Related Research Articles

The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocalisation including speech possible.

A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as fourth order, fifth order, and sixth order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi.
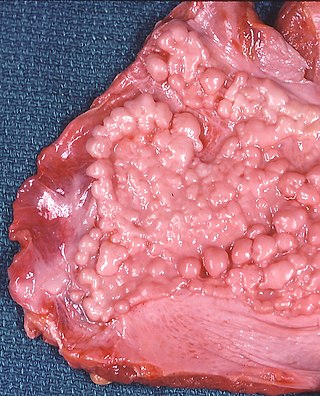
Asbestosis is long-term inflammation and scarring of the lungs due to asbestos fibers. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, and chest tightness. Complications may include lung cancer, mesothelioma, and pulmonary heart disease.
Radiology (X-rays) is used in the diagnosis of tuberculosis. Abnormalities on chest radiographs may be suggestive of, but are never diagnostic of TB, but can be used to rule out pulmonary TB.
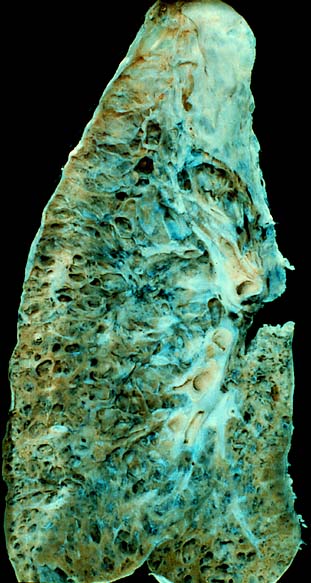
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium and space around the alveoli of the lungs. It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with this disease is between three and five years. The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.

A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine.

A pulmonary sequestration is a medical condition wherein a piece of tissue that ultimately develops into lung tissue is not attached to the pulmonary arterial blood supply, as is the case in normally developing lung. This sequestered tissue is therefore not connected to the normal bronchial airway architecture, and fails to function in, and contribute to, respiration of the organism.

A hemothorax is an accumulation of blood within the pleural cavity. The symptoms of a hemothorax may include chest pain and difficulty breathing, while the clinical signs may include reduced breath sounds on the affected side and a rapid heart rate. Hemothoraces are usually caused by an injury, but they may occur spontaneously due to cancer invading the pleural cavity, as a result of a blood clotting disorder, as an unusual manifestation of endometriosis, in response to pneumothorax, or rarely in association with other conditions.

A pulmonary consolidation is a region of normally compressible lung tissue that has filled with liquid instead of air. The condition is marked by induration of a normally aerated lung. It is considered a radiologic sign. Consolidation occurs through accumulation of inflammatory cellular exudate in the alveoli and adjoining ducts. The liquid can be pulmonary edema, inflammatory exudate, pus, inhaled water, or blood. Consolidation must be present to diagnose pneumonia: the signs of lobar pneumonia are characteristic and clinically referred to as consolidation.

High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) is a type of computed tomography (CT) with specific techniques to enhance image resolution. It is used in the diagnosis of various health problems, though most commonly for lung disease, by assessing the lung parenchyma. On the other hand, HRCT of the temporal bone is used to diagnose various middle ear diseases such as otitis media, cholesteatoma, and evaluations after ear operations.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.
A pulmonary laceration is a chest injury in which lung tissue is torn or cut. An injury that is potentially more serious than pulmonary contusion, pulmonary laceration involves disruption of the architecture of the lung, while pulmonary contusion does not. Pulmonary laceration is commonly caused by penetrating trauma but may also result from forces involved in blunt trauma such as shear stress. A cavity filled with blood, air, or both can form. The injury is diagnosed when collections of air or fluid are found on a CT scan of the chest. Surgery may be required to stitch the laceration, to drain blood, or even to remove injured parts of the lung. The injury commonly heals quickly with few problems if it is given proper treatment; however it may be associated with scarring of the lung or other complications.

A lung nodule or pulmonary nodule is a relatively small focal density in the lung. A solitary pulmonary nodule (SPN) or coin lesion, is a mass in the lung smaller than three centimeters in diameter. A pulmonary micronodule has a diameter of less than three millimetres. There may also be multiple nodules.
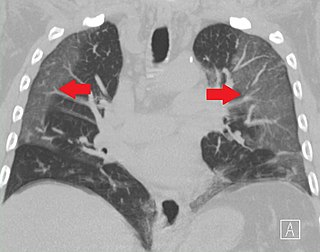
Ground-glass opacity (GGO) is a finding seen on chest x-ray (radiograph) or computed tomography (CT) imaging of the lungs. It is typically defined as an area of hazy opacification (x-ray) or increased attenuation (CT) due to air displacement by fluid, airway collapse, fibrosis, or a neoplastic process. When a substance other than air fills an area of the lung it increases that area's density. On both x-ray and CT, this appears more grey or hazy as opposed to the normally dark-appearing lungs. Although it can sometimes be seen in normal lungs, common pathologic causes include infections, interstitial lung disease, and pulmonary edema.

Asbestos-related diseases are disorders of the lung and pleura caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibres. Asbestos-related diseases include non-malignant disorders such as asbestosis, diffuse pleural thickening, pleural plaques, pleural effusion, rounded atelectasis and malignancies such as lung cancer and malignant mesothelioma.

The pleurae are the two flattened closed sacs filled with pleural fluid, each ensheathing each lung and lining their surrounding tissues, locally appearing as two opposing layers of serous membrane separating the lungs from the mediastinum, the inside surfaces of the surrounding chest walls and the diaphragm. Although wrapped onto itself resulting in an apparent double layer, each lung is surrounded by a single, continuous pleural membrane.

Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis (PAM) is a rare, inherited disorder of lung phosphate balance that is associated with small stone formation in the airspaces of the lung. Mutations in the gene SLC34A2 result in loss of a key sodium, phosphate co-transporter, known to be expressed in distal alveolar type II cells, as well as in the mammary gland, and to a lesser extent in intestine, kidney, skin, prostate and testes. As the disease progresses, the lung fields become progressively more dense (white) on the chest xray, and low oxygen level, lung inflammation and fibrosis, elevated pressures in the lung blood vessels, and respiratory failure ensue, usually in middle age. The clinical course of PAM can be highly variable, with some patients remaining asymptomatic for decades, and others progressing more rapidly. There is no effective treatment, and the mechanisms of stone formation, inflammation and scarring are not known.

Emphysema is any air-filled enlargement in the body's tissues. Most commonly emphysema refers to the permanent enlargement of air spaces (alveoli) in the lungs, and is also known as pulmonary emphysema.
Thoracic endometriosis is a rare form of endometriosis where endometrial-like tissue is found in the lung parenchyma and/or the pleura. It can be classified as either pulmonary, or pleural, respectively. Endometriosis is characterized by the presence of tissue similar to the lining of the uterus forming abnormal growths elsewhere in the body. Usually these growths are found in the pelvis, between the rectum and the uterus, the ligaments of the pelvis, the bladder, the ovaries, and the sigmoid colon. The cause is not known. The most common symptom of thoracic endometriosis is chest pain occurring right before or during menstruation. Diagnosis is based on clinical history and examination, augmented with X-ray, CT scan, and magnetic resonance imaging of the chest. Treatment options include surgery and hormones.

A focal lung pneumatosis is an enclosed pocket of air or gas in the lung and includes blebs, bullae, pulmonary cysts, and lung cavities. Blebs and bullae can be classified by their wall thickness.
References
- 1 2 3 Ufuk, Furkan (March 2021). "Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis". Radiology. 298 (3): 567. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021203272. ISSN 0033-8419. PMID 33434115 . Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ↑ Khaladkar, SM; Kondapavuluri, SK; Kamal, A; Kalra, R; Kuber, R (January 2016). "Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis - Clinico-Radiological dissociation - A case report with Radiological review". Journal of Radiology Case Reports. 10 (1): 14–21. doi:10.3941/jrcr.v10i1.2528. PMC 4861584 . PMID 27200151.
- ↑ Luong, Hoang Van; Anh, Lam Viet; Nguyen, Pham Thanh (3 October 2023). "Losing vigilance in diagnosing pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: A report on four cases". Journal of Clinical Imaging Science. 13: 32. doi:10.25259/JCIS_56_2023. ISSN 2156-7514. PMC 10629246 . PMID 37941922 . Retrieved 19 December 2024.
- ↑ Zhang, Xu-Dong; Gao, Jin-Ming; Luo, Jin-Mei; Zhao, Yu (1 January 2018). "Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: A case report and review of the literature". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine. 15 (1): 831–837. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.5457. ISSN 1792-0981. PMC 5772952 . PMID 29434686.