Related Research Articles
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental and behavioral disorder that develops from experiencing a traumatic event, such as sexual assault, warfare, traffic collisions, child abuse, domestic violence, or other threats on a person's life or well-being. Symptoms may include disturbing thoughts, feelings, or dreams related to the events, mental or physical distress to trauma-related cues, attempts to avoid trauma-related cues, alterations in the way a person thinks and feels, and an increase in the fight-or-flight response. These symptoms last for more than a month after the event and can include triggers such as misophonia. Young children are less likely to show distress, but instead may express their memories through play. A person with PTSD is at a higher risk of suicide and intentional self-harm.
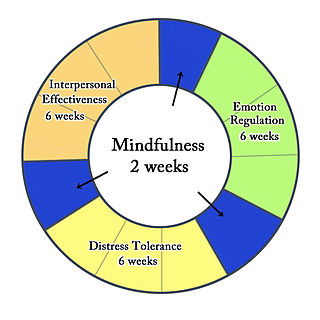
Dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy that began with efforts to treat personality disorders and interpersonal conflicts. Evidence suggests that DBT can be useful in treating mood disorders and suicidal ideation as well as for changing behavioral patterns such as self-harm and substance use. DBT evolved into a process in which the therapist and client work with acceptance and change-oriented strategies and ultimately balance and synthesize them—comparable to the philosophical dialectical process of thesis and antithesis, followed by synthesis.
Psychological trauma is an emotional response caused by severe distressing events that are outside the normal range of human experiences. It must be understood by the affected person as directly threatening the affected person or their loved ones generally with death, severe bodily injury, or sexual violence; indirect exposure, such as from watching television news, may be extremely distressing and can produce an involuntary and possibly overwhelming physiological stress response, but does not produce trauma per se. Examples of distressing events include violence, rape, or a terrorist attack.
Derek Summerfield is an honorary senior lecturer at London's Institute of Psychiatry and a member of the Executive Committee of Transcultural Special Interest Group at the Royal College of Psychiatry. He is also an Honorary Fellow of the Egyptian Psychiatric Association. He has published around 150 papers and has made other contributions in medical and social sciences literature.

Betrayal is the breaking or violation of a presumptive contract, trust, or confidence that produces moral and psychological conflict within a relationship amongst individuals, between organizations or between individuals and organizations. Often betrayal is the act of supporting a rival group, or it is a complete break from previously decided upon or presumed norms by one party from the others. Someone who betrays others is commonly known as a traitor or betrayer.

Complex post-traumatic stress disorder is a stress-related mental disorder generally occurring in response to complex traumas, i.e., commonly prolonged or repetitive exposures to a series of traumatic events, within which individuals perceive little or no chance to escape.
Childhood trauma is often described as serious adverse childhood experiences (ACEs). Children may go through a range of experiences that classify as psychological trauma; these might include neglect, abandonment, sexual abuse, emotional abuse, and physical abuse, witnessing abuse of a sibling or parent, or having a mentally ill parent. These events have profound psychological, physiological, and sociological impacts and can have negative, lasting effects on health and well-being such as unsocial behaviors, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and sleep disturbances. Similarly, children whose mothers have experienced traumatic or stressful events during pregnancy have an increased risk of mental health disorders and other neurodevelopmental disorders.

Yuval Neria is a Professor of Medical Psychology at the Departments of Psychiatry and Epidemiology at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC), and Director of Trauma and PTSD Program, and a Research Scientist at the New York State Psychiatric Institute (NYSPI) and Columbia University Department of Psychiatry. He is a recipient of the Medal of Valor, Israel's highest decoration, for his exploits during the 1973 Yom Kippur War.
The Trauma Symptom Inventory (TSI) is a psychological evaluation/assessment instrument that taps symptoms of Posttraumatic stress disorder and other posttraumatic emotional problems. It was originally published in 1995 by its developer, John Briere. It is one of the most widely used measures of posttraumatic symptomatology.
Childbirth-related post-traumatic stress disorder is a psychological disorder that can develop in women who have recently given birth. This disorder can also affect men or partners who have observed a difficult birth. Its symptoms are not distinct from post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It may also be called post-traumatic stress disorder following childbirth (PTSD-FC).
Psychological first aid (PFA) is a technique designed to reduce the occurrence of post-traumatic stress disorder. It was developed by the National Center for Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (NC-PTSD), a section of the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, in 2006. It has been endorsed and used by the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies, Community Emergency Response Team (CERT), the American Psychological Association (APA) and many others. It was developed in a two-day intensive collaboration, involving more than 25 disaster mental health researchers, an online survey of the first cohort that used PFA and repeated reviews of the draft.
Trauma focused cognitive behavioral therapy (TF-CBT) is an evidence-based psychotherapy or counselling that aims at addressing the needs of children and adolescents with post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other difficulties related to traumatic life events. This treatment was developed and proposed by Drs. Anthony Mannarino, Judith Cohen, and Esther Deblinger in 2006. The goal of TF-CBT is to provide psychoeducation to both the child and non-offending caregivers, then help them identify, cope, and re-regulate maladaptive emotions, thoughts, and behaviors. Research has shown TF-CBT to be effective in treating childhood PTSD and with children who have experienced or witnessed traumatic events, including but not limited to physical or sexual victimization, child maltreatment, domestic violence, community violence, accidents, natural disasters, and war. More recently, TF-CBT has been applied to and found effective in treating complex posttraumatic stress disorder.
Trauma risk management (TRiM) is a method of secondary PTSD prevention. The TRiM process enables non-healthcare staff to monitor and manage colleagues. TRiM training provides practitioners with a background understanding of psychological trauma and its effects.
The University of California at Los Angeles Posttraumatic Stress Disorder Reaction Index for DSM-5 is a psychiatric assessment tool used to assess symptoms of PTSD in children and adolescents. This assessment battery includes four measures: the Child/Adolescent Self-Report version; the Parent/Caregiver Report version; the Parent/Caregiver Report version for Children Age 6 and Younger; and a Brief Screen for Trauma and PTSD. Questions may differ among the indexes depending on the target age, however the indexes are identical in format. The target age groups for this assessment are children and adolescents between 7-18 and children age 6 and younger. Versions of the UCLA PTSD Reaction Index for DSM-5 have been translated into many languages, including Spanish, Japanese, Simplified Chinese, Korean, German, and Arabic. The DSM-IV version of the UCLA PTSD Reaction Index Index has been updated for DSM-5.
The Child PTSD Symptom Scale (CPSS) is a free checklist designed for children and adolescents to report traumatic events and symptoms that they might feel afterward. The items cover the symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), specifically, the symptoms and clusters used in the DSM-IV. Although relatively new, there has been a fair amount of research on the CPSS due to the frequency of traumatic events involving children. The CPSS is usually administered to school children within school boundaries, or in an off-site location to assess symptoms of trauma. Some, but not all, people experience symptoms after a traumatic event, and in serious cases, these people may not get better on their own. Early and accurate identification, especially in children, of experiencing distress following a trauma could help with early interventions. The CPSS is one of a handful of promising measures that has accrued good evidence for reliability and validity, along with low cost, giving it good clinical utility as it addresses a public health need for better and larger scale assessment.

Conflicts and emergencies around the world pose detrimental risks to the health, safety, and well-being of children. There are many different kinds of conflicts and emergencies, for example, violence, armed conflicts, war, and natural disasters. Some 13 million children are displaced by armed conflicts and violence around the world. Where violent conflicts are the norm, the lives of young children are significantly disrupted and their families have great difficulty in offering the sensitive and consistent care that young children need for their healthy development. One impact is the high rates of PTSD seen in children living with natural disasters or chronic conflict.
Secondary trauma can be incurred when an individual is exposed to people who have been traumatized themselves, disturbing descriptions of traumatic events by a survivor, or others inflicting cruelty on one another. Symptoms of secondary trauma are similar to those of PTSD. Secondary trauma has been researched in first responders, nurses and physicians, mental health care workers, and children of traumatized parents.
Betty Pfefferbaum is a psychiatrist known for her early work in mental health treatment for children after a disaster. She is the director of the Terrorism and Disaster Center in the College of Medicine at Oakland University.
Over the last fifty years, there has been an increase in the different types of media that are accessible to the public. Most people use online search engines, social media, or other online news outlets to find out what is going on in the world. This increase can lead to people easily viewing negative images and stories about traumatic events that they would not have been exposed to otherwise. One thing to consider is how the dissemination of this information may be impacting the mental health of people who identify with the victims of the violence they hear and see through the media. The viewing of these traumatic videos and stories can lead to the vicarious traumatization of the viewers.
Hispanic immigrants living in the United States have been found to have higher levels of exposure to trauma and lower mental health service utilization than the general population. Those who met the criteria for asylum and experience trauma before migrating are vulnerable to post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) symptoms. Higher levels of trauma-related symptoms are associated with increased post-migration living difficulties. Despite the need for mental health services for Hispanic immigrants living in the United States, cultural and structural barriers make accessing treatment challenging.
References
- ↑ Green, Bonnie L. (1993). "Editorial note". Journal of Traumatic Stress. 6 (1): 1–2. doi:10.1002/jts.2490060102. ISSN 0894-9867.
- ↑ Green, Bonnie L. (1997). "Editorial note". Journal of Traumatic Stress. 10 (1): 1–2. doi:10.1002/jts.2490100102. ISSN 0894-9867.
- ↑ "Past Presidents". International Society for Traumatic Stress Studies. Retrieved May 24, 2024.
- ↑ "Psychology's top honors Congratulations to the psychologists who received awards at APA's 2012 Annual Convention last month". Vol. 43, no. 8. September 2012. p. 72.
- ↑ "Bonnie L. Green, PhD". Center for Trauma and the Community. Retrieved 2023-11-27.
- ↑ Elias, Marilyn (28 September 2005). "Storms' collateral damage ; 'Danger signs' point to stress disorders after disasters". USA TODAY; McLean, Va. pp. D.10 – via Proquest.
- ↑ Suplee, Curt Suplee (April 27, 1995). "TRAGEDY WILL TAKE A TOLL ON MENTAL HEALTH OF SURVIVORS". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286 . Retrieved 2024-07-13.
- ↑ Eisenman, David; Weine, Stevan; Green, Bonnie; Jong, Joop de; Rayburn, Nadine; Ventevogel, Peter; Keller, Allen; Agani, Ferid (2006-02-01). "The ISTSS/Rand Guidelines on Mental Health Training of Primary Healthcare Providers for Trauma-Exposed Populations in Conflict-Affected Countries". Journal of Traumatic Stress. 19 (1): 5–17. doi:10.1002/jts.20094. ISSN 0894-9867. PMID 16568460.
- ↑ Green, Bonnie L.; Krupnick, Janice L.; Rowland, Julia H.; Epstein, Steven A.; Stockton, Patricia; Spertus, Ilyse; Stern, Nicole (2000-03-01). "Trauma History as a Predictor of Psychologic Symptoms in Women With Breast Cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 18 (5): 1084–1093. doi:10.1200/JCO.2000.18.5.1084. ISSN 0732-183X. PMID 10694561.
- ↑ Miranda, Jeanne; Chung, Joyce Y.; Green, Bonnie L.; Krupnick, Janice; Siddique, Juned; Revicki, Dennis A.; Belin, Tom (2003-07-02). "Treating Depression in Predominantly Low-Income Young Minority Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial". JAMA. 290 (1): 57–65. doi:10.1001/jama.290.1.57. ISSN 0098-7484. PMID 12837712.