
Blood on the Tracks is the fifteenth studio album by American singer-songwriter Bob Dylan, released on January 20, 1975 by Columbia Records. The album marked Dylan's return to Columbia Records after a two-album stint with Asylum Records. Dylan commenced recording the album in New York City in September 1974. In December, shortly before Columbia was due to release the album, Dylan abruptly re-recorded much of the material in a studio in Minneapolis. The final album contains five tracks from New York and five from Minneapolis.
Blood is a body fluid in humans and other animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells.

Color, or colour, is the characteristic of visual perception described through color categories, with names such as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, or purple. This perception of color derives from the stimulation of photoreceptor cells by electromagnetic radiation. Color categories and physical specifications of color are associated with objects through the wavelength of the light that is reflected from them. This reflection is governed by the object's physical properties such as light absorption, emission spectra, etc.

The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.

A blood type is a classification of blood, based on the presence and absence of antibodies and inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. Some of these antigens are also present on the surface of other types of cells of various tissues. Several of these red blood cell surface antigens can stem from one allele and collectively form a blood group system. Blood types are inherited and represent contributions from both parents. A total of 36 human blood group systems and 346 antigens are now recognized by the International Society of Blood Transfusion (ISBT). The two most important blood group systems are ABO and Rh; they determine someone's blood type for suitability in blood transfusion.

The urinary system, also known as the renal system or urinary tract, consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulate blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, wastes exit the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled from the body by urination (voiding). The female and male urinary system are very similar, differing only in the length of the urethra.

Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles, haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek erythros for "red" and kytos for "hollow vessel", with -cyte translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or gills of fish, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries.

In humans and most mammals and birds, the iris is a thin, circular structure in the eye, responsible for controlling the diameter and size of the pupil and thus the amount of light reaching the retina. Eye color is defined by that of the iris. In optical terms, the pupil is the eye's aperture, while the iris is the diaphragm.

Fibrin is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with platelets, forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site.

Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology and in the medical fields of histopathology, hematology, and cytopathology that focus on the study and diagnoses disease at a microscopic level. Stains may be used to define biological tissues, cell populations, or organelles within individual cells.

Venous blood is deoxygenated blood which travels from the peripheral vessels, through the venous system into the right atrium of the heart. Deoxygenated blood is then pumped by the right ventricle to the lungs via the pulmonary artery which is divided in two branches, left and right to the left and right lungs respectively. Blood is oxygenated in the lungs and returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins.

"Tangled Up in Blue" is a song by Bob Dylan. It appeared on his album Blood on the Tracks in 1975. Released as a single, it reached #31 on the Billboard Hot 100. Rolling Stone ranked it #68 on their list of the 500 Greatest Songs of All Time.

The ABO blood group system is used to denote the presence of one, both, or neither of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes. In human blood transfusions it is the most important of the 36 different blood type classification systems currently recognized. A very rare mismatch in this, or any other serotype, can cause a serious, potentially fatal, adverse reaction after a transfusion, or a contra-indicated immune response to an organ transplant. The associated anti-A and anti-B antibodies are usually IgM antibodies, which are produced in the first years of life by sensitization to environmental substances, such as food, bacteria, and viruses.
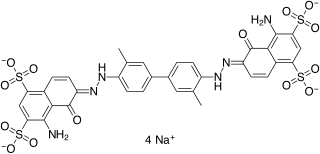
T-1824 or Evans blue, often incorrectly rendered as Evan's blue, is an azo dye that has a very high affinity for serum albumin. Because of this, it can be useful in physiology in estimating the proportion of body water contained in blood plasma. It fluoresces with excitation peaks at 470 and 540 nm and an emission peak at 680 nm.
The term human blood group systems is defined by International Society of Blood Transfusion as systems in the human species where cell-surface antigens—in particular, those on blood cells—are "controlled at a single gene locus or by two or more very closely linked homologous genes with little or no observable recombination between them", and include the common ABO and Rh (Rhesus) antigen systems, as well as many others; thirty-nine major human systems are identified as of July 2019.
A is the first letter of the Latin and English alphabet.

Idiot Pilot is an alternative rock duo from Bellingham, Washington, United States consisting of Michael Harris and Daniel Anderson.

Human feces are the solid or semisolid remains of food that could not be digested or absorbed in the small intestine of humans, but has been rotted down by bacteria in the large intestine. It also contains bacteria and a relatively small amount of metabolic waste products such as bacterially altered bilirubin, and the dead epithelial cells from the lining of the gut. It is discharged through the anus during a process called defecation.

White blood cells (WBCs), also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system.
Blue Blood or blue blood may refer to:















