Riverton, officially Riverton / Aparima, is a small New Zealand town 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Invercargill, on the south-eastern shorelines of the Jacobs River Estuary. The estuary is formed by the Aparima and Pourakino rivers, leading through a narrow outflow channel into Foveaux Strait. Accessible via State Highway 99 on the Southern Scenic Route, the main part of the town is on flat land and the northern end of Oreti Beach. South Riverton is built on the hills between the eastern shore of the estuary and Taramea Bay.

Bluff, previously known as Campbelltown and often referred to as "The Bluff", is a town and seaport in the Southland region, on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It is the southernmost town in mainland New Zealand and, despite Slope Point and Stewart Island being further south, Bluff is colloquially used to refer to the southern extremity of the country. According to the 2018 census, the resident population was 1,797, a decrease of 6 since 2013.

Tiwai Point lies at the entrance to Bluff Harbour on the southern coast of the South Island of New Zealand. A spit which extends from the western end of the Awarua Plain, it lies between Awarua Bay to the north and Foveaux Strait to the south. It is known for the Tiwai Point Aluminium Smelter, one of the largest industrial facilities in New Zealand.
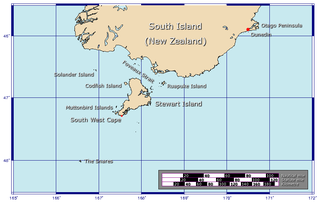
Foveaux Strait is a strait that separates Stewart Island from the South Island of New Zealand. The width of the strait ranges from about 23 to 53 km and the depth varies between 18 and 46 m. Captain James Cook passed around the southern tip of Stewart Island during his circumnavigation of the South Island in 1770 but did not record the presence of a seaway between Stewart Island and the mainland. The strait was not charted until 1804 when an American sealer, Owen Folger Smith, mapped it.

Port Chalmers is a town serving as the main port of the city of Dunedin, New Zealand. Port Chalmers lies ten kilometres inside Otago Harbour, some 15 kilometres northeast of Dunedin's city centre.
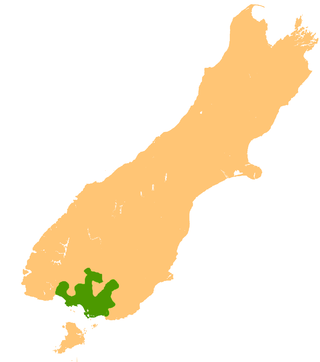
The Southland Plains is a general name given to several areas of low-lying land in the South Island of New Zealand, separated by the rise of the Hokonui Hills in the north. It forms a sizeable area of Southland region and encompasses its two principal settlements the city of Invercargill and the town of Gore. The Southland Plains include some of New Zealand's most fertile farmland.

Toetoes Bay is the easternmost of three large bays lying on the Foveaux Strait coast of Southland, New Zealand, the others being Te Waewae Bay and Oreti Beach. The 240 km Mataura River drains to sea at Toetoes Bay, first passing through the Toetoes Harbour estuary. Thirty kilometres in length, the bay is the southern end of the Awarua Plain, an area of swampy land stretching inland for about fifteen kilometres. The eastern end of the bay is close to Slope Point, the South Island's southernmost point, and the western end of the Catlins.

Moturoa / Rabbit Island is a small island that lies across the southernmost part of Tasman Bay / Te Tai-o-Aorere, on the northern coast of New Zealand's South Island. The long narrow island runs east–west for 8 kilometres (5 mi), and covers 15 km2 (5.8 sq mi).

The Southland Province was a province of New Zealand from March 1861, when it split from Otago Province, until 1870, when it rejoined Otago.

Dacre is a small town in the South Island of New Zealand. It is situated on the Southland Plains between Invercargill and Edendale on State Highway 1. In Dacre, SH 1 is met by State Highway 98, which runs west to Makarewa via Rakahouka. Nearby villages include Mabel Bush to the northwest and Woodlands to the southeast. Dacre is 25 km north east of Invercargill, the closest city. The Main South Line railway passes just to the south of Dacre. It is a dairy farming community, that currently has a community hall and a small engine garage.

The New Zealand Maritime Museum Hui Te Ananui A Tangaroa is a maritime museum in Auckland, New Zealand. It is located on Hobson Wharf, adjacent to the Viaduct Harbour in central Auckland. It houses exhibitions spanning New Zealand's maritime history, from the first Polynesian explorers and settlers to modern day triumphs at the America's Cup. Its Maori name is 'Te Huiteanaui-A-Tangaroa' – holder of the treasures of Tangaroa.
Te Tipua is a rural farming community in the eastern Southland region of New Zealand's South Island.
Gorge Road is a locality in the Southland region of New Zealand's South Island. It is on the Southern Scenic Route and is situated on the western bank of the Mataura River. Nearby settlements include Ashers to the west, and across the Mataura, Pine Bush and Titiroa to the east.

Southland is New Zealand's southernmost region. It consists of the southwestern portion of the South Island and includes Stewart Island. Southland is bordered by the culturally similar Otago Region to the north and east, and the West Coast Region in the extreme northwest. The region covers over 3.1 million hectares and spans 3,613 km of coastline. As of June 2023, Southland has a population of 103,900, making it the eleventh-most-populous New Zealand region, and the second-most sparsely populated. Approximately half of the region's population lives in Invercargill, Southland's only city.

Ocean Beach is an industrial area in the Southland Region of New Zealand. For around 100 years it was the site of a freezing works. This closed in 1991, and the site has been redeveloped as an aquaculture facility.

Bluff Harbour is a harbour and lagoon in the South Island of New Zealand, adjacent to the town of Bluff. The main port facilities are located close to the entrance from Foveaux Strait of a large natural inlet which includes a large, low-lying eastern arm, Awarua Bay, immediately to the east of the promontory which gives the town and harbour its name.

Stirling Point is a landmark at the southern end of the New Zealand town of Bluff, New Zealand. It is notable as the southern end of both State Highway 1 and Te Araroa; both these facilities span the length of the country. Stirling Point hosts a signpost with multiple directional signs; it is one of the most photographed items in Southland. Stirling Point has an anchor chain sculpture which replicates the sculpture on Stewart Island.

The Paua House was a tourist attraction in the southern New Zealand town of Bluff, but now on display at the Canterbury Museum in Christchurch.

The Southern District Health Board was a district health board which provided healthcare to an area covering the southern half of the South Island of New Zealand. In July 2022, the Southern DHB was dissolved as part of a nationwide overhaul of the district health board system. Its former functions and responsibilities were taken over by Te Whatu Ora.
Southland County was one of the counties of New Zealand in the South Island. Created in 1876, it was in the eastern part of Southland Region. The surrounding counties were Wallace County, Lake County, Vincent County, Tuapeka County and Clutha County. Within the county, but not part of it, were the city of Invercargill, where the county headquarters were located, and the boroughs of Bluff, Winton, Gore and Mataura, as well as the town district of Wyndham; Lumsden, on the boundary with Wallace County, had its own boundary. The county was abolished in 1989, with most of it being merged into Southland District, the exceptions were the Gore and Mataura areas taken into Gore District, and Bluff became part of Invercargill, which had its boundaries expanded considerably; many places near Invercargill, formerly in the county, became part of the city.