
Fahrenheit 451 is a dystopian novel by American writer Ray Bradbury, first published in 1953. Often regarded as one of his best works, the novel presents a future American society where books are outlawed and "firemen" burn any that are found. The book's tagline explains the title: "Fahrenheit 451 – the temperature at which book paper catches fire, and burns..." The lead character, Guy Montag, is a fireman who becomes disillusioned with his role of censoring literature and destroying knowledge, eventually quitting his job and committing himself to the preservation of literary and cultural writings.

Ray Douglas Bradbury was an American author and screenwriter. He worked in a variety of genres, including fantasy, science fiction, horror, and mystery fiction.

Bradbury is a city in the San Gabriel Valley region of Los Angeles County, California, United States. It is located in the foothills of the San Gabriel Mountains below Angeles National Forest. Bradbury is bordered by the city of Monrovia to the west and south, and Duarte to the south and east. The population was 1,048 at the 2010 census, up from 855 at the 2000 census. The city has three distinct areas—the Bradbury Estates, which is a gated community consisting of 5-acre (20,000 m2) minimum estates; Woodlyn Lane, which is also a gated community with minimum 2-acre (8,100 m2) lots; and the balance of the city, which is not gated, which has lots generally ranging in size from 7,500 square feet (700 m2) to 1-acre (4,000 m2). A significant portion of the properties in Bradbury Estates and Woodlyn Lane are zoned for horses, and several horse ranches still exist within these communities today.

Airds is a suburb of Sydney, in the state of New South Wales, Australia. Airds is 56 kilometres south-west of the Sydney central business district, in the local government area of the City of Campbelltown and is part of the Macarthur region.

Bradbury is a village in County Durham, England. It is situated between Sedgefield and Newton Aycliffe, close to the A1(M) and A689, and is approximately 16 km (9.9 mi) from Middlesbrough. Bradbury is a small agricultural village. The moorland around it is of glacial origin.
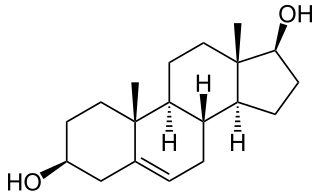
Androstenediol, or 5-androstenediol, also known as androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol, is an endogenous weak androgen and estrogen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenedione (androst-4-ene-3,17-dione).
The Golden Mileis the name given to the stretch of Dublin Road, Great Victoria Street, Bradbury Place and University Road between the City Hall and the university area in Belfast, Northern Ireland. Both the Crown Liquor Saloon and the Grand Opera House are on this stretch of road, as are a large number of pubs, bars and restaurants.
Maghaberry or Magaberry is a village and townland in County Antrim, Northern Ireland. It is 9 kilometres (5.6 mi) west of Lisburn and 4 kilometres (2.5 mi) north of Moira. In the 2001 Census it had a population of 1,690 people. It is one of the biggest villages within the Lisburn City Council area.

The River Skerne is a tributary of the River Tees. It flows through County Durham in England.

Queen Alexandra College (QAC) is an independent specialist college of further education based in Harborne, Birmingham for students above the age of sixteen with visual impairment, autism and other disabilities. Students can develop their academic, social, employment and independent skills through individualised programmes. QAC also offers many leisure activities. Its registered charity number 1065794.

Cockermouth Castle is in the town of Cockermouth in Cumbria on a site by the junction of the Rivers Cocker and Derwent. It is a grade I listed building and a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

The KiSS1-derived peptide receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor which binds the peptide hormone kisspeptin (metastin). Kisspeptin is encoded by the metastasis suppressor gene KISS1, which is expressed in a variety of endocrine and gonadal tissues. Activation of the kisspeptin receptor is linked to the phospholipase C and inositol trisphosphate second messenger cascades inside the cell.

Potassium intermediate/small conductance calcium-activated channel, subfamily N, member 4, also known as KCNN4, is a human gene encoding the KCa3.1 protein.
Basal cell adhesion molecule, also known as Lutheran antigen, is a plasma membrane glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the BCAM gene. BCAM has also recently been designated CD239.
In geometry, 1k2 polytope is a uniform polytope in n-dimensions constructed from the En Coxeter group. The family was named by their Coxeter symbol 1k2 by its bifurcating Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with a single ring on the end of the 1-node sequence. It can be named by an extended Schläfli symbol {3,3k,2}.

Durham Priory was a Benedictine priory associated with Durham Cathedral, in Durham in the north-east of England. Its head was the Prior of Durham. It was founded in 1083 and when dissolved in 1540 was succeeded by a chapter of secular canons led by a dean.

Bradbury Motor Cycles was a British motorcycle manufacturer based in Oldham, England and established in 1902. Originally involved in the manufacture of machine tools, sewing machines and cycles, their first motorcycles were bicycles with clip-on Minerva engines. The Bradbury factory went on to develop and produce a range of single-cylinder motorcycle, V-twins and horizontally opposed twins. The 1912 Bradbury motorcycles were one of the earliest with variable gearing. Although the factory survived the First World War it closed in 1924.

The ciliates are a group of protozoans characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation.

The Scottish Centre for Regenerative Medicine (SCRM) is a stem cell research centre at the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, dedicated to the study and development of new regenerative treatments for human diseases. The £54 million facility is part of a total £600 million joint investment in stem cell biology and medicine by the Scottish Government and the University of Edinburgh. Designed by Sheppard Robson, the SCRM is part of the BioQuarter cluster at Little France.
Garrett Bradbury is an American football center for the Minnesota Vikings of the National Football League (NFL). He played college football at NC State and was selected by the Vikings in the first round of the 2019 NFL Draft.


















