
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.
The services of communication in Jersey comprise Internet, telephone, broadcasting and postal services, which allow islanders to contact people and receive information.

Bermuda was first documented by a European in 1503 by Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez. In 1609, the English Virginia Company, which had established Jamestown in Virginia two years earlier, permanently settled Bermuda in the aftermath of a hurricane, when the crew and passengers of Sea Venture steered the ship onto the surrounding reef to prevent it from sinking, then landed ashore. Bermuda's first capital, St. George's, was established in 1612.

A privateer is a private person or vessel which engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or delegated authority issued commissions, also referred to as letters of marque, during wartime. The commission empowered the holder to carry on all forms of hostility permissible at sea by the usages of war. This included attacking foreign vessels and taking them as prizes and taking crews prisoner for exchange. Captured ships were subject to condemnation and sale under prize law, with the proceeds divided by percentage between the privateer's sponsors, shipowners, captains and crew. A percentage share usually went to the issuer of the commission.

The British Overseas Territories (BOTs) are the fourteen territories with a constitutional and historical link with the United Kingdom that, while not forming part of the United Kingdom itself, are part of its sovereign territory. The permanently inhabited territories are delegated varying degrees of internal self-governance, with the United Kingdom retaining responsibility for defence, foreign relations, and internal security, and ultimate responsibility for "good" governance. Three of the territories are chiefly or only inhabited by military or scientific personnel, the rest hosting significant civilian populations. All fourteen have the British monarch as head of state. These UK government responsibilities are assigned to various departments of the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office and are subject to change.
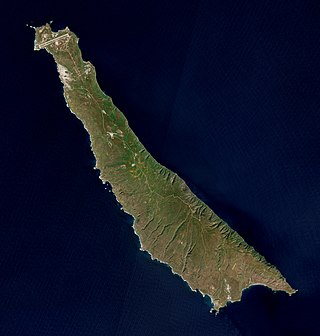
San Clemente Island is the southernmost of the Channel Islands of California. It is owned and operated by the United States Navy, and is a part of Los Angeles County. It is administered by Naval Base Coronado. It is 21 miles (34 km) long and has 147.13 km2 (56.81 sq mi) of land. The 2018 census estimates 148 military and civilian personnel reside on the island. The city of San Clemente in Orange County, California is named after the island.

William Wallace Denslow was an American illustrator and caricaturist remembered for his work in collaboration with author L. Frank Baum, especially his illustrations of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz. Denslow was an editorial cartoonist with a strong interest in politics, which has fueled political interpretations of The Wonderful Wizard of Oz.

The North America and West Indies Station was a formation or command of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy stationed in North American waters from 1745 to 1956, with main bases at the Imperial fortresses of Bermuda and Halifax, Nova Scotia. The North American Station absorbed the separate Newfoundland Station in 1825, and the Jamaica Station in 1830, to form the North America and West Indies Station. It was briefly abolished in 1907 before being restored in 1915. It was renamed the America and West Indies Station in 1926, absorbing what had been the South East Coast of America Station and the Pacific Station. It was commanded by Commanders-in-Chief whose titles changed with the changing of the formation's name, eventually by the Commander-in-Chief, America and West Indies Station.
Ruakura is a semi-rural suburb of Hamilton City, in the Waikato region of New Zealand. The University of Waikato is nearby.
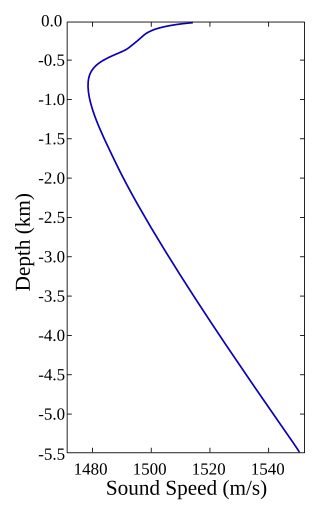
The SOFAR channel, or deep sound channel (DSC), is a horizontal layer of water in the ocean at which depth the speed of sound is at its minimum. The SOFAR channel acts as a waveguide for sound, and low frequency sound waves within the channel may travel thousands of miles before dissipating. An example was reception of coded signals generated by the US Navy-chartered ocean surveillance vessel Cory Chouest off Heard Island, located in the southern Indian Ocean, by hydrophones in portions of all five major ocean basins and as distant as the North Atlantic and North Pacific.

Royal Navy Dockyards were state-owned harbour facilities where ships of the Royal Navy were built, based, repaired and refitted. Until the mid-19th century the Royal Dockyards were the largest industrial complexes in Britain.

United States border preclearance is the United States Department of Homeland Security's (DHS) practice of operating prescreening border control facilities at airports and other ports of departure located outside of the United States pursuant to agreements between the United States and host countries. Travelers are subject to immigration and customs inspections by Customs and Border Protection (CBP) officers before boarding their transportation onward to the United States. Preclearance applies to all passengers regardless of their nationality or purpose of travel. Upon arrival, precleared passengers arrive in the United States as domestic travelers, but may still be subject to re-inspection at the discretion of CBP. This process is intended to streamline border procedures, reduce congestion at American ports of entry, and facilitate travel into airports that otherwise lack immigration and customs processing facilities for commercial flights.
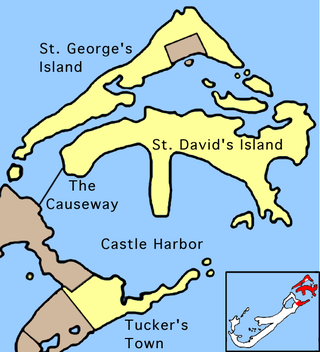
St. George's Parish is one of the nine parishes of Bermuda. It is named after the founder of the Bermuda colony, Admiral Sir George Somers.

Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the current research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rocks or on ice that are fixed in place.

Bermuda land snails, scientific name Poecilozonites, are an endemic genus of pulmonate land snail in the family Gastrodontidae. 12 species are known from the fossil record, and 4 of these species survived into modern times, but due to the highly negative effects of human development, the extant species has been reduced down to only bermudensis and circumfirmatus.

HMD Bermuda was the principal base of the Royal Navy in the Western Atlantic between American independence and the Cold War. The Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda had occupied a useful position astride the homeward leg taken by many European vessels from the New World since before its settlement by England in 1609. French privateers may have used the islands as a staging place for operations against Spanish galleons in the 16th century. Bermudian privateers certainly played a role in many English and British wars following settlement, with its utility as a base for his privateers leading to the Earl of Warwick, the namesake of Warwick Parish, becoming the most important investor of the Somers Isles Company. Despite this, it was not until the loss of bases on most of the North American Atlantic seaboard threatened Britain's supremacy in the Western Atlantic that the island assumed great importance as a naval base. In 1818 the Royal Naval Dockyard, Bermuda officially replaced the Royal Naval Dockyard, Halifax, as the British headquarters for the North America Station (which would become the North America and West Indies Station after absorbing the Jamaica Station in 1830.

The ASU Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences is a non-profit marine science and education institute located in Ferry Reach, St. George's, Bermuda and affiliated with the Julie Ann Wrigley Global Futures Laboratory at Arizona State University. The institute, founded in 1903 as the Bermuda Biological Station, hosts a full-time faculty of oceanographers, biologists, and environmental scientists, graduate and undergraduate students, K-12 groups, and Road Scholar groups. ASU BIOS's strategic mid-Atlantic Ocean location has at its doorstep a diverse marine environment, with close proximity to deep ocean as well as coral reef and near shore habitats.

The Bali Aga, Baliaga, or Bali Mula are the indigenous people of Bali. Linguistically they are an Austronesian people. Bali Aga people are predominantly located in the eastern part of the island, in Bangli especially the mountains Kintamani, East Buleleng, West Buleleng and East Karangasem, but they can also be found in north-western and central regions. The term Bali Aga or Bali Pégunungan is regarded as an insult with an additional meaning of "the mountain people that are fools"; therefore, they prefer the term Bali Mula instead.
The British Overseas Territories (BOT) or alternatively, United Kingdom Overseas Territories (UKOTs), are 14 territories under the jurisdiction and sovereignty of the United Kingdom. They are the parts of the British Empire that have not been granted independence or have voted to remain British territories. These territories do not form part of the United Kingdom. Most of the inhabited territories are internally self-governing, with the UK retaining responsibility for defence and foreign relations. The rest are either uninhabited or have a transitory population of military or scientific personnel.
















