The United Daughters of the Confederacy (UDC) is an American neo-Confederate hereditary association for female descendants of Confederate Civil War soldiers engaging in the commemoration of these ancestors, the funding of monuments to them, and the promotion of the pseudohistorical Lost Cause ideology and corresponding white supremacy.

The Judah P. Benjamin Confederate Memorial at Gamble Plantation Historic State Park, also known as the Gamble Mansion or Gamble Plantation, is a Florida State Park, located in Ellenton, Florida, on 37th Avenue East and US 301. It is home to the Florida Division United Daughters of the Confederacy (UDC).

The Confederate Memorial State Historic Site is a state-owned property occupying approximately 135 acres (55 ha) near Higginsville, Missouri. From 1891 to 1950, the site was used as an old soldiers' home for veterans of the Confederate States Army after the American Civil War. The Missouri state government then took over operation of the site after the last veteran died in 1950, using it as a state park. In 1981, a cottage, a chapel, and the Confederate cemetery were listed on the National Register of Historic Places as the Confederate Chapel, Cemetery and Cottage. The chapel was moved from its original position in 1913, but was returned in 1978. It has a tower and a stained glass window. The cottage is a small wooden building, and the cemetery contains 723 graves. Within the cemetery is a monument erected by the United Daughters of the Confederacy which is modeled on the Lion of Lucerne. In addition to the cemetery and historic structures, the grounds also contain trails, picnic sites, and fishing ponds.
The Baker Peters House is an antebellum house located on the south side of Kingston Pike in Knoxville, Tennessee, near the intersection of Peters Road and Kingston Pike. The house is a two-story Greek Revival structure. It has a porte-cochere on the east side for carriages, and a rear wing that projects out on the southwest side of the house. It also has a columned, two-story front porch. The main body of the house is brick, but the rear wing was originally finished in wood siding.

Knollwood is an antebellum historic house at 6411 Kingston Pike in Knoxville, Tennessee, United States. It is also known as Knollwood Hall, Major Reynolds House, the Tucker Mansion and Bearden Hill. The home is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Ramsey House is a two-story stone house in Knox County, Tennessee, United States. Also known as Swan Pond, the house was constructed in 1797 by English architect Thomas Hope for Colonel Francis Alexander Ramsey (1764–1820), whose family operated a plantation at the site until the U.S. Civil War. In 1969, the house was added to the National Register of Historic Places for its architecture and its role in the region's early 19th-century history.

Westwood is a historic home located at 3425 Kingston Pike at the edge of the Sequoyah Hills area of Knoxville, Tennessee. Also known as the Adelia Armstrong Lutz House, the house was built in 1890 by John Lutz and his wife, artist Adelia Armstrong Lutz, on land given to them by Adelia's father, Robert H. Armstrong. In 1984, the house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places for its architecture.

Crescent Bend is a historic home at 2728 Kingston Pike in Knoxville, Tennessee. The building is known as Crescent Bend because of its location on a bend of the Tennessee River. It is also known as the Armstrong-Lockett House, Longview and Logueval.

The Knox County Courthouse is a historic building located at 300 Main Street in Knoxville, Tennessee, United States. Built in 1886, it served as Knox County's courthouse until the completion of the City-County Building in 1980, and continues to house offices for several county departments. John Sevier, Tennessee's first governor, is buried on the courthouse lawn. The courthouse is listed on the National Register of Historic Places for its architecture and its role in the county's political history.

Old City Hall is a complex of historic buildings located at 601 West Summit Hill Drive in Knoxville, Tennessee, United States. Originally constructed in 1848 as the Tennessee School for the Deaf and Dumb, the complex served as Knoxville's city hall from 1925 until 1980. The complex has been listed on the National Register of Historic Places and has been documented by the Historic American Buildings Survey. It currently houses Lincoln Memorial University's Duncan School of Law.

Kingston Pike is a highway in Knox County, Tennessee, United States, that connects Downtown Knoxville with West Knoxville, Farragut, and other communities in the western part of the county. The road follows a merged stretch of U.S. Route 11 (US 11) and US 70. From its initial construction in the 1790s until the development of the Interstate Highway System in the 1960s, Kingston Pike was the main traffic artery in western Knox County, and an important section of several cross-country highways. The road is now a major commercial corridor, containing hundreds of stores, restaurants, and other retail establishments.

Market Square is a historic district and pedestrian mall located in downtown Knoxville, Tennessee, United States. Established in 1854 as a market place for regional farmers, the square has developed over the decades into a multipurpose venue that accommodates events ranging from concerts to political rallies, and has long provided a popular gathering place for artists, street musicians, war veterans, and activists. Along with the Market House, Market Square was home to Knoxville's City Hall from 1868 to 1924. Market Square was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

The Rutherford County Courthouse in Murfreesboro, Tennessee, is a Classical Revival building from 1859. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. It is one of six remaining antebellum county courthouses in Tennessee
Confederate monuments and memorials in the United States include public displays and symbols of the Confederate States of America (CSA), Confederate leaders, or Confederate soldiers of the American Civil War. Many monuments and memorials have been or will be removed under great controversy. Part of the commemoration of the American Civil War, these symbols include monuments and statues, flags, holidays and other observances, and the names of schools, roads, parks, bridges, buildings, counties, cities, lakes, dams, military bases, and other public structures. In a December 2018 special report, Smithsonian Magazine stated, "over the past ten years, taxpayers have directed at least $40 million to Confederate monuments—statues, homes, parks, museums, libraries, and cemeteries—and to Confederate heritage organizations."
James Churchwell Luttrell II was an American attorney and politician who served as Mayor of Knoxville, Tennessee, during the Civil War. His eight-year term (1859–1867) was the longest for any Knoxville mayor until the late 20th century, when it was surpassed by Victor Ashe's 16-year term. Luttrell also served as state comptroller in the late 1850s, and was elected to the state senate following his term as mayor.

The John Pope House, also known as Eastview, is a historic house in Burwood, Williamson County, Tennessee. It incorporates hall-parlor plan architecture and single pen architecture.
Charles Ives Barber was an American architect, active primarily in Knoxville, Tennessee, and vicinity, during the first half of the 20th century. He was cofounder of the firm, Barber & McMurry, through which he designed or codesigned buildings such as the Church Street Methodist Episcopal Church, South, the General Building, and the Knoxville YMCA, as well as several campus buildings for the University of Tennessee and numerous elaborate houses in West Knoxville. Several buildings designed by Barber have been listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
The Civil War Trust's Civil War Discovery Trail is a heritage tourism program that links more than 600 U.S. Civil War sites in more than 30 states. The program is one of the White House Millennium Council's sixteen flagship National Millennium Trails. Sites on the trail include battlefields, museums, historic sites, forts and cemeteries.
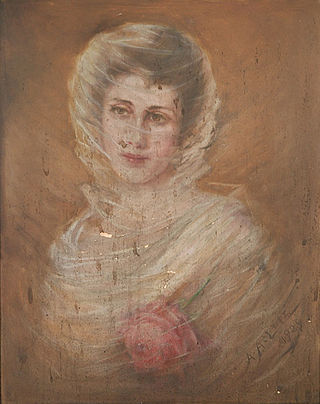
Adelia Armstrong Lutz was an American artist active in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. She organized art circles in Knoxville, Tennessee, as director of the Knoxville Art Club and as a co-organizer of the Nicholson Art League. Her still lifes and portraits were exhibited throughout the American South, and they are to be the subject of a permanent exhibit at her former home, Historic Westwood.
Edith D. Pope was an American editor. She was the second editor of the Confederate Veteran from 1914 to 1932, and the president of the Nashville No. 1 chapter of the United Daughters of the Confederacy from 1927 to 1930. She played a critical role in the promotion of the Lost Cause of the Confederacy.