Related Research Articles
The 49th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 49° north of Earth's equator. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
There are 45 streams named Willow Creek in the U.S. state of Montana.

The Canada–United States border is the longest international border in the world between two countries. The terrestrial boundary is 8,891 kilometers (5,525 mi) long. The land border has two sections: Canada's border with the U.S. to its south, and with the U.S. state of Alaska to its west. The bi-national International Boundary Commission deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the International Joint Commission deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies currently responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).

Carway is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within Cardston County. It is a port of entry into the U.S. state of Montana opposite of Port of Piegan. Just on the other side of the border is the Blackfeet Indian Reservation in Glacier County, Montana.

Coutts is a village in Alberta and a port of entry into the U.S. state of Montana. It is one of the busiest ports of entry on the Canada–United States border in western Canada. It connects Highway 4 to Interstate 15, an important trade route between Alberta, American states along I-15, and Mexico.
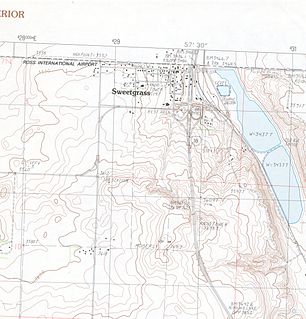
Sweet Grass is a census-designated place and unincorporated community in Toole County, Montana, United States, on the Canada–US border. It is the northern terminus of Interstate 15, an important route connecting western Canada, the western United States, and Mexico.
There are several lakes named Mud Lake within the Canadian province of Alberta.
Petitot is a river in northern Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. It is a tributary of the Liard River.

Waterton Lake is a mountain lake in southern Alberta, Canada and northern Montana, United States. The lake is composed of two bodies of water, connected by a shallow channel known locally as the Bosporus. The two parts are referred to as Middle Waterton Lake, and Upper Waterton Lake, the latter of which is divided by the Canada–United States border with Canada containing about two thirds of the lake while the Southern third falls in the United States. The Boundary Commission Trail ends at the lake as the last border marker was placed there on 8 August, 1874. The United States Geological Survey gives the geocoordinates of 49°03′00″N113°54′03″W for Upper Waterton Lake. Lower Waterton Lake is north of Middle Waterton Lake and is separated by a channel known as the Dardanelles.

Del Bonita is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within Cardston County. It is located approximately 49 km (30 mi) south of Magrath at the junction of Highway 62 and Highway 501. Due to its location near the Canada–United States border, it serves as a port of entry into the U.S. state of Montana at the nearby Del Bonita Border Crossing which is located 3 km (1.9 mi) to the south. Del Bonita is a name derived from Spanish meaning "of the pretty".

Kimball is a hamlet in southern Alberta, Canada within Cardston County. It is located on Highway 501, approximately 16 kilometres (9.9 mi) southeast of Cardston between the St. Mary River and the Milk River Ridge. The community is named after the Mormon ward which was named after the descendants of Heber C Kimball.

The Ashnola River is a tributary of the Similkameen River, rising in the northeastern part of the North Cascades in Washington, United States, and flowing north into British Columbia, Canada, to join the Similkameen River about halfway along that river's course between the towns of Princeton and Keremeos. The river crosses the international boundary at 49°00′00″N120°19′37″W and transits Cathedral Provincial Park. It has one main tributary, Ewart Creek, which is about 25 kilometres (16 mi) long and begins virtually at the border and is entirely within Cathedral Park.
The extreme points of British Columbia are four in number:
Beaver Creek is a stream in Alberta, Canada. It is a tributary of the Oldman River.
Drywood Creek is a stream in Alberta, Canada.
References
- ↑ "Boundary Creek". Geographical Names Data Base. Natural Resources Canada.
- ↑ U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Boundary Creek
- ↑ Place-names of Alberta. Ottawa: Geographic Board of Canada. 1928. p. 23.
Coordinates: 49°00′00″N113°21′24″W / 49°N 113.3566667°W