles - Paramabhattaraka, Maharajadhiraja, and Paramesvara after conquest of Kannauj.
Dharmapala was the second ruler of the Pala Empire of Bengal region in the Indian subcontinent. He was the son and successor of Gopala, the founder of the Pala Dynasty. Dharmapala was mentioned as the great king of Vangala in the Nesari plates of Rashtrakuta dynasty. He greatly expanded the boundaries of the empire, and made the Palas a dominant power in the northern and eastern India.
Udayāditya was a Paramara ruler of Malwa region of central India, who succeeded Jayasimha I. He was succeeded by his son, either Lakshmadeva or Naravarman.
Mahipala I (913–944) ascended the throne of Pratihara Empire after his half brother Bhoja II. He was a son of Queen Mahidevi. Mahipala I was also known by the names: Ksitipala, Vinayakapala, Herambapala and Uttarapatha Swami.
Vatsaraja (780–800) or Vatsraja was an Emperor of the Pratihara dynasty in Northern India. He was grand-nephew of Nagabhata I and his mother was queen Bhuyikadevi. He was the first ruler of Rajasthan to win victories over the distant regions of Kanauj and Bengal. His extensive conquests mark the rise of the Imperial Pratiharas.
Bhoja II (910–913), according to the Asiatic Society's Plate of Vinakapala, acceded to the throne of the Pratihara empire after his father Mahendrapala I. His mother was queen Dehanaga-Devi. He reigned for a short time and was overthrown by his half-brother Mahipala I.

Yashovarman was the ruler of the Kingdom of Kannauj and first king of the Varman dynasty.
Jayasimha was the ruler of the Kingdom of Malwa in central India. He was the successor, and possibly the son, of the dynasty's most powerful king Bhoja. He appears to have ascended the throne with the support of the Kalyani Chalukya prince Vikramaditya VI, and appears to have been dethroned by Vikramaditya's rival brother Someshvara II.
Vakpatiraja II was an Indian king belonging to the Shakambhari Chahamana dynasty. He ruled the Sapadalaksha country, which included parts of present-day Rajasthan in north-western India.
Āma was a medieval Indian king who ruled Kannauj and surrounding areas during the 8th and the 9th centuries. According to the Jain chronicles, he was the son and successor of Yashovarman.
Lakshmikarna, also known as Karna, was a ruler of the Kalachuri dynasty of Tripuri in central India. His kingdom was centered around the Chedi or Dahala region in present-day Madhya Pradesh.
Dunduka was a king of the state of Kannauj in North India during the early 8th century CE.
The Ayudha dynasty was the short-lived ruling dynasty of the Kingdom of Kannauj from the late 8th to the early 9th century CE. It was established when Vajrayudha deposed the Varmans and started ruling over Kannauj.

The Kingdom of Kannauj was a kingdom in Northern India during the early medieval era. It was established by Harivarman in 510 as a vassal state of the Magadhan Empire. The kingdom of Kannauj expanded into a vast realm that spanned across northern India during the reign of Harshavardhana in the early seventh century. In the early ninth century, the city was conquered by Nagabhata II of the Pratihara dynasty after the Tripartite Struggle who proclaimed himself King of Kannauj. His descendents ruled Kannauj until Ghaznavid invasions.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Rama Shankar Tripathi (1964). History of Kanauj: To the Moslem Conquest. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 211. ISBN 978-81-208-0478-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Mishra, Shyam Manohar (1977). Yaśovarman of Kanauj: a study of political history, social, and cultural life of northern India during the reign of Yaśovarman. New Delhi: Abhinav Publications. pp. 120–121. OCLC 5782454.
- ↑ Sen, Sailendra Nath (1999). Ancient Indian History and Civilization (Paperback ed.). New Age International. pp. 264–668. ISBN 9788122411980.