The Bison industrialised building system is a precast concrete building system used in high rise flats, developed by Bison Manufacturing Ltd, Dartford, Kent, England.
The Bison industrialised building system is a precast concrete building system used in high rise flats, developed by Bison Manufacturing Ltd, Dartford, Kent, England.
Bison Manufacturing was founded in 1919 to build military pill-boxes.
The Bison wall-frame construction system was a construction method used in tower block construction. It was launched in 1963 by Concrete Ltd who set up factories across the UK to pre-fabricate the parts it. It was not a frame structure as such, instead precast concrete panels formed the structure of high rise blocks. It evolved into a rapid construction method.
In tower blocks over 12 storeys in height, all of the walls were loadbearing - external and internal. Whilst there were no partition walls, the internal walls were still thinner at 6 inches in thickness. Two-bedroom flats could be constructed out of 21 pre-cast concrete pieces. The bathroom and toilet elements could be constructed from a similarly few number of pre-fabricated pieces. The lift shaft and staircases could be constructed out of pieces that were 3 storeys high. The method was limited in that it was only really practical for two and three-bedroom flats. [1]

Stonemasonry or stonecraft is the creation of buildings, structures, and sculpture using stone as the primary material. Stonemasonry is the craft of shaping and arranging stones, often together with mortar and even the ancient lime mortar, to wall or cover formed structures.

The large panel system building is a building constructed of large, prefabricated concrete slabs. Such buildings are often found in housing development areas.
A load-bearing wall or bearing wall is a wall that is an active structural element of a building, which holds the weight of the elements above it, by conducting its weight to a foundation structure below it.
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located. Some researchers refer it to “various materials joined together to form a component of the final installation procedure“.

Ronan Point was a 22-storey tower block in Canning Town in Newham, East London, that partly collapsed on 16 May 1968, only two months after it had opened. A gas explosion blew out some load-bearing walls, causing the collapse of one entire corner of the building; four people died and 17 were injured. The nature of the failure led to a loss of public confidence in high-rise residential buildings, and major changes in British building regulations resulted.

Precast concrete is a construction product produced by casting concrete in a reusable mold or "form" which is then cured in a controlled environment, transported to the construction site and maneuvered into place; examples include precast beams, and wall panels for tilt up construction. In contrast, cast-in-place concrete is poured into site-specific forms and cured on site.
Studcast concrete, also called "pre-framed concrete", combines relatively thin concrete layers with cold formed steel framing to create hybrid panels; the result is a panelized system usable for cladding, curtain walls, shaft walls, and load-bearing exterior and interior walls. Studcast panels install in the same manner as prefabricated steel stud panels. The technology is applicable for both factory prefabrication and site-cast (tilt-up) wall construction on almost all types of buildings, including multifamily housing, schools, industrial, commercial and institutional structures.

Prefabs were a major part of the delivery plan to address the United Kingdom's post–World War II housing shortage. They were envisaged by war-time prime minister Winston Churchill in March 1944, and legally outlined in the Housing Act 1944.
The 1950s and 1960s saw the construction of numerous brutalist apartment blocks in Sheffield, England. The Sheffield City Council had been clearing inner-city residential slums since the early 1900s. Prior to the 1950s these slums were replaced with low-rise council housing, mostly constructed in new estates on the edge of the city. By the mid-1950s the establishment of a green belt had led to a shortage of available land on the edges of the city, whilst the government increased subsidies for the construction of high-rise apartment towers on former slum land, so the council began to construct high-rise inner city estates, adopting modernist designs and industrialised construction techniques, culminating in the construction of the award-winning Gleadless Valley and Park Hill estates.

Elmbank Gardens is a multi-use commercial complex in the Charing Cross area of Glasgow, Scotland. Best known for its signature 13-storey tower which overlooks the M8 motorway and stands directly opposite the Mitchell Library, it was designed by Richard Seifert and constructed between 1970 and 1972. It is one of the tallest and most prominent high rise buildings on the western side of Glasgow city centre, beyond Blythswood Hill. The surface buildings of the subterranean railway station which serves Charing Cross are also an integral part of the complex.

Q3A is an abbreviation for a type of three, four and five storey prefabricated buildings constructed in the GDR in the 1950s and 1960s. The letter "Q" in the word stands for "Querwandbau".
Robustness is the ability of a structure to withstand events like fire, explosions, impact or the consequences of human error, without being damaged to an extent disproportionate to the original cause – as defined in EN 1991-1-7 of the Accidental Actions Eurocode.

Kolbjørn Saether P.E., M.ASCE was an American structural engineer in the City of Chicago for 47 years. Saether dedicated his life to engineering and was known as a leader in his field. He was a past director of the Structural Engineers Association of Illinois and was the organization's president from 1980 to 1981. During his career he developed innovative engineering solutions for skyrise building construction that are now part of the Chicago skyline, published theoretical insights to enhance the state of the art in structural engineering, and patented novel techniques to advance the art of building construction.

Edgewater Towers is a high rise apartment block located in the suburb of St Kilda in Melbourne, Australia. The building, completed in 1961, was Melbourne's first, high rise residential apartment block and the tallest in Victoria until Domain Park Flats was completed in 1962. The building was designed by émigré architect Mordechai Benshemesh who designed many multi-storey buildings in St Kilda and Elwood. Edgewater Towers is considered to be Benshemesh's most iconic design. Edgewater Towers stands at 44 m tall (architectural), 39 m tall, and 13 storeys tall.

Kinkabool is a heritage-listed apartment block at 32–34 Hanlan Street, Surfers Paradise, Queensland, Australia. It was designed by John M. Morton of Lund Hutton Newell Black & Paulsen and built from 1959 to 1960 by J D Booker Constructions Pty Ltd. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 5 February 2009.

Torbreck, or the Torbreck Home Units, was the first high-rise and mix-use residential development in Queensland, Australia. These heritage-listed home units are located at 182 Dornoch Terrace, Highgate Hill, Brisbane. Designed by architects Aubrey Horswill Job and Robert Percival Froud, construction began in 1957 and was completed three years later in 1960 by Noel Austin Kratzmann. The project acquired the name 'Torbreck' to recognise a small, gabled timber cottage that previously occupied the site. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 17 December 1999.
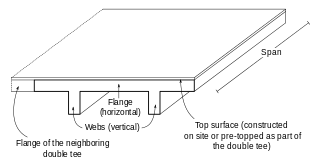
A double tee or double-T beam is a load-bearing structure that resembles two T-beams connected to each other side by side. The strong bond of the flange and the two webs creates a structure that is capable of withstanding high loads while having a long span. The typical sizes of double tees are up to 15 feet (4.6 m) for flange width, up to 5 feet (1.5 m) for web depth, and up to 80 feet (24 m) or more for span length. Double tees are pre-manufactured from prestressed concrete which allows construction time to be shortened.

The Ledbury Estate is a large estate of social housing, in Peckham in the London Borough of Southwark. The estate is just south of the Old Kent Road, part of the A2 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) from both Tower Bridge and the Elephant & Castle it is adjacent to land used by George Livesey for the South London Gasworks.
Torin Building is a heritage-listed former factory and now factory and office space located at 26 Coombes Drive in the western Sydney suburb of Penrith in the City of Penrith local government area of New South Wales, Australia. It was designed by Marcel Breuer and built from 1975 to 1976. It is also known as the Former Torin Corporation Building and Breuer Building. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 15 May 2009.

Post-tensioned stone is a high-performance composite construction material: stone held in compression with tension elements. The tension elements can be connected to the outside of the stone, but more typically uses tendons threaded internally through a duct formed from aligned drilled holes.
Contains text from an article on wikia cc-by-sa