Related Research Articles

The unified modeling language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
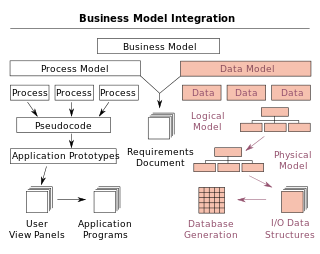
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
A modeling language is any artificial language that can be used to express data, information or knowledge or systems in a structure that is defined by a consistent set of rules. The rules are used for interpretation of the meaning of components in the structure of a programming language.

Computer-aided software engineering (CASE) is a domain of software tools used to design and implement applications. CASE tools are similar to and are partly inspired by computer-aided design (CAD) tools used for designing hardware products. CASE tools are intended to help develop high-quality, defect-free, and maintainable software. CASE software was often associated with methods for the development of information systems together with automated tools that could be used in the software development process.
A functional software architecture (FSA) is an architectural model that identifies enterprise functions, interactions and corresponding IT needs. These functions can be used as a reference by different domain experts to develop IT-systems as part of a co-operative information-driven enterprise. In this way, both software engineers and enterprise architects can create an information-driven, integrated organizational environment.
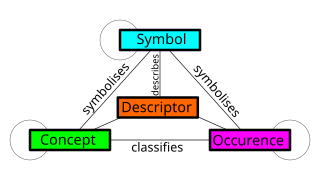
A metamodel is a model of a model, and metamodeling is the process of generating such metamodels. Thus metamodeling or meta-modeling is the analysis, construction, and development of the frames, rules, constraints, models, and theories applicable and useful for modeling a predefined class of problems. As its name implies, this concept applies the notions of meta- and modeling in software engineering and systems engineering. Metamodels are of many types and have diverse applications.
Houman Younessi was a Kurdish-American educator, practitioner, consultant and investigator in informatics, large scale software development processes, computer science, decision science, molecular biology and functional genomics. He was a research professor at University of Connecticut, and was previously the head of faculty and professor at Hartford Graduate Campus of Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute in Hartford, Connecticut and prior to that, a member of the faculty at Swinburne University of Technology in Hawthorn, Victoria, Australia where he attained tenure in 1997.
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality.
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to software engineering.
Model-driven engineering (MDE) is a software development methodology that focuses on creating and exploiting domain models, which are conceptual models of all the topics related to a specific problem. Hence, it highlights and aims at abstract representations of the knowledge and activities that govern a particular application domain, rather than the computing concepts.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.
Service-oriented modeling is the discipline of modeling business and software systems, for the purpose of designing and specifying service-oriented business systems within a variety of architectural styles and paradigms, such as application architecture, service-oriented architecture, microservices, and cloud computing.
Enterprise engineering is the body of knowledge, principles, and practices used to design all or part of an enterprise. An enterprise is a complex socio-technical system that comprises people, information, and technology that interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. One definition is: "an enterprise life-cycle oriented discipline for the identification, design, and implementation of enterprises and their continuous evolution", supported by enterprise modelling. The discipline examines each aspect of the enterprise, including business processes, information flows, material flows, and organizational structure. Enterprise engineering may focus on the design of the enterprise as a whole, or on the design and integration of certain business components.
Colette Rolland is a French computer scientist and Professor of Computer Science in the department of Mathematics and Informatics at the University of Paris 1 Pantheon-Sorbonne. She is a leading researcher in the area of information and knowledge systems, known for her work on meta-modeling, particularly goal modelling and situational method engineering.
Jacobus Nicolaas (Sjaak) Brinkkemper is a Dutch computer scientist, and Full Professor of organisation and information at the Department of Information and Computing Sciences of Utrecht University.

Donald G. Firesmith is an American software engineer, consultant, and trainer at the Software Engineering Institute.
Subject-oriented business process management (S-BPM) is a communication based view on actors, which compose a business process orchestration or choreography. The modeling paradigm uses five symbols to model any process and allows direct transformation into executable form.

Juan Pavón is a Spanish computer scientist, full professor of the Complutense University of Madrid (UCM). He is a pioneer researcher in the field of Software Agents, co-creator of the FIPA MESSAGE and INGENIAS methodologies, and founder and director of the research group GRASIA: GRoup of Agent-based, Social and Interdisciplinary Applications at UCM. He is known for his work in the field of Artificial Intelligence, specifically in agent-oriented software engineering. He has been often cited by mainstream media, as a reference in Artificial Intelligence.

INGENIAS is an open-source software framework for the analysis, design and implementation of multi-agent systems (MAS).
John Mylopoulos is a Greek-Canadian computer scientist, Professor at the University of Toronto, Canada, and at the University of Trento, Italy. He is known for his work in the field of conceptual modeling, specifically the development an agent-oriented software development methodology. called TROPOS.
References
- 1 2 3 4 Home Page Archived 24 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine of Brian Henderson-Sellers. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ↑ Enterprise Modelling and Information Systems Architectures: An International Journal Archived 22 June 2007 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved 26 May 2009.
- ↑ Awards and Appointments - November 2001 Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ↑ Object-oriented Process, Environment and Notation. Retrieved 27 May 2009.
- ↑ Brian Henderson-Sellers List of publications from the DBLP Bibliography Server. Retrieved 27 May 2009.