The Book Item and Component Identifier, or BICI, is a draft standard of the United States National Information Standards Organization (NISO) that would provide a unique identifier for items or components within a book or publication to which an International Standard Book Number (ISBN) has been assigned. It is related to the Serial Item and Contribution Identifier (SICI).

The International Standard Book Number (ISBN) is a numeric commercial book identifier that is intended to be unique. Publishers purchase ISBNs from an affiliate of the International ISBN Agency.

A serial number is a unique identifier assigned incrementally or sequentially to an item, to uniquely identify it.
In computing, AAP DTD is a set of three SGML Document Type Definitions for scientific documents, defined by the Association of American Publishers. It was ratified as a U.S. standard under the name ANSI/NISO Z39.59 in 1988, and evolved into the international ISO 12083 standard in 1993. It was supplanted as a U.S. standard by ANSI/ISO 12083 in 1995.
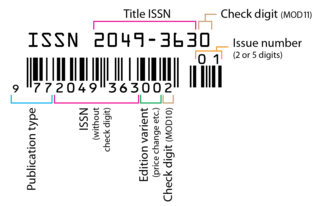
An International Standard Serial Number (ISSN) is an eight-digit serial number used to uniquely identify a serial publication, such as a magazine. The ISSN is especially helpful in distinguishing between serials with the same title. ISSNs are used in ordering, cataloging, interlibrary loans, and other practices in connection with serial literature.

A digital object identifier (DOI) is a persistent identifier or handle used to identify objects uniquely, standardized by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). An implementation of the Handle System, DOIs are in wide use mainly to identify academic, professional, and government information, such as journal articles, research reports, data sets, and official publications. DOIs have also been used, however, to identify other types of information resources, such as commercial videos.
The National Information Standards Organization is a United States non-profit standards organization that develops, maintains and publishes technical standards related to publishing, bibliographic and library applications. It was founded in 1939, incorporated as a not-for-profit education association in 1983, and assumed its current name in 1984.
An OpenURL is similar to a web address, but instead of referring to a physical website, it refers to an article, book, patent, or other resource within a website.
The Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) is an identifier for trade items, developed by the international organization GS1. Such identifiers are used to look up product information in a database which may belong to a retailer, manufacturer, collector, researcher, or other entity. The uniqueness and universality of the identifier is useful in establishing which product in one database corresponds to which product in another database, especially across organizational boundaries.
The Serial Item and Contribution Identifier (SICI) was a code used to uniquely identify specific volumes, articles or other identifiable parts of a serial. It was "intended primarily for use by those members of the bibliographic community involved in the use or management of serial titles and their contributions". Developed over 1993–1995, NISO adopted SICI as a standard in 1996, then reaffirmed it in 2002. It was withdrawn in 2012.
The Publisher Item Identifier (PII) is a unique identifier used by a number of scientific journal publishers to identify documents. It uses the pre-existing ISSN or ISBN of the publication in question, and adds a character for source publication type, an item number, and a check digit.
ContextObjects in Spans (COinS) is a method to embed bibliographic metadata in the HTML code of web pages. This allows bibliographic software to publish machine-readable bibliographic items and client reference management software to retrieve bibliographic metadata. The metadata can also be sent to an OpenURL resolver. This allows, for instance, searching for a copy of a book at a specific library.
UKSG is an international association that exists to "connect the information community" and "encourage the exchange of ideas on scholarly communication". The name UKSG originally stood for United Kingdom Serials Group, but the association is now known simply as UKSG as it has expanded beyond the UK and beyond serials to include e-books and other electronic resources.
BICI can refer to:
NISO Circulation Interchange Protocol (NCIP) is a protocol that is limited to the exchange of messages between and among computer-based applications to enable them to perform functions necessary to lend and borrow items, to provide controlled access to electronic resources, and to facilitate cooperative management of these functions.
Unique Identification Marking, UID marking, Item Unique Identification or IUID, is a part of the compliance process mandated by the United States Department of Defense. It is a permanent marking method used to give equipment a unique ID. Marking is essential for all equipment with an acquisition cost of over $5,000, equipment which is mission essential, controlled inventory, or serially-controlled. UID-marking is a set of data for assets that is globally unique and unambiguous. The technology used to mark an item is 2D Data Matrix ECC 200 Symbol. UID marking can be used to ensure data integrity and data quality throughout an item's lifecycle; it also supports multi-faceted business applications.

EPUB is an e-book file format that uses the ".epub" file extension. The term is short for electronic publication and is sometimes styled ePub. EPUB is supported by many e-readers, and compatible software is available for most smartphones, tablets, and computers. EPUB is a technical standard published by the International Digital Publishing Forum (IDPF). It became an official standard of the IDPF in September 2007, superseding the older Open eBook standard.
An OpenURL knowledge base is an extensive database containing information about electronic resources such as electronic journals or ebooks and their availability and accessibility. Using the knowledge base, an OpenURL link resolver can determine if an item is available electronically and what the appropriate copy for a user is.

The Journal Article Tag Suite (JATS) is an XML format used to describe scientific literature published online. It is a technical standard developed by the National Information Standards Organization (NISO) and approved by the American National Standards Institute with the code Z39.96-2012.
ISO 12083 is an international SGML standard for document interchange between authors and publishers. It features separate Document Type Definitions for books, serials, articles, and math. Derived from AAP DTD, it was first published in 1993, revised in 1994, and last confirmed in 2016.