Related Research Articles
Hamburger Flugzeugbau (HFB) was an aircraft manufacturer, located primarily in the Finkenwerder quarter of Hamburg, Germany. Established in 1933 as an offshoot of Blohm & Voss shipbuilders, it later became an operating division within its parent company and was known as Abteilung Flugzeugbau der Schiffswerft Blohm & Voss from 1937 until it ceased operation at the end of World War II. In the postwar period it was revived as an independent company under its original name and subsequently joined several consortia before being merged to form Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB). It participates in the present day Airbus and European aerospace programs.

The Hamburger Flugzeugbau Ha 137 was a German ground-attack aircraft of the 1930s. It was Blohm & Voss' entry into the contest to equip the re-forming Luftwaffe with its first purpose-built dive bomber. Although the contest would eventually be won by the Junkers Ju 87, the Ha 137 demonstrated that B&V's Hamburger Flugzeugbau, not even two years old at this point, had a truly capable design team of its own. One Ha 137 single-seat prototype competed against the Henschel Hs 123 at Rechlin.

A variable-incidence wing has an adjustable angle of incidence relative to its fuselage. This allows the wing to operate at a high angle of attack for take-off and landing while allowing the fuselage to remain close to horizontal.

The Blohm & Voss P 194 was a German design for a mixed-power Stuka or ground-attack aircraft and tactical bomber, during World War II.
The Arado Ar 81 was a German prototype dive bomber. Because the Reich Air Ministry decided to purchase the competing Junkers Ju 87, only three prototypes of the Ar 81 were completed.

The Blohm & Voss P 212 was a proposed jet fighter designed by Blohm & Voss for the Emergency Fighter Program Luftwaffe design competition during the Second World War.
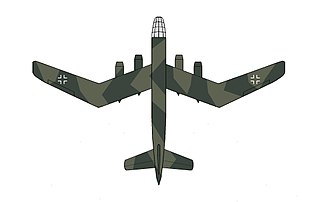
The Blohm & Voss Bv P 188 was a long-range, heavy jet bomber design project by the Blohm & Voss aircraft manufacturing division during the last years of the Third Reich. It featured a novel W-wing planform with variable incidence.
The Blohm & Voss BV 237 was a German proposed dive bomber with an unusual asymmetric design based on the Blohm & Voss BV 141.
The Blohm & Voss P215 was an advanced jet night fighter project by Blohm & Voss during the Second World War. With a crew of three and twin jet engines, it featured a tailless swept-wing layout and heavy armament. An order for three prototypes was received just weeks before the war ended.
The Blohm & Voss P 163 was a design project for an unconventional bomber during World War II. Constructed mainly from steel, its crew were accommodated in large wingtip nacelles, giving it a triple-fuselage appearance. Its propeller drive system was also unusual, with the central fuselage containing twin engines coupled to a front-mounted contra-prop.
The Blohm & Voss P 203 was a design project for a heavy fighter during World War II. Capable of filling the roles of night fighter, light bomber and ground-attack, it had mixed propulsion, having both piston engine driven propellers and jet engines.
The Blohm & Voss P 196 was the last of Blohm & Voss's World War II design projects for a "stuka" dive bomber and close support aircraft to replace the aging Junkers Ju 87.
The Blohm & Voss P 204 was one of several design studies by Blohm & Voss for asymmetric dive bombers during World War II. It was also unusual in having hybrid propulsion comprising both piston and jet engines.
The Blohm & Voss P 192 was a design study for a dive bomber/ground attack aircraft intended to replace the Junkers Ju 87.
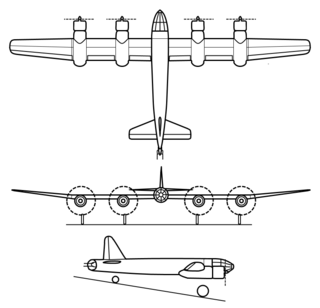
The Blohm & Voss P 184 was a German design for a long-range reconnaissance aircraft during World War II. Carrying a crew of five, it was of aerodynamically clean appearance and its wing had an unusually high aspect ratio.
References
Notes
Bibliography
- Hugh Cowin; "Blohm und Voss Projects of World War II: Part I", Air Pictorial, October 1963, pp. 312–316.