AB Bofors is a former Swedish arms manufacturer which today is part of the British arms manufacturer BAE Systems. The name has been associated with the iron industry and artillery manufacturing for more than 350 years.
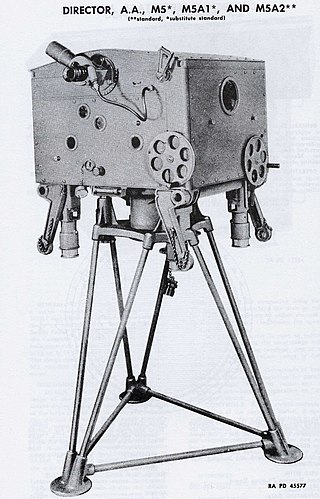
The Kerrison Predictor was one of the first fully automated anti-aircraft fire-control systems. It was used to automate the aiming of the British Army's Bofors 40 mm guns and provide accurate lead calculations through simple inputs on three main handwheels.

A directed-energy weapon (DEW) is a ranged weapon that damages its target with highly focused energy without a solid projectile, including lasers, microwaves, particle beams, and sound beams. Potential applications of this technology include weapons that target personnel, missiles, vehicles, and optical devices.
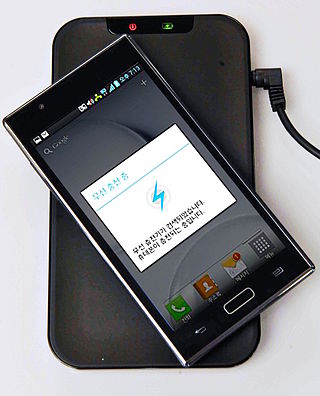
Wireless power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, an electrically powered transmitter device generates a time-varying electromagnetic field that transmits power across space to a receiver device; the receiver device extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. The technology of wireless power transmission can eliminate the use of the wires and batteries, thereby increasing the mobility, convenience, and safety of an electronic device for all users. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.

The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60 is an anti-aircraft autocannon, designed in the 1930s by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors. The gun was designed as an intermediate anti-aircraft gun, filling the gap between fast firing close-range small calibre anti-aircraft guns and slower firing long-range high calibre anti-aircraft guns. For its time, the Bofors 40 mm L/60 was perfectly suited for this role and outperformed competing designs in the years leading up to World War II in both effectiveness and reliability.

Sonic and ultrasonic weapons (USW) are weapons of various types that use sound to injure or incapacitate an opponent. Some sonic weapons make a focused beam of sound or of ultrasound; others produce an area field of sound. As of 2023 military and police forces make some limited use of sonic weapons.

Joint Unmanned Combat Air Systems, or J-UCAS, was the name for the joint U.S. Navy and U.S. Air Force unmanned combat air vehicle procurement project. Originally two separate projects of the U.S. Air Force and Navy respectively: UCAV and UCAV-N; both programs merged in 2003. The two vehicles involved in J-UCAS were the Boeing X-45 and Northrop Grumman X-47A Pegasus, originally part of UCAV and UCAV-N respectively. J-UCAS was managed by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency. In the 2006 Quadrennial Defense Review, it was stated that the J-UCAS program would be terminated and instead a new long-range strategic bomber program, Next-Generation Bomber, for the Air Force would launch. The program was revitalized into a Navy-only program named UCAS-D.

The 2-pounder gun, officially the QF 2-pounder and universally known as the pom-pom, was a 40 mm (1.6 in) British autocannon, used as an anti-aircraft gun by the Royal Navy. The name came from the sound that the original models make when firing. This QF 2-pounder was not the same gun as the Ordnance QF 2-pounder, used by the British Army as an anti-tank gun and a tank gun, although they both fired 2 lb (0.91 kg), 40 mm (1.6 in) projectiles.
Dielectric wireless receiver is a type of radiofrequency receiver front-end featuring a complete absence of electronic circuitry and metal interconnects. It offers immunity against damage from intense electromagnetic radiation, produced by EMP and HPM sources. This receiver is known as ADNERF. ADNERF is a type of Electro-Magnetic Pulse Tolerant Microwave Receiver (EMPiRe).
The Teledyne Ryan BQM-145 Peregrine is a reconnaissance unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) developed in the United States in the 1990s as a joint U.S. Navy/Marine Corps and Air Force "Medium Range UAV" program, with the Navy developing the airframe and the Air Force providing the payload. The BQM-145A was designed to precede airstrike packages into a target area and relay reconnaissance information in real time.
The Counter-electronics High Power Microwave Advanced Missile Project (CHAMP) is a joint concept technology demonstration led by the Air Force Research Laboratory, Directed Energy Directorate at Kirtland Air Force Base to develop an air-launched directed-energy weapon capable of incapacitating or damaging electronic systems by means of an EMP.

Bofors 105 mm Coastal Automatic Gun L/54, was a Swedish fully automatic dual purpose gun turret system for coastal defence designed by Bofors around the turn of the decade 1950 for use in the Swedish Coastal Artillery and for export. It was the first modern weapon system designed for the Swedish Coastal Artillery and was designed to be embedded in concrete or granite mixes for camouflage and protection.
The Vigilant Eagle Airport Protection System is a proposed directed-energy weapon under development by the U.S. military under a Defense Department contract with Raytheon. It would create an invisible microwave dome around an airport that could block missiles heading toward incoming and outgoing aircraft.
An electromagnetic pulse (EMP), also referred to as a transient electromagnetic disturbance (TED), is a brief burst of electromagnetic energy. The origin of an EMP can be natural or artificial, and can occur as an electromagnetic field, as an electric field, as a magnetic field, or as a conducted electric current. The electromagnetic interference caused by an EMP can disrupt communications and damage electronic equipment. An EMP such as a lightning strike can physically damage objects such as buildings and aircraft. The management of EMP effects is a branch of electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) engineering.
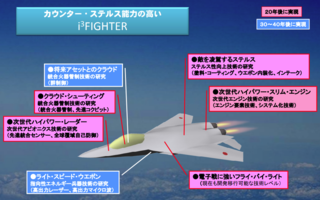
The i3 Fighter is a conceptual jet fighter proposed by the Ministry of Defense of Japan in 2010 in association with development of the successor to the Mitsubishi F-2 fighter. The i3 stands for Informed, Intelligent and Instantaneous.

James Nelson Benford is an American physicist, High-Power Microwave (HPM) scientist, book author, science-fiction writer, and entrepreneur, best known for introducing novel technological concepts and conjectures related to the exploration of outer space, among these the design of laser-driven sailships, the possible use of co-orbital objects by alien probes to spy on earth, and the appraisal of technical and safety issues associated with the Search for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). He was born in Mobile, Alabama in 1941, as was his twin brother, science-fiction author Greg Benford. He has two children, the eldest being Dominic Benford, an astrophysicist and the Program Scientist for the Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope.

The Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/70,, is a multi-purpose autocannon developed by the Swedish arms manufacturer AB Bofors during the second half of the 1940s as a modern replacement for their extremely successful World War II-era Bofors 40 mm L/60 gun-design. It was initially intended as a dedicated anti-aircraft weapon, being sold as Bofors 40 mm Automatic A.A. Gun L/70, but has since its conception been redeveloped into a dedicated multi-purpose weapon capable of firing both sabot projectiles and programmable ammunition. The Bofors 40 mm L/70 design never achieved the same popularity and historical status as the original L/60 design but has still seen great export and popularity to this day, having been adopted by around 40 different nations and even being accepted as NATO-standard in November 1953. It is still being produced and sold, and several variants exist for both field and naval applications. A notable variant is the Bofors 40/70B "light armored vehicle variant" which is in use on the Swedish Strf 9040 and Korean K21 infantry fighting vehicles.
The Leonidas is a high-power microwave (HPM) weapon developed to disable unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarms. It was named after Leonidas of Epirus.
The Tactical High-power Operational Responder (THOR) is a high-power microwave directed energy weapon developed by the United States Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL).










