
Maracaibo is a city and municipality in northwestern Venezuela, on the western shore of the strait that connects Lake Maracaibo to the Gulf of Venezuela. It is the second-largest city in Venezuela, after the national capital, Caracas, and the capital of the state of Zulia. The population of the city is approximately 2,658,355 with the metropolitan area estimated at 5,278,448 as of 2010. Maracaibo is nicknamed "The Beloved Land of the Sun".

José Cipriano Castro Ruiz was a high-ranking officer of the Venezuelan military, politician and the president of Venezuela from 1899 to 1908. He was the first man from the Venezuelan Andes to rule the country, and was the first of four military strongmen from the Andean state of Táchira to rule the country over the next 46 years.

Puerto Cabello is a city on the north coast of Venezuela. It is located in Carabobo State, about 210 km west of Caracas. As of 2011, the city had a population of around 182,400. The city is home to the largest and busiest port in the country and is thus a vital cog in the country's vast oil industry. The word 'cabello' translates to 'hair'. The Spanish took to saying that the sea was so calm there that a ship could be moored to the dock with a single hair.

The Battle of Lake Maracaibo also known as the "Naval Battle of the Lake" was fought on 24 July 1823 on Venezuela's Lake Maracaibo between fleets under the commands of Republican Admiral José Prudencio Padilla and royalist Captain Ángel Laborde.

SMS Panther was one of six Iltis-class gunboats of the Kaiserliche Marine that, like its sister ships, served in Germany's overseas colonies. The ship was launched on 1 April 1901 in the Kaiserliche Werft, Danzig. It had a crew of 9 officers and 121 men.

SMS Vineta was a protected cruiser of the Victoria Louise class, built for the German Imperial Navy in the 1890s. Vineta was laid down at the AG Vulcan shipyard in 1895, launched in April 1897, and commissioned into the Navy in July 1898. The ship, named for the earlier screw frigate SMS Vineta, was armed with a battery of two 21 cm guns and eight 15 cm guns and had a top speed of 19 knots. Though the five Victoria Louise-class cruisers proved to be disappointing in some ways, they marked the beginning of a decade of German cruiser construction.

The Raid on Yarmouth, on 3 November 1914, was an attack by the Imperial German Navy on the British North Sea port and town of Great Yarmouth. German shells only landed on the beach causing little damage to the town, after German ships laying mines offshore were interrupted by British destroyers. The British submarine HMS D5 was sunk by a German mine as it was leaving harbour to attack the German ships. A German armoured cruiser was sunk after striking two German mines outside its home port.
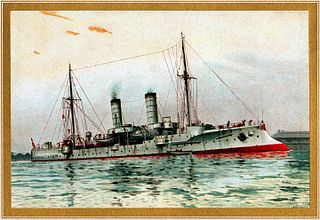
SMS Gazelle was the lead ship of the ten-vessel Gazelle class of light cruisers that were built for the German Kaiserliche Marine in the late 1890s. The Gazelle class was the culmination of earlier unprotected cruiser and aviso designs, combining the best aspects of both types in what became the progenitor of all future light cruisers of the Imperial fleet. Built to be able to serve with the main German fleet and as a colonial cruiser, she was armed with a battery of ten 10.5 cm (4.1 in) guns and a top speed of 19.5 knots. Her Niclausse boilers proved to be troublesome in service, and these were later replaced in the mid-1900s.

The Bombardment of San Juan, or the First Battle of San Juan, on 12 May 1898 was an engagement between United States Navy warships and the Spanish fortifications of San Juan, Puerto Rico. It was the first major action of the Puerto Rican Campaign during the Spanish–American War.

The Venezuelan crisis of 1902–1903 was a naval blockade imposed against Venezuela by Great Britain, Germany, and Italy from December 1902 to February 1903, after President Cipriano Castro refused to pay foreign debts and damages suffered by European citizens in recent Venezuelan civil wars. Castro assumed that the American Monroe Doctrine would see Washington intervene to prevent European military intervention. However, at the time, United States president Theodore Roosevelt and his State Department saw the doctrine as applying only to European seizure of territory, rather than intervention per se. With prior promises that no such seizure would occur, the U.S. was officially neutral and allowed the action to go ahead without objection. The blockade saw Venezuela's small navy quickly disabled, but Castro refused to give in, and instead agreed in principle to submit some of the claims to international arbitration, which he had previously rejected. Germany initially objected to this, arguing that some claims should be accepted by Venezuela without arbitration.

United Kingdom–Venezuela relations are the bilateral relations between the United Kingdom and Venezuela since 1817 when so-called "British Legions" of former British soldiers fought to defend the Third Republic of Venezuela against Spanish royalists in the Venezuelan War of Independence.
Toas Island is a small limestone island in Venezuela. It is in the north-west of the country, north of Maracaibo Lake, just southwest of Zapara island and to the south of San Carlos peninsula, forming part of the "Barra del Lago de Maracaibo". Administratively it falls under the jurisdiction of Almirante Padilla Municipality in the state of Zulia.
Jose Antonio Arizabalo Orobio was a Spanish military who played an important role in the Spanish American wars of independence.

Herbert Wolcott Bowen was an American diplomat and poet. He served as ambassador to Venezuela, and consul-general in Spain and Iran.
Heinrich Paul Christian Richard Eckermann was an officer of the German Imperial Navy, rising to Vizeadmiral in the First World War.

SMS Falke was an unprotected cruiser of the Bussard class, built for the Imperial German Navy. She was the second member of the class of six vessels. The cruiser was laid down in 1890, launched in April 1891, and commissioned into the fleet in September of that month. Designed for overseas service, she carried a main battery of eight 10.5-centimeter (4.1 in) guns and had a top speed of 15.5 knots.
Events in the year 1902 in Venezuela.

San Felipe Castle is an eighteenth-century star fort protecting Puerto Cabello in Venezuela. It was named in honour of Philip V, King of Spain at the time of its construction in the 1730s. It has an alternative name Castillo Libertador, explained by its connection with Simón Bolívar, known as El Libertador because of his role in Latin American independence.

San Carlos de la Barra Fortress is a 17th-century star fort protecting Lake Maracaibo in Venezuela.
The civil war of 1848-1849 was an armed conflict in Venezuela between the conservatives, led by José Antonio Páez, against the newly established Great Liberal Party, founded and led by José Tadeo Monagas.
















