
General George Augustus Eliott, 1st Baron Heathfield, was a Scottish officer of the British Army, who served in three major wars during the 18th century. He rose to distinction during the Seven Years' War when he fought in Germany and participated in the British attacks on Belle Île (France) and Cuba. Eliott is most notable for his command of the Gibraltar garrison during the Great Siege of Gibraltar, which lasted from 1779 to 1783, during the American War of Independence. He was celebrated for his successful defence of the fortress and decisive defeat of Spanish and French attackers.

The Great Siege of Gibraltar was an unsuccessful attempt by Spain and France to capture Gibraltar from the British during the American Revolutionary War. It was the largest battle in the war by number of combatants.

The Battle of Cape Spartel was an indecisive naval battle between a Franco-Spanish fleet under Admiral Luis de Córdova y Córdova and a British fleet under Admiral Richard Howe. These forces met on 20 October 1782 after Howe successfully resupplied Gibraltar, then under siege by Bourbon forces during the American Revolutionary War.

The Defeat of the Floating Batteries at Gibraltar is the title of a 1791 oil-on-canvas painting by Boston-born American artist John Singleton Copley. It depicts a coastal view of the naval action of the Great Siege of Gibraltar, part of the European theatre of the American Revolutionary War. The Spanish Empire's infamous floating batteries lie crippled and aflame in the background, while the shoreward waters are choked with surrendering Spaniards. The British rescue efforts are commanded from horseback by the Governor of Gibraltar, General George Augustus Eliott.

The Sortie Made by the Garrison of Gibraltar is a 1789 oil-on-canvas painting by American artist John Trumbull. The painting shows a key point in Gibraltar's history when the Great Siege of Gibraltar was undertaken by the Spanish against the British at Gibraltar in November 1781. The Spanish officer Don Jose de Barboza is being given respect as he lies dying. Although left behind by his own retreating troops, he still unsuccessfully attacked the British troops with chivalry.

The Great Siege Tunnels in the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar, also known as the Upper Galleries, are a series of tunnels inside the northern end of the Rock of Gibraltar. They were dug out from the solid limestone by the British during the Great Siege of Gibraltar of the late 18th century.
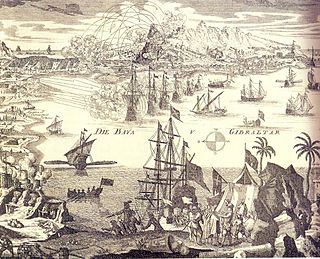
The Anglo-Spanish War of 1727–1729 was a limited war that took place between Great Britain and Spain during the late 1720s, and consisted of a failed Spanish attempt to capture Gibraltar and an unsuccessful British Blockade of Porto Bello with a high British death toll. It eventually ended with a return to the previous status quo ante bellum following the Treaty of Seville.

The siege of Gibraltar of 1727 saw Spanish forces besiege the British garrison of Gibraltar as part of the Anglo-Spanish War. Depending on the sources, Spanish troops numbered between 12,000 and 25,000. British defenders were 1,500 at the beginning of the siege, increasing up to about 5,000. After a five-month siege with several unsuccessful and costly assaults, Spanish troops gave up and withdrew. Following the failure the war drew to a close, opening the way for the 1728 Treaty of El Pardo and the Treaty of Seville signed in 1729.

The history of Gibraltar, a small peninsula on the southern Iberian coast near the entrance of the Mediterranean Sea, spans over 2,900 years. The peninsula has evolved from a place of reverence in ancient times into "one of the most densely fortified and fought-over places in Europe", as one historian has put it. Gibraltar's location has given it an outsized significance in the history of Europe and its fortified town, established in the Middle Ages, has hosted garrisons that sustained numerous sieges and battles over the centuries.

The first siege of Gibraltar was a battle of the Spanish Reconquista that took place in 1309. The battle pitted the forces of the Crown of Castile under the command of Juan Núñez II de Lara and Alonso Pérez de Guzmán, against the forces of the Emirate of Granada who were under the command of Sultan Muhammed III and his brother, Abu'l-Juyush Nasr.

The North Bastion, formerly the Baluarte San Pablo was part of the fortifications of Gibraltar, in the north of the peninsula, protecting the town against attack from the mainland of Spain. The bastion was based on the older Giralda tower, built in 1309. The bastion, with a mole that extended into the Bay of Gibraltar to the west and a curtain wall stretching to the Rock of Gibraltar on its east, was a key element in the defenses of the peninsula. After the British took Gibraltar in 1704 they further strengthened these fortifications, flooding the land in front and turning the curtain wall into the Grand Battery.

The fifth siege of Gibraltar, mounted between August 1349 and March 1350, was a second attempt by King Alfonso XI of Castile to retake the fortified town of Gibraltar. It had been held by the Moors since 1333. The siege followed years of intermittent conflict between the Christian kingdoms of Spain and the Moorish Emirate of Granada, which was supported by the Marinid sultanate of Morocco. A series of Moorish defeats and reverses had left Gibraltar as a Moorish-held enclave within Castilian territory. Its geographical isolation was compensated for by the strength of its fortifications, which had been greatly improved since 1333. Alfonso brought an army of around 20,000 men, along with his mistress and their five illegitimate children, to dig in to the north of Gibraltar for a lengthy siege. In the New Year of 1350, however, bubonic plague – the Black Death – broke out in the Castilian camp. Alfonso refused to abandon the siege but fell victim to the plague on 27 March 1350, becoming the only monarch to die of the disease.

The twelfth siege of Gibraltar was fought between September 1704 and May 1705 during the War of the Spanish Succession. It followed the capture in August 1704 of the fortified town of Gibraltar, at the southern tip of Spain, by an Anglo–Dutch naval force led by Sir George Rooke and Prince George of Hesse-Darmstadt. The members of the Grand Alliance, the Holy Roman Empire, England, the Netherlands, Pro-Habsburg Spain, Portugal and Savoy, had allied to prevent the unification of the French and Spanish thrones by supporting the claim of the Habsburg pretender Archduke Charles VI of Austria as Charles III of Spain. They were opposed by the rival claimant, the Bourbon Philip, Duke of Anjou, ruling as Philip V of Spain, and his patron and ally, Louis XIV of France. The war began in northern Europe and was largely contained there until 1703, when Portugal joined the confederate powers. From then, English naval attentions were focused on mounting a campaign in the Mediterranean to distract the French navy and disrupt French and Bourbon Spanish shipping or capture a port for use as a naval base. The capture of Gibraltar was the outcome of that initial stage of the Mediterranean campaign.
Willis' Battery is a former artillery battery on the north side of the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar. It overlooks the isthmus between Spain and Gibraltar.

The Gibraltar peninsula, located at the far southern end of Iberia, has great strategic importance as a result of its position by the Strait of Gibraltar where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean. It has repeatedly been contested between European and North African powers and has endured fourteen sieges since it was first settled in the 11th century. The peninsula's occupants – Moors, Spanish, and British – have built successive layers of fortifications and defences including walls, bastions, casemates, gun batteries, magazines, tunnels and galleries. At their peak in 1865, the fortifications housed around 681 guns mounted in 110 batteries and positions, guarding all land and sea approaches to Gibraltar. The fortifications continued to be in military use until as late as the 1970s and by the time tunnelling ceased in the late 1960s, over 34 miles (55 km) of galleries had been dug in an area of only 2.6 square miles (6.7 km2).

The Lines of Contravallation of Gibraltar, known in English as the "Spanish Lines", were a set of fortifications built by the Spanish across the northern part of the isthmus linking Spain with Gibraltar. They later gave their name to the Spanish town of La Línea de la Concepción. The Lines were constructed after 1730 to establish a defensive barrier across the peninsula, with the aim of preventing any British incursions, and to serve as a base for fresh Spanish attempts to retake Gibraltar. They played an important role in the Great Siege of Gibraltar between 1779 and 1783 when they supported the unsuccessful French and Spanish assault on the British-held fortress. The siege was ended after the lines of contravallation were attacked by British and Dutch forces under the command of the Governor of Gibraltar, General Augustus Eliot. The attack caused the Spanish forces to retreat and abandon the fortifications and the combined British led forces virtually destroyed all the Spanish gun batteries and the enemy cannon and munitions either captured or destroyed. This attack is still commemorated to this day and is known as 'Sortie Day'.

The King's Lines are a walled rock-cut trench on the lower slopes of the north-west face of the Rock of Gibraltar. Forming part of the Northern Defences of the fortifications of Gibraltar, they were originally created some time during the periods when Gibraltar was under the control of the Moors or Spanish. They are depicted in a 1627 map by Don Luis Bravo de Acuña, which shows their parapet following a tenaille trace. The lines seem to have been altered subsequently, as maps from the start of the 18th century show a more erratic course leading from the Landport, Gibraltar's main land entrance, to the Round Tower, a fortification at their western end. A 1704 map by Johannes Kip calls the Lines the "Communication Line of the Round Tower".













