
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus Prunus, and is a fleshy drupe.

Prunus is a genus of trees and shrubs in the flowering plant family Rosaceae that includes plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution, being native to the North American temperate regions, the neotropics of South America, and temperate and tropical regions of Eurasia and Africa, There are about 340 accepted species as of March 2024. Many members of the genus are widely cultivated for their fruit and for decorative purposes. Prunus fruit are drupes, or stone fruits. The fleshy mesocarp surrounding the endocarp is edible while the endocarp itself forms a hard, inedible shell called the pyrena. This shell encloses the seed, which is edible in some species, but poisonous in many others. Besides being eaten off the hand, most Prunus fruit are also commonly used in processing, such as jam production, canning, drying, and the seeds for roasting.
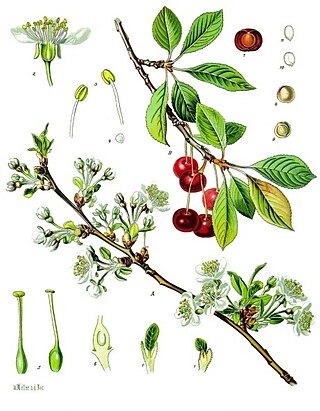
Prunus cerasus is a species of Prunus in the subgenus Cerasus (cherries), native to much of Europe, North Africa and West Asia. It is closely related to the sweet cherry, but has a fruit that is more acidic. Its sour pulp is edible.

Prunus subg. Padus is a subgenus of Prunus, characterised by having racemose inflorescences. Padus was originally a distinct genus, but genetic and morphological studies have shown that Padus is polyphyletic. It has been proposed that all the racemose taxa within Prunus are incorporated into a broad-sense Prunus subg. Padus.

Prunus padus, known as bird cherry, hackberry, hagberry, or Mayday tree, is a flowering plant in the rose family. It is a species of cherry, a deciduous small tree or large shrub up to 16 metres (52 ft) tall. It is the type species of the subgenus Padus, which have flowers in racemes. It is native to northern Europe and northern and northeast Asia, and is grown as an ornamental in North America.

Prunus serrulata or Japanese cherry is a species of cherry tree that grows naturally in Japan, China, Korea, and Vietnam, and it also refers to a cultivar produced from Prunus speciosa, a cherry tree endemic in Japan. Historically, the Japanese have developed many cultivars by selective breeding of cherry trees, which are produced by the complicated crossing of several wild species, and they are used for ornamental purposes all over the world. Of these, the cultivars produced by complex interspecific hybrids based on the Oshima cherry are also known as the Cerasus Sato-zakura Group.

Prunus serotina, commonly called black cherry, wild black cherry, rum cherry, or mountain black cherry, is a deciduous tree or shrub in the rose family Rosaceae. Despite being called black cherry, it is not very closely related to the commonly cultivated cherries such as sweet cherry, sour cherry and Japanese flowering cherries which belong to Prunus subg. Cerasus. Instead, P. serotina belongs to Prunus subg. Padus, a subgenus also including Eurasian bird cherry and chokecherry. The species is widespread and common in North America and South America.
Dwarf cherry as a name has been used for at least three species of small cherry trees:

The grey dagger is a moth of the family Noctuidae.

Prunus emarginata, the bitter cherry or Oregon cherry, is a species of Prunus native to western North America, from British Columbia south to Baja California, and east as far as western Wyoming and New Mexico. It is often found in recently disturbed areas or open woods on nutrient-rich soil.

Prunus ilicifolia is native to the chaparral areas of coastal California, Baja California, and Baja California Sur. as well as the desert chaparral areas of the Mojave desert.

Prunus grayana is a species of bird cherry native to Japan and China, occurring at medium altitudes of 1,000–3,800 m in the temperate zone. It prefers sunshine and moist soil.

Prunus fruticosa, the European dwarf cherry, dwarf cherry, Mongolian cherry or steppe cherry is a deciduous, xerophytic, winter-hardy, cherry-bearing shrub. It is also called ground cherry and European ground cherry, but is not to be confused with plants in the distinct "Groundcherry" genus of Physalis.

Lomographa temerata, the clouded silver, is a moth of the family Geometridae. The species is found in Asia and Europe and was first described by Michael Denis and Ignaz Schiffermüller in 1775.

Prunus avium, commonly called wild cherry, sweet cherry or gean is a species of cherry, a flowering plant in the rose family, Rosaceae. It is native to Europe, Anatolia, Maghreb, and Western Asia, from the British Isles south to Morocco and Tunisia, north to the Trondheimsfjord region in Norway and east to the Caucasus and northern Iran, with a small isolated population in the western Himalaya. The species is widely cultivated in other regions and has become naturalized in North America, New Zealand and Australia.
Wild cherry is a common name for species of cherries growing outside of cultivation, especially:

Bird cherry-oat aphid is an aphid in the superfamily Aphidoidea in the order Hemiptera. It is a true bug and sucks sap from plants. It is considered a major pest in cereal crops, especially in temperate regions, as well as other hosts in parts of Northern Europe. It is the principal vector of many viruses in economically important field crops.

Prunus buergeriana, in Japanese イヌザクラ (inu-zakura), meaning dog cherry, is a species of bird cherry native to Japan, Korea, Taiwan, China, northeast India (Sikkim), and Bhutan. In China it prefers to grow on mountain slopes at 1000 to 3400 m above sea level. Its closest relative is Prunus perulata, from which it is morphologically and genetically distinct.

Prunus subg. Cerasus is a subgenus of Prunus. Species of the subgenus have a single winter bud per axil. The flowers are usually in small corymbs or umbels of several together, but some species have short racemes. The fruit is a drupe and has no obvious groove along the side. The subgenus is native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with two species in North America, four in Europe, two in North Africa, and the remainder in Asia.















