Nepal is a landlocked mountainous country where transportation is difficult due to the terrain.
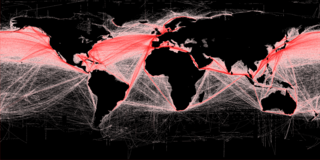
Freight transport is the physical process of transporting commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea, but in American English, it has been extended to refer to transport by land or air as well. "Logistics", a term borrowed from the military environment, is also fashionably used in the same sense.

Intermodal freight transport involves the transportation of freight in an intermodal container or vehicle, using multiple modes of transportation, without any handling of the freight itself when changing modes. The method reduces cargo handling, and so improves security, reduces damage and loss, and allows freight to be transported faster. Reduced costs over road trucking is the key benefit for inter-continental use. This may be offset by reduced timings for road transport over shorter distances.

Narayani was one of the fourteen zones of Nepal until the restruction of zones to Provinces, located in the central south of the country. Narayani Zone is named after the Narayani River which is on the western border of the zone, separating it from the Gandaki and Lumbini zones. Narayani means beloved of Narayan which is Parvati his sister, and Narayan refers to Lord Vishnu in the Hindu religion.

Birgunj is a metropolitan city and border town in Parsa District in the Narayani Zone of southern Nepal. It lies 135 km (84 mi) south of the capital Kathmandu, attached in the north to Raxaul in the border of the Indian state of Bihar. As an entry point to Nepal from Patna and Kolkata, it is known as the "Gateway to Nepal". The town has significant economic importance for Nepal as most of the trade with India is via Birgunj and the Indian town of Raxaul. Tribhuvan Highway links Birgunj to Nepal's capital, Kathmandu. It was declared a Metropolitan City on 22 May 2017 along with Biratnagar and Pokhara. Birgunj is currently the second largest city in the Terai region of Nepal, and the sixth most populated metropolis of the nation.
Himalayan Bank Limited (HBL) is one of the largest private banks of Nepal. The Bank was incorporated in 1992 by a few eminent individuals of Nepal in partnership with the Employees Provident Fund and Habib Bank Limited of Pakistan. The bank commenced its operations in January 1993. Himalayan Bank is also the first commercial bank of Nepal with most of its shares held by the private sector of Nepal. Besides commercial banking services, the bank also offers industrial and merchant banking service.
The Virginia Port Authority (VPA) is an autonomous agency of the Commonwealth of Virginia that owns The Port of Virginia, a group of facilities with their activity centered on the harbor of Hampton Roads, Virginia.

The Ministry of Shipping, a branch of the Government of India, is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to shipping. Since 2014 it has been under Transport minister Nitin Gadkari.

Container Corporation of India Ltd. (CONCOR),is a Navratna Public Sector Undertaking under the Indian Ministry of Railways. Incorporated in March 1988 under the Companies Act, CONCOR commenced operations in November 1989 taking over an existing network of seven inland container depots (ICDs) from Indian Railways.

The Nepal Railways Corporation Ltd. is a state-owned company which operates railways in Nepal.

Pakistan Customs is one of the elite cadres of the Civil Service of Pakistan. It is serving as the guardian of Pakistan's borders against movement of contra band goods and is a facilitator of bona fide trade. It provides a major source of revenue to the Government of Pakistan in the form of taxes levied on the goods traded across the borders. It also helps to protect the domestic industry, discourage consumptions of luxury goods and stimulate development in the under -developed areas. Customs and Regulatory duties amount up to 15% of the total receipts collected by the Federal Board of Revenue. Pakistan Customs is manned by officers from the Pakistan Customs Service (PCS) which has been one of the premier occupational group amongst Pakistan's civil services. Previously known as the “Customs & Excise group”, it was re-classified as Pakistan Customs Service in November 2010, when the responsibility of Sales Tax & Federal Excise was taken away and a new occupational service developed to collect Sales Tax, Federal Excise and Income Tax namely Inland Revenue Service (IRS). This has given PCS officers an opportunity to focus on their core function of acting as guardian of the nation’s borders against illegitimate trade and regulating bona fide trade. While the role of Pakistan Customs Service has been greatly diminished because of the loss of sales tax and federal excise to IRS, the move has allowed Pakistan Customs Service to become a lean and mean service with enhanced focus on border control.

Dharamtar port is on the right bank of the Amba river and is 10 miles (16 km) from its mouth. Approximately 2 km (1.2 mi) from Wadkhal village on NH-17. The port is 0.5 km (0.31 mi) from the state highway that runs through Pen to Alibag and is 2 km (1.2 mi) away from National Highway 17 (Mumbai—Goa). The port is also adjacent to Mumbai–Goa–Konkan railway line with an approved rail siding. It is a tri-modal port with rail.
MIT is a project partly funded by the European Union under the Programme “Research for the benefit of SMEs“ – Call ID “FP7-SME-2011” and managed by Research Executive Agency. Metrocargo is a concept of intermodal shipment based on horizontal loading and unloading containers and swap bodies on standard flatbed wagons under the overhead electric feeding line. The system being fully automated and very efficient, it is time and cost effective for the distributed intermodal transport over a territory and for processing full trains in port to dry port shuttling. The promoters constructed a full-scale prototype unit and the EC-funded research pro-ject VIT Vision for Innovative Transport successfully researched the remaining technical issues. This MIT Metrocargo Intermodal Transport project is about bringing Metrocargo from research to market stage and promoting its dissemination among logistic decision-makers throughout Europe. Technically, MIT will implement specific technical improvements and the scaling up from single prototypal unit to full industrial installation, developing typical plant design and SW applications to automate and optimise the work flow and provide interfaces with operators and external systems. Promotion and dissemination will be the main goal, carrying out market studies in several EU member states and subsequent market plans to exploit the Metrocargo features in terms of installation and operating costs, limited use of dock area, safety and environmental impact. Economic advantages to operators in typical situations will be deter-mined effecting specific feasibility studies. Dissemination events will be organised centred on the full scale Metrocargo prototype installed in the port of Vado Ligure. The SMEs will exhibit the system in main logistic and transport shows in Europe and will organise road-show presentations in several countries, using videos and a dynamic simulation SW tool to illustrate the solutions for specific needs. At the end of this Project the Metrocargo technology will be a fully developed market-ready system that will be widely known among European logistic decision makers.
Doncaster iPort or Doncaster Inland Port is an intermodal rail terminal; a Strategic Rail Freight Interchange, under construction in Rossington, Doncaster at junction 3 of the M18 motorway in England. It is to be connected to the rail network via the line of the former South Yorkshire Joint Railway, and from an extension of the former Rossington Colliery branch from the East Coast Main Line.
Riyadh Dry Port is a dry port in the city of Riyadh. It is the largest inland port in Saudi Arabia. The port is located on off Exit 16 in Al Malaz, adjacent to the Riyadh railway station. Riyadh Dry Port covers an area of 918,639 m2 and accommodates six 6,480 m2 warehouses.
The Government agencies in Bangladesh are state controlled organizations that act independently to carry out the policies of the Government of Bangladesh. The Government Ministries are relatively small and merely policy-making organizations, allowed to control agencies by policy decisions. Some of the work of the government is carried out through state enterprises or limited companies.

Gaunpalika or gaupalika is the newly formed lower administrative division in Nepal. The Ministry of Federal Affairs and Local Development (Nepal) dissolved the existing village development committees and announced the establishment of this new local body. There are currently 460 rural municipalities.