
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the boron group it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride.

Kernite, also known as rasorite, is a hydrated sodium borate hydroxide mineral with formula Na
2B
4O
6(OH)
2·3H
2O. It is a colorless to white mineral crystallizing in the monoclinic crystal system typically occurring as prismatic to acicular crystals or granular masses. It is relatively soft with Mohs hardness of 2.5 to 3 and light with a specific gravity of 1.91. It exhibits perfect cleavage and a brittle fracture.

Boric acid, more specifically orthoboric acid, is a compound of boron, oxygen, and hydrogen with formula B(OH)3. It may also be called hydrogen borate, boron hydroxide or boracic acid. It is usually encountered as colorless crystals or a white powder, that dissolves in water, and occurs in nature as the mineral sassolite. It is a weak acid that yields various borate anions and salts, and can react with alcohols to form borate esters.
A borate is any of a range of boron oxyanions, anions containing boron and oxygen, such as orthoborate BO3−3, metaborate BO−2, or tetraborate B4O2−7; or any salt of such anions, such as sodium metaborate, Na+[BO2]− and borax (Na+)2[B4O7]2−. The name also refers to esters of such anions, such as trimethyl borate B(OCH3)3.

Borax is a salt, a hydrated or anhydrous borate of sodium, with the chemical formula Na2H20B4O17. It is a colorless crystalline solid, that dissolves in water to make a basic solution.

Boron is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kern County, California, United States. Boron is 15 miles (24 km) southwest of Red Rock Mountain at an elevation of 2,467 feet (752 m). The population was 2,086 at the 2020 census, up from 2,025 at the 2000 census. Boron is named after the element boron and is the site of the world's largest source of the boron compound boric acid.

The boron group are the chemical elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron (B), aluminium (Al), gallium (Ga), indium (In), thallium (Tl), and nihonium (Nh). The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three valence electrons. These elements have also been referred to as the triels.

Ulexite (NaCaB5O6(OH)6·5H2O, hydrated sodium calcium borate hydroxide), sometimes known as TV rock or Television stone, is a mineral occurring in silky white rounded crystalline masses or in parallel fibers. The natural fibers of ulexite conduct light along their long axes, by internal reflection. Ulexite was named for the German chemist Georg Ludwig Ulex (1811–1883) who first discovered it.
Boron deficiency is a common deficiency of the micronutrient boron in plants. It is the most widespread micronutrient deficiency around the world and causes large losses in crop production and crop quality. Boron deficiency affects vegetative and reproductive growth of plants, resulting in inhibition of cell expansion, death of meristem, and reduced fertility.
A period 2 element is one of the chemical elements in the second row of the periodic table of the chemical elements. The periodic table is laid out in rows to illustrate recurring (periodic) trends in the chemical behavior of the elements as their atomic number increases; a new row is started when chemical behavior begins to repeat, creating columns of elements with similar properties.

Colemanite (Ca2B6O11·5H2O) or (CaB3O4(OH)3·H2O) is a borate mineral found in evaporite deposits of alkaline lacustrine environments. Colemanite is a secondary mineral that forms by alteration of borax and ulexite.
Sodium borate is a generic name for any salt of sodium with an anion consisting of boron and oxygen, and possibly hydrogen, or any hydrate thereof. It can be seen as a hydrated sodium salt of the appropriate boroxy acid, although the latter may not be a stable compound.

In chemistry, tetraborate or pyroborate is an anion with formula B4O2−7; or a salt containing that anion, such as sodium tetraborate, Na2B4O7. It is one of the boron oxoacids, that is, a borate.
Sodium perborate is chemical compound whose chemical formula may be written NaH2BO4, Na2H4B2O8, or, more properly, [Na+]2[B2O4(OH)4]2−. Its name is sometimes abbreviated as PBS.
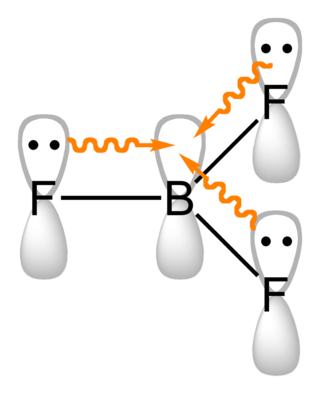
Boron compounds are compounds containing the element boron. In the most familiar compounds, boron has the formal oxidation state +3. These include oxides, sulfides, nitrides, and halides.

Tincalconite is a hydrous sodium borate mineral closely related to borax, and is a secondary mineral that forms as a dehydration product of borax. Its formula is Na2B4O7·5H2O or Na2[B4O5(OH)4]·3H2O.

Disodium octaborate is a borate of sodium, a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen — a salt with elemental formula Na2B8O13 or (Na+)2[B8O13]2−, also written as Na2O·4B2O3. It is a colorless crystalline solid, soluble in water.
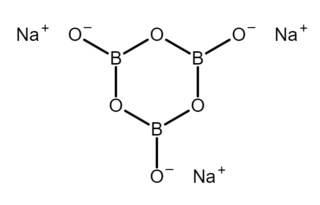
Sodium metaborate is a chemical compound of sodium, boron, and oxygen with formula NaBO2. However, the metaborate ion is trimeric in the anhydrous solid, therefore a more correct formula is Na3B3O6 or (Na+)3[B3O6]3−. The formula can be written also as Na2O·B2O3 to highlight the relation to the main oxides of sodium and boron. The name is also applied to several hydrates whose formulas can be written NaBO2·nH2O for various values of n.

Borax Lake is a 10-acre (4.0 ha) alkaline lake in the Alvord Desert of southeastern Oregon in the United States. The lake is fed by geothermal springs 100 feet (30 m) below the surface that range in temperature from 104 to 300 °F. Surface water temperatures usually range from 61 to 100 °F but occasionally go higher. The springs lie along the Steens fault zone, which runs north–south through the Alvord Valley east of Steens Mountain.

The Rio Tinto Boron Mine in Boron, California is California's largest open-pit mine and the largest borax mine in the world, producing nearly half the world's borates. Ore reserves are sufficient for production through at least 2050. It is operated by the Borax division of the Rio Tinto Group.














