Related Research Articles
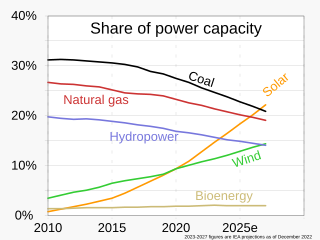
Renewable energy is energy from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. Renewable resources include sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy sources are sustainable, some are not. For example, some biomass sources are considered unsustainable at current rates of exploitation. Renewable energy is often used for electricity generation, heating and cooling. Renewable energy projects are typically large-scale, but they are also suited to rural and remote areas and developing countries, where energy is often crucial in human development. Renewable energy is often deployed together with further electrification, which has several benefits: electricity can move heat or objects efficiently, and is clean at the point of consumption.

A hydrogen vehicle is a vehicle that uses hydrogen fuel for motive power. Hydrogen vehicles include hydrogen-fueled space rockets, as well as ships and aircraft. Motive power is generated by converting the chemical energy of hydrogen to mechanical energy, either by reacting hydrogen with oxygen in a fuel cell to power electric motors or, less commonly, by burning hydrogen in an internal combustion engine.
Eskom Hld SOC Ltd or Eskom (Afrikaans: Elektrisiteitsvoorsieningskommissie) is a South African electricity public utility. Eskom was established in 1923 as the Electricity Supply Commission (ESCOM). Eskom represents South Africa in the Southern African Power Pool. The utility is the largest producer of electricity in Africa, and was among the top utilities in the world in terms of generation capacity and sales. It is the largest of South Africa's state owned enterprises. Eskom operates a number of notable power stations, including Matimba Power Station and Medupi Power Station in Lephalale, Kusile Power Station in Witbank, Kendal Power Station, and Koeberg Nuclear Power Station in the Western Cape Province, the only nuclear power plant in Africa.

India is the third largest producer of electricity in the world. During the fiscal year (FY) 2022–23, the total electricity generation in the country was 1,844 TWh, of which 1,618 TWh was generated by utilities.

Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used for energy storage on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when electricity is plentiful and inexpensive or when demand is low, and later returned to the grid when demand is high, and electricity prices tend to be higher.

Many countries and territories have installed significant solar power capacity into their electrical grids to supplement or provide an alternative to conventional energy sources. Solar power plants use one of two technologies:
The energy policy of India is to increase the locally produced energy in India and reduce energy poverty, with more focus on developing alternative sources of energy, particularly nuclear, solar and wind energy. Net energy import dependency was 40.9% in 2021-22.
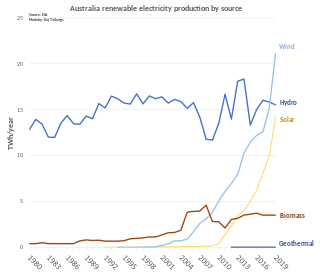
Renewable energy in Australia includes wind power, hydroelectricity, solar photovoltaics, heat pumps, geothermal, wave and solar thermal energy.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. As of 2012, renewable energy accounts for about half of new nameplate electrical capacity installed and costs are continuing to fall.

Solar power is a fast developing industry in India. The country's solar installed capacity was 71.61 GWAC as of 31 August 2023. Solar power generation in India ranks fourth globally in 2021.

According to data from the US Energy Information Administration, renewable energy accounted for about 13.1% of total primary energy consumption and about 21.5% of total utility-scale electricity generation in the United States in 2022.

A battery electric vehicle (BEV), pure electric vehicle, only-electric vehicle, fully electric vehicle or all-electric vehicle is a type of electric vehicle (EV) that exclusively uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs, with no secondary source of propulsion. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of internal combustion engines (ICEs) for propulsion. They derive all power from battery packs and thus have no internal combustion engine, fuel cell, or fuel tank. BEVs include – but are not limited to – motorcycles, bicycles, scooters, skateboards, railcars, watercraft, forklifts, buses, trucks, and cars.

The Solana Generating Station is a solar power plant near Gila Bend, Arizona, about 70 miles (110 km) southwest of Phoenix. It was completed in 2013. When commissioned, it was the largest parabolic trough plant in the world, and the first U.S. solar plant with molten salt thermal energy storage. Built by the Spanish company Abengoa Solar, the project can produce up to 280 megawatts (MW) gross, supplied by two 140 MW gross (125 MW net) steam turbine generators: enough electricity to meet the needs of approximately 70,000 homes and obviate the emission of roughly 475,000 tons of CO2 every year. Its name is the Spanish term for "sunny spot".
SolarReserve was a developer of utility-scale solar power projects which include Concentrated Solar Power (CSP) and Photovoltaic (PV) technology. The company has commercialized solar thermal energy storage technology that enables solar power tower CSP plants to deliver electricity day and night. In this technology, a molten salt is used to capture the energy from the sun and store it. When electricity is needed, the stored liquid salt is used to turn water into steam to turn a turbine and generate electricity.

EnergyinSaudi Arabia involves petroleum and natural gas production, consumption, and exports, and electricity production. Saudi Arabia is the world's leading oil producer and exporter. Saudi Arabia's economy is petroleum-based; oil accounts for 90% of the country's exports and nearly 75% of government revenue. The oil industry produces about 45% of Saudi Arabia's gross domestic product, against 40% from the private sector. Saudi Arabia has per capita GDP of $20,700. The economy is still very dependent on oil despite diversification, in particular in the petrochemical sector.

5-hour Energy is an American-made "energy shot" manufactured by Living Essentials LLC. The company was founded by CEO Manoj Bhargava and launched in 2004.

India is world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity and world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 40% of energy capacity installed in the year 2022 coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's (EY) 2021 Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index (RECAI) ranked India 3rd behind USA and China. In FY2023-24, India is planning to issue 50 GW tenders for wind, solar and hybrid projects. India has committed for a goal of 500 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030. In line with this commitment, India's installed renewable energy capacity has been experiencing a steady upward trend. From 94.4 GW in 2021, the capacity has gone up to 119.1 GW in 2023 as of Q4.

Husk Power Systems, founded in 2008, is a company based in Fort Collins, Colorado, US, that provides clean energy services to off-grid or weak grid rural communities in East Africa, West Africa and South Asia, primarily by building renewable energy mini-grids/micro-grids. Its original technology generated electricity using a biomass gasifier that created fuel from rice husks, a waste product of rice hullers that separate the husks as chaff from the rice, a staple food in both Asia and Africa. In the mid-2010s, with the rapid decline in the price of solar PV and batteries, Husk pivoted its business model to focus more on solar-plus-storage mini-grids, while continuing to use biomass in combination with solar to serve communities with larger electricity demand. In 2021, Husk Power was recognized in the REN21 Renewables Global Status Report as the first mini-grid company to achieve significant scale, by surpassing 100 solar hybrid community mini-grids, and 5,000 small business customers. In 2022, Husk signed an Energy Compact with the United Nations, in which it set a target of building 5,000 mini-grids and connecting at least 1 million customers by 2030.
Manoj Bhargava is an Indian American billionaire businessman and philanthropist. He is the founder and CEO of Innovations Ventures LLC, the company known for producing the 5-hour Energy drink. By 2012, the brand had grown to do an estimated $1 billion in sales. In 2015, Bhargava pledged 99% of his net worth to improving the well-being of the world's less fortunate.
The Australia–Asia Power Link (AAPowerLink) is a proposed electricity infrastructure project that is planned to include the world's largest solar plant, the world's largest battery, and the world's longest submarine power cable.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Walsh, Tom (October 5, 2015). "How the 5-Hour Energy Founder Plans to Save the World". Detroit Free Press. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- 1 2 Kumar, Bhaswar (October 22, 2015). "Manoj Bhargava's Crusade: From Energy Drinks to Limitless Energy". Business Standard. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Staff Writer. "Website Terms of Use". Billions In Change. Retrieved Dec 22, 2015.
- ↑ "Introducing Billions in Change, A Movement to Save the World". Billions in Change. September 18, 2015. Archived from the original on November 25, 2015. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Derek Markham (October 6, 2015). "5-Hour Energy Creator to Roll Out Pedal-Powered Energy Solution in India". Tree Hugger. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- ↑ Koch, Wendy (October 6, 2015). "Creator of 5-Hour Energy Wants to Power the World's Homes-With Bikes". National Geographic. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Shoot, Brittany (October 29, 2015). "This Billionaire Wants to Solve California's Water Problem". Fortune. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Mochari, Ilan (October 15, 2015). "Inside the Mind of the Billionaire Who Built the 5 Hour Energy Empire". Inc. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Korman, Alexandria (October 20, 2015). "5-Hour Energy Creator's New Inventions to Help Stop Poverty". Borgen Magazine. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Niland, Olivia (October 8, 2015). "5 Hour Energy Creator Wants to Power Thousands of Indian Homes With Bikes". Mashable. Retrieved November 24, 2015.
- ↑ Olewitz, Chloe (October 12, 2015). "5-Hour Energy Creator to Distribute 10,000 Stationary Bikes to Power Homes in India". Digital Trends. Retrieved November 24, 2015.