
The ancient Egyptians believed that a soul was made up of many parts. In addition to these components of the soul, there was the human body.
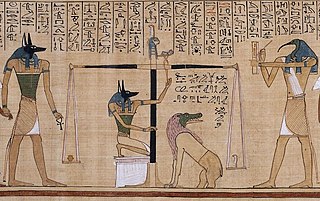
The Book of the Dead is the name given to an ancient Egyptian funerary text generally written on papyrus and used from the beginning of the New Kingdom to around 50 BC. "Book" is the closest term to describe the loose collection of texts consisting of a number of magic spells intended to assist a dead person's journey through the Duat, or underworld, and into the afterlife and written by many priests over a period of about 1,000 years. In 1842, the Egyptologist Karl Richard Lepsius introduced for these texts the German name Todtenbuch, translated to English as 'Book of the Dead'. The original Egyptian name for the text, transliterated rw nw prt m hrw, is translated as Spells of Coming Forth by Day.

Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt, which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of Thebes. Luxor had a population of 1,333,309 in 2020, with an area of approximately 417 km2 (161 sq mi) and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the oldest inhabited cities in the world.

The tomb of Tutankhamun, also known by its tomb number, KV62, is the burial place of Tutankhamun, a pharaoh of the Eighteenth Dynasty of ancient Egypt, in the Valley of the Kings. The tomb consists of four chambers and an entrance staircase and corridor. It is smaller and less extensively decorated than other Egyptian royal tombs of its time, and it probably originated as a tomb for a non-royal individual that was adapted for Tutankhamun's use after his premature death. Like other pharaohs, Tutankhamun was buried with a wide variety of funerary objects and personal possessions, such as coffins, furniture, clothing and jewelry, though in the unusually limited space these goods had to be densely packed. Robbers entered the tomb twice in the years immediately following the burial, but Tutankhamun's mummy and most of the burial goods remained intact. The tomb's low position, dug into the floor of the valley, allowed its entrance to be hidden by debris deposited by flooding and tomb construction. Thus, unlike other tombs in the valley, it was not stripped of its valuables during the Third Intermediate Period.

The Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) is a museum of art, world culture and natural history in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the largest museums in North America and the largest in Canada. It attracts more than one million visitors every year, making it the most-visited museum in Canada. It is north of Queen's Park, in the University of Toronto district, with its main entrance on Bloor Street West. Museum subway station is named after it and, since a 2008 renovation, is decorated to resemble the ROM's collection at the platform level.
Djer is considered the third pharaoh of the First Dynasty of ancient Egypt in current Egyptology. He lived around the mid 31st century BC and reigned for c. 40 years. A mummified forearm of Djer or his wife was discovered by Egyptologist Flinders Petrie, but was discarded by Émile Brugsch.

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. These rituals included mummifying the body, casting magic spells, and burials with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the afterlife.

Luxor Museum is an archaeological museum in Luxor, Egypt. It stands on the corniche, overlooking the east bank of the River Nile.

The Papyrus of Ani is a papyrus manuscript in the form of a scroll with cursive hieroglyphs and colour illustrations that was created c. 1250 BCE, during the Nineteenth Dynasty of the New Kingdom of ancient Egypt. Egyptians compiled an individualized book for certain people upon their death, called the Book of Going Forth by Day, more commonly known as the Book of the Dead, typically containing declarations and spells to help the deceased in their afterlife. The Papyrus of Ani is the manuscript compiled for the Theban scribe Ani; it is now in the British Museum.

El-Assasif is a necropolis near Luxor on the West Bank at Thebes, Egypt, Upper Egypt. It is located in the dry bay that leads up to Deir el-Bahari and south of the necropolis of Dra' Abu el-Naga'.

The Royal Cache, technically known as TT320, is an Ancient Egyptian tomb located next to Deir el-Bahari, in the Theban Necropolis, opposite the modern city of Luxor.

Mutnedjmet, also spelled Mutnodjmet, Mutnedjemet, etc., was an ancient Egyptian queen, the Great Royal Wife of Horemheb, the last ruler of the 18th Dynasty. The name, Mutnedjmet, translates as: "The sweet Mut" or "Mut is sweet." She was the second wife of Horemheb after Amenia who died before Horemheb became pharaoh.

The Joseph Smith Papyri (JSP) are Egyptian funerary papyrus fragments from ancient Thebes dated between 300 and 100 BC which, along with four mummies, were once owned by Joseph Smith, the founder of the Latter Day Saint movement. Smith purchased the mummies and papyrus documents from a traveling exhibitor in Kirtland, Ohio in 1835. Smith said that the papyrus contained the records of the ancient patriarchs Abraham and Joseph.

The lost Tomb of Nebamun was an ancient Egyptian tomb from the Eighteenth Dynasty located in the Theban Necropolis located on the west bank of the Nile at Thebes in Egypt. The tomb was the source of a number of famous decorated tomb scenes that are currently on display in the British Museum, London.

Setau was the Viceroy of Kush in the second half of Ramesses II's reign. Contemporary records show that Setau served in this position from Year 38 until at least Year 63 of Ramesses II's reign. Setau was "a graduate of the royal school" and already enjoyed an impressive record of royal service which is detailed in a long autobiographical inscription carved at Wadi es-Sebua. The temple of Wadi es-Sebua was built for Ramesses II by Setau around 1236 BC or Year 44 of this pharaoh's reign. Eleven of his stela, now in the Cairo Museum, were found in the courtyard of this temple and make it possible to establish his career and understand the precise duties of a viceroy. Setau states:
I was one whom his Lord caused to instructed....as a ward of the palace. I grew up in the royal abode when I was a youth...I was provided for with bread and beer from all the royal meals. I came forth as a scribe from the school, I was appointed to be Chief Scribe of the Vizier; I assessed the whole land with a scroll. A task I being equal to the task.

The colossal quartzite statue of Amenhotep III is an ancient Egyptian sculpture dating from the 18th Dynasty. It was found in the massive mortuary temple of the pharaoh Amenhotep III on the West Bank of the River Nile at Thebes (Luxor) in Egypt. Only the head of the broken colossal statue survives. It is part of the British Museum's Department of Ancient Egypt and Sudan collection.
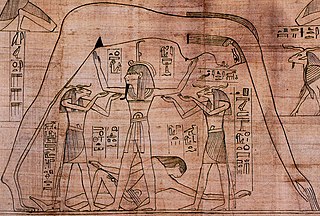
The Greenfield Papyrus is a papyrus that contains an ancient Egyptian Book of the Dead and is named after Mrs. Edith Mary Greenfield, who presented it to the Trustees of the British Museum in May 1910. Now in the collections of the British Museum, London, it is one of the longest papyri in existence with a length of 37 metres.

The mask of Tutankhamun is a gold funerary mask of the 18th-dynasty ancient Egyptian pharaoh Tutankhamun. After being buried for over 3,000 years, it was excavated by Howard Carter in 1925 from tomb KV62 in the Valley of the Kings. It has been displayed in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo from 1925 to present. The death mask is one of the best-known works of art in the world and a prominent symbol of ancient Egypt.
The Art Institute of Chicago contains a Book of the Dead scroll, an Ancient Egyptian papyrus depicting funerary spells. This scroll of funerary spells serves as a protection from "Second Death". In ancient Egyptian spiritual practice, the term "Second Death" refers to the phenomenon of the body permanently separating from the soul. The Book of the Dead scroll is made of papyrus, a material made of reed plants cultivated on marshy plantations, which is then cut into strips and left to dry in horizontal and vertical rows. The scroll also contains pigments used to inscribe the funerary spells.

Ancient Egyptian afterlife beliefs were centered around a variety of complex rituals that were influenced by many aspects of Egyptian culture. Religion was a major contributor, since it was an important social practice that bound all Egyptians together. For instance, many of the Egyptian gods played roles in guiding the souls of the dead through the afterlife. With the evolution of writing, religious ideals were recorded and quickly spread throughout the Egyptian community. The solidification and commencement of these doctrines were formed in the creation of afterlife texts which illustrated and explained what the dead would need to know in order to complete the journey safely.




















