Boreal, northern, of the north. Derived from the name of the god of the north wind from Ancient Greek civilisation, Boreas. It may also refer to:
Boreal, northern, of the north. Derived from the name of the god of the north wind from Ancient Greek civilisation, Boreas. It may also refer to:

A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds in situ. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020 found that forests covered 4.06 billion hectares, or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020.

Taiga or tayga, also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga or boreal forest is the world's largest land biome. In North America, it covers most of inland Canada, Alaska, and parts of the northern contiguous United States. In Eurasia, it covers most of Sweden, Finland, much of Russia from Karelia in the west to the Pacific Ocean, much of Norway and Estonia, some of the Scottish Highlands, some lowland/coastal areas of Iceland, and areas of northern Kazakhstan, northern Mongolia, and northern Japan.
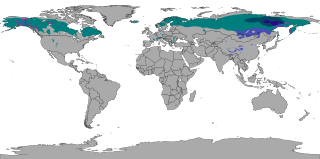
The subarctic climate is a continental climate with long, cold winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Like other Class D climates, they are rare in the Southern Hemisphere, only found at some isolated highland elevations. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification Dfc, Dwc, Dsc, Dfd, Dwd and Dsd.

The Adirondack Mountains are a massif of mountains in Northeastern New York which form a circular dome approximately 160 miles (260 km) wide and covering about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The region contains more than 100 peaks, including Mount Marcy, which is the highest point in New York at 5,344 feet (1,629 m). The Adirondack High Peaks, a traditional list of 46 peaks over 4,000 feet (1,200 m), are popular hiking destinations. There are over 200 named lakes with the number of smaller lakes, ponds, and other bodies of water reaching over 3,000. Among the named lakes around the mountains are Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds. The region has over 1,200 miles (1,900 km) of river.

The Palearctic or Palaearctic is a biogeographic realm of the Earth, the largest of eight. Confined almost entirely to the Eastern Hemisphere, it stretches across all of Eurasia north of the foothills of the Himalayas, and North Africa.
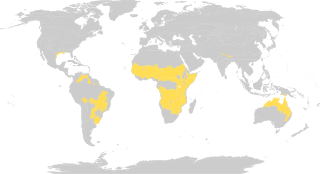
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and tropical latitudes. Tropical grasslands are mainly found between 5 degrees and 20 degrees in both North and south of the Equator.

An old-growth forest or primary forest is a forest that has developed over a long period of time without disturbance. Due to this, old-growth forests exhibit unique ecological features. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations defines primary forests as naturally regenerated forests of native tree species where there are no clearly visible indications of human activity and the ecological processes are not significantly disturbed. One-third of the world's forests are primary forests. Old-growth features include diverse tree-related structures that provide diverse wildlife habitats that increases the biodiversity of the forested ecosystem. Virgin or first-growth forests are old-growth forests that have never been logged. The concept of diverse tree structure includes multi-layered canopies and canopy gaps, greatly varying tree heights and diameters, and diverse tree species and classes and sizes of woody debris.

Hemiboreal means halfway between the temperate and subarctic zones. The term is most frequently used in the context of climates and ecosystems.

The Laurentian Mixed Forest Province, also known as the North Woods, is a forested ecoregion in eastern North America. Among others, this terminology has been adopted by the Minnesota Department of Natural Resources. Similar, though not necessarily entirely identical regions, are identified by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as Northern Lakes and Forests, and by the World Wildlife Fund by regions such as the Western Great Lakes forests and Eastern forest-boreal transition.

A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest terrestrial biome, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers about 33%. These forests cover both hemispheres at latitudes ranging from 25 to 50 degrees, wrapping the planet in a belt similar to that of the boreal forest. Due to its large size spanning several continents, there are several main types: deciduous, coniferous, mixed forest, and rainforest.

The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region, and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region.

Temperate deciduous or temperate broad-leaf forests are a variety of temperate forest 'dominated' by deciduous trees that lose their leaves each winter. They represent one of Earth's major biomes, making up 9.69% of global land area. These forests are found in areas with distinct seasonal variation that cycle through warm, moist summers, cold winters, and moderate fall and spring seasons. They are most commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere, with particularly large regions in eastern North America, East Asia, and a large portion of Europe, though smaller regions of temperate deciduous forests are also located in South America. Examples of trees typically growing in the Northern Hemisphere's deciduous forests include oak, maple, basswood, beech and elm, while in the Southern Hemisphere, trees of the genus Nothofagus dominate this type of forest. Temperate deciduous forests provide several unique ecosystem services, including habitats for diverse wildlife, and they face a set of natural and human-induced disturbances that regularly alter their structure.

A boreal ecosystem is an ecosystem with a subarctic climate located in the Northern Hemisphere, approximately between 50° and 70°N latitude. These ecosystems are commonly known as taiga and are located in parts of North America, Europe, and Asia. The ecosystems that lie immediately to the south of boreal zones are often called hemiboreal. There are a variety of processes and species that occur in these areas as well.

Hemispherical photography, also known as canopy photography, is a technique to estimate solar radiation and characterize plant canopy geometry using photographs taken looking upward through an extreme wide-angle lens or a fisheye lens. Typically, the viewing angle approaches or equals 180-degrees, such that all sky directions are simultaneously visible. The resulting photographs record the geometry of visible sky, or conversely the geometry of sky obstruction by plant canopies or other near-ground features. This geometry can be measured precisely and used to calculate solar radiation transmitted through plant canopies, as well as to estimate aspects of canopy structure such as leaf area index. Detailed treatments of field and analytical methodology have been provided by Paul Rich and Robert Pearcy (1989).

Canada's boreal forest is a vast region comprising about one third of the circumpolar boreal forest that rings the Northern Hemisphere, mostly north of the 50th parallel. Other countries with boreal forest include Russia, which contains the majority; the United States in its northernmost state of Alaska; and the Scandinavian or Northern European countries. In Europe, the entire boreal forest is referred to as taiga, not just the northern fringe where it thins out near the tree line. The boreal region in Canada covers almost 60% of the country's land area. The Canadian boreal region spans the landscape from the most easterly part of the province of Newfoundland and Labrador to the border between the far northern Yukon and Alaska. The area is dominated by coniferous forests, particularly spruce, interspersed with vast wetlands, mostly bogs and fens. The boreal region of Canada includes eight ecozones. While the biodiversity of regions varies, each ecozone has characteristic native flora and fauna.

The wildlife of Canada or biodiversity of Canada consist of over 80,000 classified species, and an equal number thought yet to be recognized. Known fauna and flora have been identified from five kingdoms: protozoa represent approximately 1% of recorded species; chromist ; fungis ; plants ; and animals. Insects account for nearly 70 percent of documented animal species in Canada. More than 300 species are found exclusively in Canada.

Paludification is the most common process by which peatlands in the boreal zone are formed.

Changing climate conditions are amplified in polar regions and northern high-latitude areas are projected to warm at twice the rate of the global average. These modifications result in ecosystem interactions and feedbacks that can augment or mitigate climatic changes. These interactions may have been important through the large climate fluctuations since the glacial period. Therefore it is useful to review the past dynamics of vegetation and climate to place recent observed changes in the Arctic into context. This article focuses on northern Alaska where there has been much research on this theme.

The North American inland temperate rainforest is a 7 million hectare disjunct temperate rainforest spreading over parts of British Columbia in Canada as well as Washington, Idaho and Montana on the US side. Its patches are located on the windward slopes of the Rocky Mountains and the Columbia Mountains, extending roughly over 1000km from 54° North to 45° North. It is one of the largest inland temperate rainforests in the world.
Jill L. Bubier is a professor emerita of environmental science at Mount Holyoke College (MHC). Her research examines how Northern ecosystems respond to climate change.