
The North Banat District is one of seven administrative districts of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It lies in the geographical regions of Banat and Bačka. According to the 2011 census, the district has a population of 146,690 inhabitants. The administrative center of the district is the city of Kikinda.

The Danube Banovina or Danube Banate, was a banovina of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia between 1929 and 1941. This province consisted of the geographical regions of Srem, Bačka, Banat, Baranja, Šumadija, and Braničevo. The capital city of the Danube Banovina was Novi Sad. The province was named after the Danube River.

Nakovo is a village located in the Kikinda municipality of the North Banat District of Serbia, in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. It is situated near the border with Romania. The population of the village numbers 2,419 inhabitants, of whom 2,301 (95.12%) are ethnic Serbs.

Čurug is a village in the municipality of Žabalj, in the South Bačka District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 8,882 people.

Bašaid is a village located in the Kikinda municipality, in the North Banat District of the Republic of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has an ethnic Serb majority (89.15%) and a population of 3,503. Administratively, the settlement of Bikač is also classified as part of Bašaid.

Novi Slankamen is a village in Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Inđija, Syrmia District, Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Novi Slankamen is situated about 15 kilometers east of Inđija, on the bank of Danube (Dunav) and has a total population of 3,421.

Sajan is a village in the Kikinda municipality, in the North Banat District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a Hungarian ethnic majority (88.64%) and a population of 1,164.
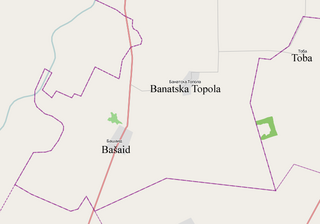
Banatska Topola is a village in the Kikinda municipality, in the North Banat District of the Republic of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a population of 1,066 of which 570 (53.47%) are ethnic Serbs and 434 (40.71%) are ethnic Hungarians. The location of the village is 18 kilometers south of the city of Kikinda. Administratively, the settlement named Vincaid is also classified as part of Banatska Topola.

The Čik or Čiker is a river in northern Serbia. A 95 km (59 mi) long right tributary to the Tisa river, it flows entirely within the Bačka region of Vojvodina province.

The Privileged District of Velika Kikinda was an administrative territorial entity of the Habsburg Monarchy between 1774 and 1876. It was an autonomous area centered around the town of Velika Kikinda, and mainly inhabited by ethnic Serbs.

The Holy Trinity Monastery is a Serbian Orthodox monastery located in the Banat region, in the northern Serbian province of Vojvodina. The monastery is situated in the town of Kikinda. It was built in 1885-87 as a foundation of Melanija Nikolić-Gajčić.

Nový Ruskov is a village and municipality in the Trebišov District in the Košice Region of south-eastern Slovakia.

Rusko Selo is a village in northeastern Serbia, located within the Kikinda municipality, North Banat District, Vojvodina.
Vincaid is a settlement (hamlet) in the municipality of Kikinda, Republic of Serbia. It is officially classified as part of the village of Banatska Topola. Located near the Kikinda-Zrenjanin motorway, the settlement was at first the estate of a family from which it got its name. Between the two world wars, the government made a futile attempt to turn this hamlet into a settlement of 120 households.

Mali Beograd, is a village in northern Serbia. It is situated in the municipality of Bačka Topola, in the North Bačka District of the Vojvodina province. The village had a population of 456 in 2011 and a Serb ethnic majority.

Voganj is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Ruma municipality, in the Srem District, Vojvodina province. The village has the population of 1,506.

Omladinski Fudbalski klub Kikinda is a football club from Kikinda, Serbia. It is one of the oldest clubs in Serbia. The club currently competes in Serbia's fourth division the Vojvodina League East.
Ghilad is a commune in Timiș County, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Gad (Gád) and Ghilad. These were part of Ciacova Commune until 2004, when they were split off.





















