Brabham is the common name for Motor Racing Developments Ltd., a British racing car manufacturer and Formula One racing team. Founded in 1960 by Australian driver Jack Brabham and British-Australian designer Ron Tauranac, the team won four Drivers' and two Constructors' World Championships in its 30-year Formula One history. Jack Brabham's 1966 FIA Drivers' Championship remains the only such achievement using a car bearing the driver's own name.

Peter Westbury was a British racing driver from England. He participated in two World Championship Formula One Grands Prix, scoring no championship points. In 1969 he raced a Formula 2 Brabham-Cosworth, driving in his first Grand Prix in the 1969 German Grand Prix. He finished ninth on the road, fifth in the F2 class. The following year he failed to qualify for the 1970 United States Grand Prix driving a works BRM, after an engine failure.

Silvio Moser was a racing driver from Switzerland.

Formula 5000 was an open wheel, single seater auto-racing formula that ran in different series in various regions around the world from 1968 to 1982. It was originally intended as a low-cost series aimed at open-wheel racing cars that no longer fit into any particular formula. The '5000' denomination comes from the maximum 5.0 litre engine capacity allowed in the cars, although many cars ran with smaller engines. Manufacturers included McLaren, Eagle, March, Lola, Lotus, Elfin, Matich and Chevron.

The Lotus 48 was a Formula 2 racing car designed by Colin Chapman and Maurice Phillippe and powered by a 1,600 cc (98 cu in) Cosworth FVA engine. It won three races in the hands of Jim Clark but was generally uncompetitive against rival machinery. Ultimately, its main claim to fame is as the car in which Clark was killed at Hockenheim on 7 April 1968.

The Tasman Series was a motor racing competition held annually from 1964 to 1975 over a series of races in New Zealand and Australia. It was named after the Tasman Sea which lies between the two countries. The Tasman Series races were held in January through to late February or early March of each year, during the Formula One off season, taking advantage of winter in the Northern Hemisphere to attract many top drivers to summer in the south. The Tasman Cup was the permanent trophy awarded to the winning driver.

The Brabham BT49 is a Formula One racing car designed by South African Gordon Murray for the British Brabham team. The BT49 competed in the 1979 to 1982 Formula One World Championships and was used by Brazilian driver Nelson Piquet to win his first World Championship in 1981.

The Repco Brabham BT24 was a Formula One racing car design. It was one of three cars used by the Brabham racing team during their championship-winning 1967 Formula One season. Only three BT24 chassis were ever raced.

The Lotus 59 is a racing car built by Lotus Components Ltd. for the 1969 and 1970 seasons of Formula 2, Formula 3, Formula Ford and Formula B.

The Brabham BT23 was a formula racing car built by Brabham in 1967.

The Brabham BT36 was an open-wheel Formula 2 race car, designed by Ron Tauranac, and developed and built by British racing team and constructor, Brabham, for the 1971 European Formula Two Championship. Its best result that season was a 2nd-place finish in the championship for Argentine Carlos Reutemann, despite only winning one race, taking one pole position. His consistency and pace made up for this, scoring 6 podium finishes, and finishing the season with 40 points. The Brabham BT36 was constructed out of a complex tubular space frame, and was powered by the naturally-aspirated 1.6 L (98 cu in) Ford-FVA Cosworth four-cylinder engine, which produced 220 hp (160 kW), and drove the rear wheels through a 5-speed Hewland F.T.200 manual transmission.

The Matra Company's racing team, under the names of Matra Sports, Equipe Matra Elf and Equipe Matra Sports, was formed in 1965 and based at Champagne-sur-Seine (1965–1967), Romorantin-Lanthenay (1967–1969) and Vélizy-Villacoublay (1969–1979). In 1979 the team was taken over by Peugeot and renamed as Automobiles Talbot.

The Brabham BT21 was an open-wheel formula racing car, designed, developed, and built by Brabham in large numbers in 1966 and delivered to private individuals; 110 vehicles were manufactured.

The Repco Brabham BT26 was a Formula One racing car design. A development of the previous BT24, its Repco engines were unreliable, but following a switch to Cosworth DFV engines it scored two World Championship Grand Prix wins and finished runner up in the 1969 World Constructors' Championship.

The Brabham BT2 is an open-wheel racing car made by Brabham in 1962.

The Brabham BT18 was an open-wheel formula racing, designed, developed, and built by British constructor Brabham, for both Formula 2 and Formula 3 racing categories. Powered by a Honda engine, it won 11 out of 12 races in 1966.

The Brabham BT14 was an open-wheel mid-engined formula racing car, designed, developed and built by British manufacturer and constructor Brabham, in 1965. A total of 10 models were produced. It was specifically constructed to compete in Formula Libre racing. It competed in motor racing between 1965 and 1968; winning a total of 10 races, scoring 22 podium finishes, and clinching 4 pole positions. It also contested the 1967 European F2 Championship season, competing in 7 races, but with no success; scoring no wins, pole positions, podium finishes, or scoring any points. It was powered by a naturally-aspirated 1.6 L (98 cu in) Ford twin-cam four-cylinder engine, which droves the rear wheels through a conventional 4-speed manual transmission.

The McLaren M4A was an open-wheel racing car designed by Robin Herd and built by British Formula One team McLaren to compete in the European Formula Two Championship.
The Hart 420R and the Hart 420S are four-stroke, naturally aspirated, 2.0 L (120 cu in), four-cylinder engine, designed, developed and made by Hart Racing Engines, and tuned by Brian Hart, for Formula 2 and sports prototype racing applications, between 1975 and 1980. The 420R is based on the Cosworth FVA, while the 420S is based on the Cosworth BDG, with the design knowledge being taken and used on both. The Hart 420R F2 engine owes much to the Cosworth BDA series, being essentially an aluminium-block derivative using similar heads. Both the 420R and 420S were naturally-aspirated, 2-litre, 16-valve DOHC, fuel-injected, straight-four engines. Displacement is 1,994 cc (121.7 cu in), and maximum power output is between 290–305 hp at 9,500 rpm, with the motor being failsafe to just over 10,000 rpm. The bore is 93.5 mm (3.68 in), and the stroke is 72.6 mm (2.86 in).
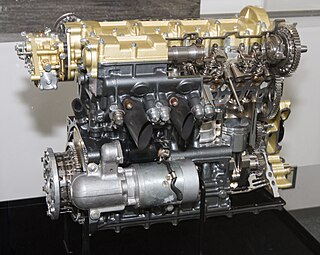
The Honda RA300E and Honda RA302E are 1 litre four-stroke, four-cylinder, naturally-aspirated, racing engines, designed, developed and built by Honda, for Formula Two racing, in 1965.


















