
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. It became the capital city of the civilisation of Ancient Carthage and later Roman Carthage.
Archaic humans emerged out of Africa between 0.5 and 1.8 million years ago. This was followed by the emergence of modern humans in East Africa around 300,000–250,000 years ago. In the 4th millenium BC written history arose in Ancient Egypt, and later in Nubia's Kush, the Horn of Africa's Dʿmt, and Ifrikiya's Carthage. Between around 3000 BC and 1000 AD, the Bantu expansion swept from north-western Central Africa across much of sub-Saharan Africa, laying the foundations for states in Central, Eastern, and Southern regions. In most African societies the oral word is revered, and as such they have generally recorded their history orally. This has led anthropologists to term them oral civilisations, contrasted with literate civilisations which pride the written word. Oral tradition often remained the preferred method of recordation in cases when a writing system was adapted or developed; for example the oral recordation of the Kouroukan Fouga in the Mali Empire while having adapted the Arabic script to be used in scholarly pursuits.

The term Moor is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim populations of the Maghreb, al-Andalus, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages. Moors are not a single, distinct or self-defined people. The 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica observed that the term had "no real ethnological value." Europeans of the Middle Ages and the early modern period variously applied the name to Arabs, Berbers, and Muslim Europeans.

French Equatorial Africa was a federation of French colonial territories in Equatorial Africa which consisted of Gabon, French Congo, Ubangi-Shari, and Chad. It existed from 1910 to 1958 and its administration was based in Brazzaville.

The Mali Empire was an empire in West Africa from c. 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws, and customs.

The Berlin Conference of 1884–1885 met on 15 November 1884 and, after an adjournment, concluded on 26 February 1885 with the signature of a General Act regulating European colonization and trade in Africa during the New Imperialism period.
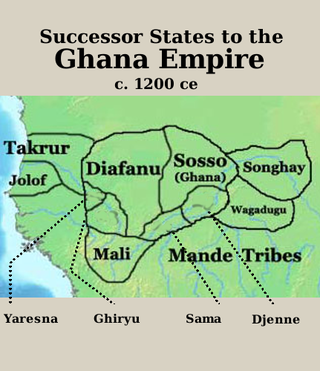
Takrur, Tekrur or Tekrour was a state based in the Senegal River valley in modern day Mauritania and Northern Senegal, Northwestern Africa, which was at its height in the 10th and 11th centuries, roughly parallel to the Ghana Empire. It lasted in some form into the 18th century.
The Bakwena or Bakoena are a large Sotho-Tswana clan in Southern Africa of the southern Bantu group. They can be found in different parts of southern Africa such as Lesotho, Botswana, South Africa and Eswatini. "Kwena" is a Sotho/Tswana/Sepedi word meaning "crocodile", the crocodile is also their totem (seboko).
Human history is the record of humankind from prehistory to the present. Modern humans evolved in Africa around 300,000 years ago and initially lived as hunter-gatherers. They migrated out of Africa during the Last Ice Age and had populated most of the Earth by the end of the Ice Age 12,000 years ago. Soon afterward, the Neolithic Revolution in West Asia brought the first systematic husbandry of plants and animals, and saw many humans transition from a nomadic life to a sedentary existence as farmers in permanent settlements. The growing complexity of human societies necessitated systems of accounting and writing.

In modern historiography, the Western Roman Empire was the western provinces of the Roman Empire, collectively, during any period in which they were administered separately from the eastern provinces by a separate, independent imperial court. Particularly during the period from AD 395 to 476, there were separate, coequal courts dividing the governance of the empire into the Western provinces and the Eastern provinces with a distinct imperial succession in the separate courts. The terms Western Roman Empire and Eastern Roman Empire were coined in modern times to describe political entities that were de facto independent; contemporary Romans did not consider the Empire to have been split into two empires but viewed it as a single polity governed by two imperial courts for administrative expediency. The Western Empire collapsed in 476, and the Western imperial court in Ravenna disappeared by AD 554, at the end of Justinian's Gothic War.

The Songhai Empire was a state located in the western part of the Sahel during the 15th and 16th centuries. At its peak, it was one of the largest African empires in history. The state is known by its historiographical name, derived from its largest ethnic group and ruling elite, the Songhai people. Sonni Ali established Gao as the empire's capital, although a Songhai state had existed in and around Gao since the 11th century. Other important cities in the kingdom were Timbuktu and Djenné, where urban-centred trade flourished; they were conquered in 1468 and 1475, respectively. Initially, the Songhai Empire was ruled by the Sonni dynasty, but it was later replaced by the Askia dynasty (1493–1591).
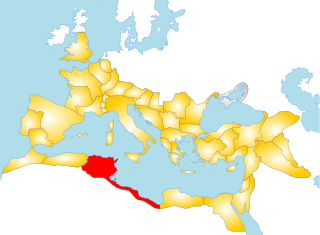
Ifriqiya, also known as al-Maghrib al-Adna or Oriental Berberia, was a medieval historical region comprising today's Tunisia, eastern Algeria, and Tripolitania. It included all of what had previously been the Byzantine province of Africa Proconsularis and extended beyond it, but did not include the Mauretanias.
The History of the Second World War is the official history of the British contribution to the Second World War and was published by Her Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO). The immense project was sub-divided into areas to ease publication, United Kingdom Military Series, the United Kingdom Civil Series for the civilian war effort; the Foreign Policy series, the Intelligence series and the Medical series are eponymous. Other volumes not under the aegis of the series but published by HMSO may be read as adjuncts, covering matters not considered in great detail or at all, in one case, in the main series. Further volumes, published after the privatisation of HMSO or in the series about the Special Operations Executive, are also useful.

The Idrisid dynasty or Idrisids were an Arab Muslim dynasty from 788 to 974, ruling most of present-day Morocco and parts of present-day western Algeria. Named after the founder, Idris I, the Idrisids were an Alid dynasty descended from Muhammad through his grandson Hasan. The Idrisids are traditionally considered to be the founders of the first Moroccan state, setting the stage for subsequent dynasties and states centered in this region. Their reign played an important role in the early Islamization of Morocco and also presided over an increase in Arab immigration and Arabization in major urban centers.

The Kingdom of Kongo was a kingdom in Central Africa. It was located in present-day northern Angola, the western portion of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Southern of Gabon and the Republic of the Congo. At its greatest extent it reached from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Kwango River in the east, and from the Congo River in the north to the Kwanza River in the south. The kingdom consisted of several core provinces ruled by the Manikongo, the Portuguese version of the Kongo title Mwene Kongo, meaning "lord or ruler of the Kongo kingdom", but its sphere of influence extended to neighbouring kingdoms, such as Ngoyo, Kakongo, Loango, Ndongo, and Matamba, the latter two located in what is Angola today.

Rawwadid, Ravvadid, or Banū Rawwād (900–1071) was a Sunni Muslim Kurdish dynasty, centered in the northwestern region of Adharbayjan (Azerbaijan) between the late 8th and early 13th centuries.

The Ethiopian Empire, historically known as Abyssinia or simply Ethiopia, was a sovereign state that encompassed the present-day territories of Ethiopia and Eritrea. It existed from the establishment of the Solomonic dynasty by Yekuno Amlak around 1270 until the 1974 coup d'état by the Derg, which ended the reign of the final Emperor, Haile Selassie. In the late 19th century, under Emperor Menelik II, the empire expanded significantly to the south, and in 1952, Eritrea was federated under Selassie's rule. Despite being surrounded by hostile forces throughout much of its history, the empire maintained a kingdom centered on its ancient Christian heritage.

The Praetorian Prefecture of Africa was an administrative division of the Byzantine Empire in the Maghreb. With its seat at Carthage, it was established after the reconquest of northwestern Africa from the Vandals in 533–534 by the Byzantine Emperor Justinian I. It continued to exist until 591, when it was replaced by the Exarchate of Africa.

The Kingdom of Aksum also known as the Kingdom of Axum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging from the earlier Dʿmt civilization, the kingdom was founded in 1st century. The city of Axum served as the kingdom's capital for many centuries until it relocated to Kubar in the 9th century due to declining trade connections and recurring external invasions.

The General History of Africa (GHA) is a two-phase project launched by UNESCO in 1964, producing a volume history of Africa first published in 1981 up to the present.















