
The Adirondack Mountains are a massif of mountains in Northeastern New York which form a circular dome approximately 160 miles (260 km) wide and covering about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The region contains more than 100 peaks, including Mount Marcy, which is the highest point in New York at 5,344 feet (1,629 m). The Adirondack High Peaks, a traditional list of 46 peaks over 4,000 feet (1,200 m), are popular hiking destinations. There are over 200 named lakes with the number of smaller lakes, ponds, and other bodies of water reaching over 3,000. Among the named lakes around the mountains are Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds. The region has over 1,200 miles (1,900 km) of river.

Indian Lake is a town in Hamilton County, New York, United States. The population was 1,352 at the 2010 census. The name is from a lake of the same name that is largely inside the town. There are no permanent stop lights in the town. Law enforcement is provided by New York State Troopers and Hamilton County Sheriff's Office.

The Adirondack Park is a park in northeastern New York protecting the Adirondack Mountains. The park was established in 1892 for "the free use of all the people for their health and pleasure", and for watershed protection. At 6.1 million acres, it is the largest park in the contiguous United States.

The Catskill Park is in the Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. It consists of 700,000 acres of land inside a Blue Line in four counties: Delaware, Greene, Sullivan, and Ulster. As of 2005, 287,500 acres (116,300 ha) or 41 percent of the land within, is owned by the state as part of the Forest Preserve; it is managed by the Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC). Another 5% is owned by New York City to protect four of the city's reservoirs in the region that lie partially within the park and their respective watersheds.

The Adirondack Mountain Club (ADK) is a nonprofit organization founded in 1922. It has approximately 30,000 members. The ADK is dedicated to the protection and responsible recreational use of the New York State Forest Preserve, parks, wild lands, and waters; it conducts conservation, and natural history programs. There are 27 local chapters in New York and New Jersey. The club has worked to increase state holdings in the Adirondack Park and to protect the area from commercial development.

Whiteface Mountain is the fifth-highest mountain in the U.S. state of New York, and one of the High Peaks of the Adirondack Mountains, located in the town of Wilmington in Essex County. Set apart from most of the other High Peaks, the summit offers a 360-degree view of the Adirondacks and clear-day glimpses of Vermont and Canada, where Montreal can be seen on a very clear day. Because of its relative isolation, the mountain is exposed to prevailing winds from the west and frequently capped with snow and ice, making it an area of interest to meteorologists. Weather data has been collected on the summit since 1937. The mountain's east slope is home to a major ski area which boasts the greatest vertical drop east of the Rockies, and which hosted the alpine skiing competitions of the 1980 Winter Olympics. Unique among the High Peaks, Whiteface features a developed summit and seasonal accessibility by motor vehicle. The Whiteface Veterans Memorial Highway reaches a parking area at an elevation shortly below the summit, with the remaining distance covered by tunnel and elevator. The peak can also be reached on two hiking trails.

The Long Path is a 357-mile (575 km) long-distance hiking trail beginning in New York City, at the West 175th Street subway station near the George Washington Bridge and ending at Altamont, New York, in the Albany area. While not yet a continuous trail, relying on road walks in some areas, it nevertheless takes in many of the popular hiking attractions west of the Hudson River, such as the New Jersey Palisades, Harriman State Park, the Shawangunk Ridge and the Catskill Mountains. It offers hikers a diversity of environments to pass through, from suburbia and sea-level salt marshes along the Hudson to wilderness and boreal forest on Catskill summits 4,000 feet (1,220 m) in elevation.

New York's Forest Preserve comprises almost all the lands owned by the state of New York within the Adirondack and Catskill parks. It is managed by the state Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC).
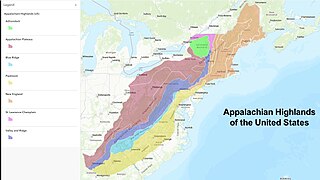
The Appalachian Highlands is one of eight government-defined physiographic divisions of the contiguous United States. It links with the Appalachian Uplands in Canada to make up the Appalachian Mountains. The Highlands includes seven physiographic provinces, which is the second level in the physiographic classification system in the United States. At the next level of physiographic classification, called section/subsection, there are 20 unique land areas with one of the provinces having no sections.

New York State Route 28N (NY 28N) is an east–west state highway in the North Country of New York in the United States. It extends for 50.95 miles (82.00 km) through the Adirondack Mountains from Blue Mountain Lake to North Creek. The route is a northerly alternate route to NY 28 between both locations; as such, it passes through several communities that NY 28 bypasses to the south. The westernmost 10 miles (16 km) of NY 28N overlap with NY 30 through the town of Long Lake. NY 28N and NY 30 split in the hamlet of Long Lake, from where NY 30 heads to the north and NY 28N proceeds eastward through mountainous regions of Adirondack Park.
The Northville–Lake Placid Trail, also known as the NPT, is a lightly traveled foot trail that runs 138 miles (214 km) through Adirondack Park in northern New York State. It was laid out by the Adirondack Mountain Club in 1922 and 1923 and is maintained by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation. From 2014-2016 the southern section of the trail was re-routed to remove most of the road leading into the village of Northville. The southern terminus is Waterfront Park in Northville, NY and the northern terminus is Averyville Rd in Lake Placid.

Black Mountain is a mountain located in Washington County, New York, of which its peak is the highest point. Isolated from the rest of the Adirondack Mountains by Lake George, Black Mtn. has the seventh highest topographic prominence of all the mountains in New York. Black Mountain also has the highest elevation of any of the peaks which surround Lake George and offers unobstructed views of the lake from its summit.

Adirondack Experience, located on NY-30 in the hamlet of Blue Mountain Lake in Hamilton County, New York, is a museum dedicated to preserving the history of the Adirondacks. The museum is located on the site of an historic summer resort hotel, the Blue Mountain House, built high above Blue Mountain Lake in 1876 by Miles Tyler Merwin, that operated until the late 1940s. The museum consists of 23 buildings, 121 acres, and 60,000 square feet of exhibition space. The opening of a brand new 19,000 square foot exhibition, Life in the Adirondacks, took place July 2017.

Balsam Lake Mountain is one of the Catskill Mountains, located in the Town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States. It is the westernmost of the range's 35 High Peaks. Its exact height has not been determined, but the highest contour line on topographic maps, 3,720 feet (1,130 m), is usually given as its elevation.

The Moose River Plains Wild Forest is a 64,322-acre tract in the Adirondack Park in Hamilton and Herkimer counties in the state of New York in the United States of America; it is designated as Wild Forest by the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation.

The Mokelumne Wilderness is a 105,165-acre federally designated wilderness area located 70 miles (110 km) east of Sacramento, California. It is within the boundaries of three national forests: Stanislaus, Eldorado and Toiyabe. First protected under the Wilderness Act of 1964, the Mokelumne's borders were expanded under the California Wilderness Act of 1984 with the addition of 55,000 acres. The wilderness takes its name from the Mokelumne River, which was named after a Mi-wok Indian village located on the riverbank in California's Central Valley.

The Balsam Lake Mountain Fire Observation Station is located at the summit of the mountain of that name in the Town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States. It comprises a steel frame fire lookout tower, the observer's cabin and privy and the jeep road to the complex.
Poke-O-Moonshine Mountain, spelled Pokamoonshine on U.S. Geological Survey maps, and sometimes known as just Poke-O, is a minor peak of the Adirondack Mountains. The name is believed to be a corruption of the Algonquin words pohqui, meaning 'broken', and moosie, meaning 'smooth'. It is located in the town of Chesterfield, New York, United States, on New York state Forest Preserve land, part of the Taylor Pond Wild Forest complex within the Adirondack Park. Due to its location next to the pass through which most travelers from the north enter the range, it has been called the "gateway to the Adirondacks".

The Northeastern Highlands Ecoregion is a Level III ecoregion designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the U.S. states of Vermont, New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Maine, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. The ecoregion extends from the northern tip of Maine and runs south along the Appalachian Mountain Range into eastern Pennsylvania. Discontiguous sections are located among New York's Adirondack Mountains, Catskill Range, and Tug Hill. The largest portion of the Northeastern Highlands ecoregion includes several sub mountain ranges, including the Berkshires, Green Mountains, Taconic, and White Mountains.



















