
Balaguer is the capital of the comarca of Noguera, in the province of Lleida, Catalonia, Spain. It is located by the river Segre, a tributary to the Ebre. The municipality includes an exclave to the east.
A bridge is a structure built so that a transportation route can cross above an obstacle.

Operation Plunder was a military operation to cross the Rhine on the night of 23 March 1945, launched by the 21st Army Group under Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery. The crossing of the river was at Rees, Wesel, and south of the river Lippe by the British Second Army under Lieutenant General Sir Miles Dempsey, and the United States Ninth Army under Lieutenant General William H. Simpson.
A bridgehead is the strategically important area of ground around the end of a bridge or other place of possible crossing over a body of water which at time of conflict is sought to be defended or taken over by the belligerent forces.
The Second Battle of Rappahannock Station took place on November 7, 1863, near the village of Rappahannock Station, on the Orange and Alexandria Railroad.
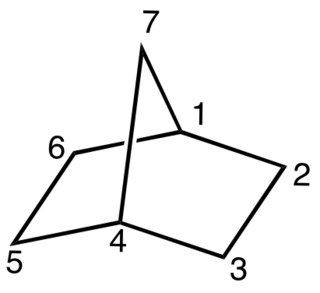
A bicyclic molecule is a molecule that features two joined rings. Bicyclic structures occur widely, for example in many biologically important molecules like α-thujene and camphor. A bicyclic compound can be carbocyclic, or heterocyclic, like DABCO. Moreover, the two rings can both be aliphatic, or can be aromatic, or a combination of aliphatic and aromatic.
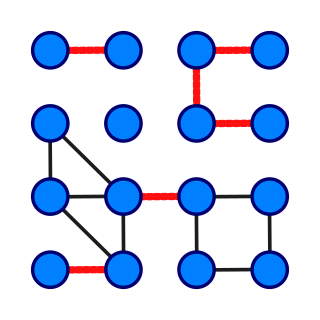
In graph theory, a bridge, isthmus, cut-edge, or cut arc is an edge of a graph whose deletion increases its number of connected components. Equivalently, an edge is a bridge if and only if it is not contained in any cycle. For a connected graph, a bridge can uniquely determine a cut. A graph is said to be bridgeless or isthmus-free if it contains no bridges.

The Ludendorff Bridge was in early March 1945 a critical remaining bridge across the river Rhine in Germany when it was captured during the Battle of Remagen by United States Army forces during the closing weeks of World War II. Built in World War I to help deliver reinforcements and supplies to the German troops on the Western Front, it connected Remagen on the west bank and the village of Erpel on the eastern side between two hills flanking the river.

Bredt's rule is an empirical observation in organic chemistry that states that a double bond cannot be placed at the bridgehead of a bridged ring system, unless the rings are large enough. The rule is named after Julius Bredt, who first discussed it in 1902 and codified it in 1924. It primarily relates to bridgeheads with carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen double bonds.

Operation Lumberjack was a military operation with the goal of capturing the west bank of the Rhine River and seizing key German cities, near the end of World War II. The First United States Army launched the operation in March 1945 to capture strategic cities in Nazi Germany and to give the Allies a foothold along the Rhine.

The Battle of the Argenta Gap was an engagement which formed part of the Allied spring 1945 offensive during the Italian Campaign in the final stages of the Second World War. It took place in northern Italy from 12–19 April 1945 between troops of British V Corps commanded by Lieutenant-General Charles Keightley and German units of LXXVI Panzer Corps commanded by Lieutenant General Gerhard von Schwerin.

The Battle of Remagen during the Allied invasion of Germany resulted in the unexpected capture of the Ludendorff Bridge over the Rhine. After capturing the Siegfried Line, the 9th Armored Division of the U.S. First Army had advanced unexpectedly quickly towards the Rhine. They were very surprised to see one of the last bridges across the Rhine still standing. The Germans had wired the bridge with about 2,800 kilograms (6,200 lb) of demolition charges. When they tried to blow it up, only a portion of the explosives detonated. U.S. forces captured the bridge and rapidly expanded their first bridgehead across the Rhine, two weeks before Field Marshal Bernard Montgomery's meticulously planned Operation Plunder. The GIs' actions prevented the Germans from regrouping east of the Rhine and consolidating their positions.

The Battle of Frankfurt was a four-day struggle for control of Frankfurt am Main during World War II. The 5th Infantry Division conducted the main attack while the 6th Armored Division provided support. The city was defended by the LXXX Corps of the Seventh Army.
BridgeHead Software is a group of computer software and services companies mainly serving the healthcare sector. The parent company BridgeHead Software Limited is unquoted and registered in London, England. The group is headquartered in Ashtead, Surrey in the UK.

Pontecorvo is a town and comune in the province of Frosinone, Lazio, Italy. Its population is c. 13,200.

The Battle of Geel, also known as the Battle of the Geel Bridgehead, was a major battle between British and German troops in Belgium during the Second World War. It occurred between 8–23 September 1944, in and around the Flemish town of Geel (Gheel), and was one of the largest and bloodiest battles to occur during the Liberation of Belgium.

The Balaguer Offensive was an offensive carried out by the Spanish Republican Army around Balaguer during the Spanish Civil War. The offensive consisted in a series of counterattacks in the spring and summer of 1938 after the disastrous Aragon Offensive. The offensive was a failure for the Spanish Republic and many lives and military material were wasted.
Operation Minden was an offensive undertaken by United Nations Command (UN) forces during the Korean War between 8–12 September 1951, as part of a general advance to extend the Wyoming Line, the UN Main line of resistance. Operation Minden was the precursor to the much larger Operation Commando, which established the Jamestown Line.

The Battle of Praga took place on October 25, 1705 near the town of Warsaw, Poland during the fifth year of the Great Northern War. The Swedish army of more than 270 men assisted by approximately 140 soldiers from the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth under the command of Valentin Dahldorf defeated a combined Polish–Saxon–Russian force of about 5,000 men under Michał Serwacy Wiśniowiecki and Aleksandr Menshikov.

Operation Abirey-Halev or Operation Abirey-lev, also known as Operation Stouthearted Men, code-named Operation Gazelle, is an Israeli operation that took place in the center of Suez Canal on 15–23 October 1973 during the Yom Kippur War.













