Related Research Articles
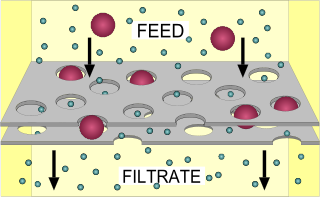
Filtration is a physical separation process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture using a filter medium that has a complex structure through which only the fluid can pass. Solid particles that cannot pass through the filter medium are described as oversize and the fluid that passes through is called the filtrate. Oversize particles may form a filter cake on top of the filter and may also block the filter lattice, preventing the fluid phase from crossing the filter, known as blinding. The size of the largest particles that can successfully pass through a filter is called the effective pore size of that filter. The separation of solid and fluid is imperfect; solids will be contaminated with some fluid and filtrate will contain fine particles. Filtration occurs both in nature and in engineered systems; there are biological, geological, and industrial forms. In everyday usage the verb "strain" is more often used; for example, using a colander to drain cooking water from cooked pasta.

An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains a growth medium solidified with agar, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.

A cleanroom or clean room is an engineered space that maintains a very low concentration of airborne particulates. It is well isolated, well controlled from contamination, and actively cleansed. Such rooms are commonly needed for scientific research and in industrial production for all nanoscale processes, such as semiconductor manufacturing. A cleanroom is designed to keep everything from dust to airborne organisms or vaporised particles away from it, and so from whatever material is being handled inside it.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents present in fluid or on a specific surface or object. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, fluid or an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

A microbiological culture, or microbial culture, is a method of multiplying microbial organisms by letting them reproduce in predetermined culture medium under controlled laboratory conditions. Microbial cultures are foundational and basic diagnostic methods used as research tools in molecular biology.

Bacteriological water analysis is a method of analysing water to estimate the numbers of bacteria present and, if needed, to find out what sort of bacteria they are. It represents one aspect of water quality. It is a microbiological analytical procedure which uses samples of water and from these samples determines the concentration of bacteria. It is then possible to draw inferences about the suitability of the water for use from these concentrations. This process is used, for example, to routinely confirm that water is safe for human consumption or that bathing and recreational waters are safe to use.
A fecal coliform is a facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped, gram-negative, non-sporulating bacterium. Coliform bacteria generally originate in the intestines of warm-blooded animals. Fecal coliforms are capable of growth in the presence of bile salts or similar surface agents, are oxidase negative, and produce acid and gas from lactose within 48 hours at 44 ± 0.5°C. The term thermotolerant coliform is more correct and is gaining acceptance over "fecal coliform".
In microbiology, a colony-forming unit is a unit which estimates the number of microbial cells in a sample that are viable, able to multiply via binary fission under the controlled conditions. Counting with colony-forming units requires culturing the microbes and counts only viable cells, in contrast with microscopic examination which counts all cells, living or dead. The visual appearance of a colony in a cell culture requires significant growth, and when counting colonies, it is uncertain if the colony arose from a single cell or a group of cells. Expressing results as colony-forming units reflects this uncertainty.

A syringe filter is a single-use filter cartridge. It is attached to the end of a syringe for use. Syringe filters may have Luer lock fittings, though not universally so. The use of a needle is optional; where desired it may be fitted to the end of the syringe filter.
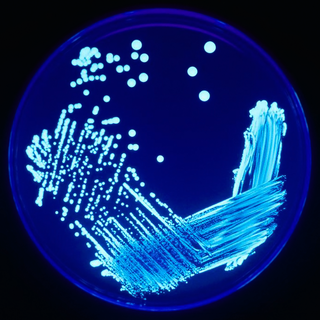
In microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested.

Trypticase soy agar or Tryptic soy agar (TSA) is a growth media for the culturing of moderately to non fastidious bacteria. It is a general-purpose, non-selective media providing enough nutrients to allow for a wide variety of microorganisms to grow. It is used for a wide range of applications, including culture storage, enumeration of cells (counting), isolation of pure cultures, or simply general culture.
Pharmaceutical microbiology is an applied branch of microbiology. It involves the study of microorganisms associated with the manufacture of pharmaceuticals e.g. minimizing the number of microorganisms in a process environment, excluding microorganisms and microbial byproducts like exotoxin and endotoxin from water and other starting materials, and ensuring the finished pharmaceutical product is sterile. Other aspects of pharmaceutical microbiology include the research and development of anti-infective agents, the use of microorganisms to detect mutagenic and carcinogenic activity in prospective drugs, and the use of microorganisms in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products like insulin and human growth hormone.
Plate count agar (PCA), also called standard methods agar (SMA), is a microbiological growth medium commonly used to assess or to monitor "total" or viable bacterial growth of a sample. PCA is not a selective medium.

In winemaking, clarification and stabilization are the processes by which insoluble matter suspended in the wine is removed before bottling. This matter may include dead yeast cells (lees), bacteria, tartrates, proteins, pectins, various tannins and other phenolic compounds, as well as pieces of grape skin, pulp, stems and gums. Clarification and stabilization may involve fining, filtration, centrifugation, flotation, refrigeration, pasteurization, and/or barrel maturation and racking.
Indoor bioaerosol is bioaerosol in an indoor environment. Bioaerosols are natural or artificial particles of biological origin suspended in the air. These particles are also referred to as organic dust. Bioaerosols may consist of bacteria, fungi, viruses, microbial toxins, pollen, plant fibers, etc. Size of bioaerosol particles varies from below 1 μm to 100 μm in aerodynamic diameter; viable bioaerosol particles can be suspended in air as single cells or aggregates of microorganism as small as 1–10 μm in size. Since bioaerosols are potentially related to various human health effects and the indoor environment provides a unique exposure situation, concerns about indoor bioaerosols have increased over the last decade.
A dip slide is a test for the presence of microorganisms in liquids. The use of dip slides is the method most frequently used to measure and observe microbial activity in liquid-based systems. It is often used in testing cooling systems. Dip slides are often used to determine the presence of slime forming bacteria in cooling & industrial water systems. The Health and Safety Executive's (HSE) recommends the use of dipslides to monitor the general activity of aerobic bacteria. The dip slide test consists of a sterile culture medium on a plastic carrier that is dipped into the liquid to be sampled. The culture is then incubated, allowing for microbial growth. Most Dip slides consist of 1 - 2 agars attached to a flexible plastic paddle, this allows full contact of the agar onto the desired area for testing. Most Dipslides come in a circular clear shatterproof tube that can be inserted into a dip-slide incubator.
Ultrapure water (UPW), high-purity water or highly purified water (HPW) is water that has been purified to uncommonly stringent specifications. Ultrapure water is a term commonly used in manufacturing to emphasize the fact that the water is treated to the highest levels of purity for all contaminant types, including: organic and inorganic compounds; dissolved and particulate matter; volatile and non-volatile; reactive, and inert; hydrophilic and hydrophobic; and dissolved gases.
Membrane technology encompasses the scientific processes used in the construction and application of membranes. Membranes are used to facilitate the transport or rejection of substances between mediums, and the mechanical separation of gas and liquid streams. In the simplest case, filtration is achieved when the pores of the membrane are smaller than the diameter of the undesired substance, such as a harmful microorganism. Membrane technology is commonly used in industries such as water treatment, chemical and metal processing, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, the food industry, as well as the removal of environmental pollutants.

A spiral plater is an instrument used to dispense a liquid sample onto a Petri dish in a spiral pattern. Commonly used as part of a CFU count procedure for the purpose of determining the number of microbes in the sample. In this setting, after spiral plating, the Petri dish is incubated for several hours after which the number of colony forming microbes (CFU) is determined. Spiral platers are also used for research, clinical diagnostics and as a method for covering a Petri dish with bacteria before placing antibiotic discs for AST.
In microbiology, the term isolation refers to the separation of a strain from a natural, mixed population of living microbes, as present in the environment, for example in water or soil, or from living beings with skin flora, oral flora or gut flora, in order to identify the microbe(s) of interest. Historically, the laboratory techniques of isolation first developed in the field of bacteriology and parasitology, before those in virology during the 20th century.
References
- ↑ Mosby's Dental Dictionary (2nd ed.). Elsevier, Inc. 2008.
- ↑ "Pace Analytical". Archived from the original on 2011-11-22. Retrieved 2012-06-12.
- ↑ 21 C.F.R. 211.110 (a) (6)
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 USP 31 <61> Microbiological Examination. https://www.uspnf.com/sites/default/files/usp_pdf/EN/USPNF/generalChapter61.pdf
- ↑ PathCon Laboratories. http://www.pathcon.com/documents/MB_USP_797.pdf
- ↑ Lowe, Christy (2011). "Operating Room HVAC Setback Strategies" (PDF). The American Society for Healthcare Engineering (ASHE). Retrieved December 13, 2017.
https://www.watertechnologies.com/products/analyzers-instruments/sievers-soleil