
Ribosomes comprise a complex macromolecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunits, which read the mRNA, and the large subunits, which join amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit consists of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of ribosomal proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.
Prokaryotic translation is the process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in prokaryotes.
Eukaryotic translation is the biological process by which messenger RNA is translated into proteins in eukaryotes. It consists of four phases: initiation, elongation, termination, and recycling.

The bag-1 internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is a cis-acting element located in the 5 ' untranslated region of the BAG-1 protein mRNA. Its effects apoptosis through IRES mediated translation of the BAG-1 protein.

The Cripavirus internal ribosome entry site is an RNA element required for the production of capsid proteins through ribosome recruitment to an intergenic region IRES.
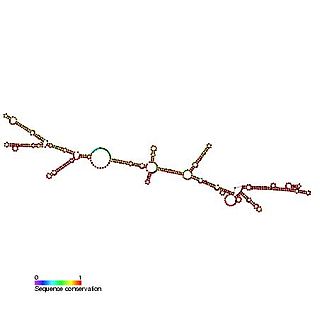
The c-sis internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is a RNA element found in the 5' UTR of the PDGF beta chain gene. The internal ribosome entry site contains three modules that can individually mediate internal ribosome entry. However, the full length sequence is required for maximal IRES activity. It is thought that the three IRES elements are somehow responsive to cellular changes and act to regulate the level of translation.
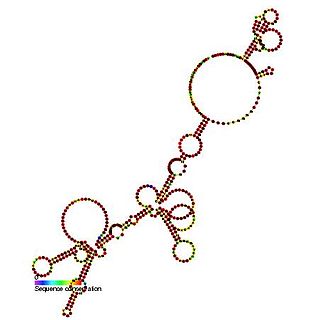
The FGF-2 internal ribosome entry site is an RNA element present in the 5' UTR of the mRNA of fibroblast growth factor-2. It has been found that the FGF-2 internal ribosome entry site (IRES) activity is strictly controlled and highly tissue specific. It is thought that translational IRES dependent activation of FGF-2 plays a vital role in embryogenesis and in the adult brain [1]. When expressed the fibroblast growth factor 2 FGF-2 protein plays a pivotal role in cell proliferation, differentiation and survival as well as being involved in wound-healing [1,2].
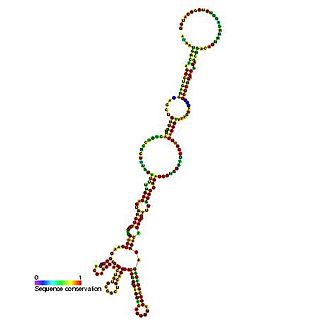
The heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is an RNA element that allows cap independent translation during conditions such as heat shock and stress. It has been shown that the 216 nucleotide long 5' UTR contains internal ribosome entry site activity.

This family represents the internal ribosome entry site (IRES) of the hepatitis A virus. HAV IRES is a 450 nucleotide long sequence located in the 735 nt long 5’ UTR of Hepatitis A viral RNA genome. IRES elements allow cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. The IRES achieves this by mediating the internal initiation of translation by recruiting a ribosomal 40S pre-initiation complex directly to the initiation codon and eliminates the requirement for eukaryotic initiation factor, eIF4F.
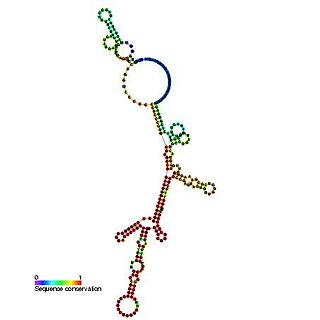
The Hepatitis C virus internal ribosome entry site, or HCV IRES, is an RNA structure within the 5'UTR of the HCV genome that mediates cap-independent translation initiation.

The L-myc internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is an RNA element present in the 5' UTR of the mRNA of L-myc that allows cap-independent translation. L-myc undergoes translation via the internal ribosome entry site and bypasses the typical eukaryotic cap-dependent translation pathway [1]. The myc family of genes when expressed are known to be involved in the control of cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis.

The N-myc internal ribosome entry site (IRES) is an RNA element found in the n-myc gene. The myc family of genes when expressed are known to be involved in the control of cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. n-myc mRNA has an alternative method of translation via an internal ribosome entry site where ribosomes are recruited to the IRES located in the 5' UTR thus bypassing the typical eukaryotic cap-dependent translation pathway.

This family represents the Picornavirus internal ribosome entry site (IRES). IRES elements allow cap and end-independent translation of mRNA in the host cell. It has been found that La autoantigen (La) is required for Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) IRES-mediated translation, and it has been suggested that La may be required for the efficient translation of the viral RNA in the pancreas.
A ribosome binding site, or ribosomal binding site (RBS), is a sequence of nucleotides upstream of the start codon of an mRNA transcript that is responsible for the recruitment of a ribosome during the initiation of protein translation. Mostly, RBS refers to bacterial sequences, although internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) have been described in mRNAs of eukaryotic cells or viruses that infect eukaryotes. Ribosome recruitment in eukaryotes is generally mediated by the 5' cap present on eukaryotic mRNAs.
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4 G (eIF4G) is a protein involved in eukaryotic translation initiation and is a component of the eIF4F cap-binding complex. Orthologs of eIF4G have been studied in multiple species, including humans, yeast, and wheat. However, eIF4G is exclusively found in domain Eukarya, and not in domains Bacteria or Archaea, which do not have capped mRNA. As such, eIF4G structure and function may vary between species, although the human eIF4G 1 has been the focus of extensive studies.

Red clover necrotic mosaic virus (RCNMV) contains several structural elements present within the 3' and 5' untranslated regions (UTR) of the genome that enhance translation. In eukaryotes transcription is a prerequisite for translation. During transcription the pre-mRNA transcript is processes where a 5' cap is attached onto mRNA and this 5' cap allows for ribosome assembly onto the mRNA as it acts as a binding site for the eukaryotic initiation factor eIF4F. Once eIF4F is bound to the mRNA this protein complex interacts with the poly(A) binding protein which is present within the 3' UTR and results in mRNA circularization. This multiprotein-mRNA complex then recruits the ribosome subunits and scans the mRNA until it reaches the start codon. Transcription of viral genomes differs from eukaryotes as viral genomes produce mRNA transcripts that lack a 5’ cap site. Despite lacking a cap site viral genes contain a structural element within the 5’ UTR known as an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). IRES is a structural element that recruits the 40s ribosome subunit to the mRNA within close proximity of the start codon.
Translational regulation refers to the control of the levels of protein synthesized from its mRNA. This regulation is vastly important to the cellular response to stressors, growth cues, and differentiation. In comparison to transcriptional regulation, it results in much more immediate cellular adjustment through direct regulation of protein concentration. The corresponding mechanisms are primarily targeted on the control of ribosome recruitment on the initiation codon, but can also involve modulation of peptide elongation, termination of protein synthesis, or ribosome biogenesis. While these general concepts are widely conserved, some of the finer details in this sort of regulation have been proven to differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms.












