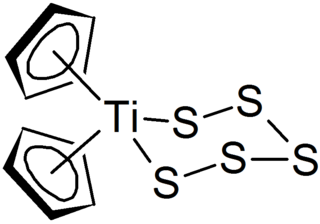A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by undesirable chemical changes. In general, preservation is implemented in two modes, chemical and physical. Chemical preservation entails adding chemical compounds to the product. Physical preservation entails processes such as refrigeration or drying. Preservative food additives reduce the risk of foodborne infections, decrease microbial spoilage, and preserve fresh attributes and nutritional quality. Some physical techniques for food preservation include dehydration, UV-C radiation, freeze-drying, and refrigeration. Chemical preservation and physical preservation techniques are sometimes combined.

Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, caucho, or caoutchouc, as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Cambodia are four of the leading rubber producers.

Vulcanization is a range of processes for hardening rubbers. The term originally referred exclusively to the treatment of natural rubber with sulfur, which remains the most common practice. It has also grown to include the hardening of other (synthetic) rubbers via various means. Examples include silicone rubber via room temperature vulcanizing and chloroprene rubber (neoprene) using metal oxides.
Bloom or blooming may refer to:
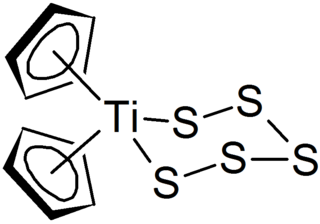
Polysulfides are a class of chemical compounds derived from anionic chains of sulfur atoms. There are two main classes of polysulfides: inorganic and organic. The inorganic polysulfides have the general formula S2−
n. These anions are the conjugate bases of polysulfanes H2Sn. Organic polysulfides generally have the formulae R1SnR2, where R is an alkyl or aryl group.

A thickening agent or thickener is a substance which can increase the viscosity of a liquid without substantially changing its other properties. Edible thickeners are commonly used to thicken sauces, soups, and puddings without altering their taste; thickeners are also used in paints, inks, explosives, and cosmetics.
Nitrile rubber, also known as nitrile butadiene rubber, NBR, Buna-N, and acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, is a synthetic rubber derived from acrylonitrile (ACN) and butadiene. Trade names include Perbunan, Nipol, Krynac and Europrene. This rubber is unusual in being resistant to oil, fuel, and other chemicals.
Autoxidation refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation.

Photodegradation is the alteration of materials by light. Commonly, the term is used loosely to refer to the combined action of sunlight and air, which cause oxidation and hydrolysis. Often photodegradation is intentionally avoided, since it destroys paintings and other artifacts. It is, however, partly responsible for remineralization of biomass and is used intentionally in some disinfection technologies. Photodegradation does not apply to how materials may be aged or degraded via infrared light or heat, but does include degradation in all of the ultraviolet light wavebands.

Pneumatic tires are manufactured according to relatively standardized processes and machinery, in around 455 tire factories in the world. With over 1 billion tires manufactured worldwide annually, the tire industry is a major consumer of natural rubber. Tire factories start with bulk raw materials such as synthetic rubber, carbon black, and chemicals and produce numerous specialized components that are assembled and cured.
Curing is a chemical process employed in polymer chemistry and process engineering that produces the toughening or hardening of a polymer material by cross-linking of polymer chains. Even if it is strongly associated with the production of thermosetting polymers, the term "curing" can be used for all the processes where a solid product is obtained from a liquid solution, such as with PVC plastisols.

Chocolate is a food product made from roasted and ground cocoa pods mixed with fat and powdered sugar to produce a solid confectionery. There are several types of chocolate, classified primarily according to the proportion of cocoa and fat content used in a particular formulation.
Gum base is the non-nutritive, non-digestible, water-insoluble masticatory delivery system used to carry sweeteners, flavors, and any other substances in chewing gum and bubble gum. It provides all the basic textural and masticatory properties of gum.
Rubber Technology is the subject dealing with the transformation of rubbers or elastomers into useful products, such as automobile tires, rubber mats and, exercise rubber stretching bands. The materials includes latex, natural rubber, synthetic rubber and other polymeric materials, such as thermoplastic elastomers. Rubber processed through such methods are components of a wide range of items.

Food contact materials or food contacting substances (FCS) are materials that are intended to be in contact with food. These can be things that are quite obvious like a glass or a can for soft drinks as well as machinery in a food factory or a coffee machine.
Polymer stabilizers are chemical additives which may be added to polymeric materials, such as plastics and rubbers, to inhibit or retard their degradation. Common polymer degradation processes include oxidation, UV-damage, thermal degradation, ozonolysis, combinations thereof such as photo-oxidation, as well as reactions with catalyst residues, dyes, or impurities. All of these degrade the polymer at a chemical level, via chain scission, uncontrolled recombination and cross-linking, which adversely affects many key properties such as strength, malleability, appearance and colour.

Chocolate bloom is either of two types of whitish coating that can appear on the surface of chocolate: fat bloom, caused by changes in the fat crystals in the chocolate; and sugar bloom, due to crystals formed by the action of moisture on the sugar. Fat and sugar bloom damage the appearance of chocolate but do not limit its shelf life. Chocolate that has "bloomed" is still safe to eat, but may have an unappetizing appearance and surface texture. Chocolate bloom can be repaired by melting the chocolate down, stirring it, then pouring it into a mould and allowing it to cool, bringing the sugar or fat back into the solution.

2-Mercaptobenzothiazole is an organosulfur compound with the formula C6H4(NH)SC=S. A white solid, it is used in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber.
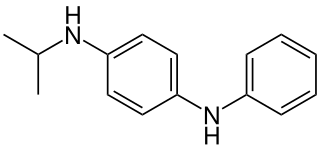
N-Isopropyl-N′-phenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (often abbreviated IPPD) is an organic compound commonly used as an antiozonant in rubbers. Like other p-phenylenediamine-based antiozonants it works by virtue of its low ionization energy, which allows it to react with ozone faster than ozone will react with rubber. This reaction converts it to the corresponding aminoxyl radical (R2N–O•), with the ozone being converted to a hydroperoxyl radical (HOO•), these species can then be scavenged by other antioxidant polymer stabilizers.

Sulfur vulcanization is a chemical process for converting natural rubber or related polymers into materials of varying hardness, elasticity, and mechanical durability by heating them with sulfur or sulfur-containing compounds. Sulfur forms cross-linking bridges between sections of polymer chains which affects the mechanical and electronic properties. Many products are made with vulcanized rubber, including tires, shoe soles, hoses, and conveyor belts. The term vulcanization is derived from Vulcan, the Roman god of fire.