A fortification is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin fortis ("strong") and facere.

A sapper, also called a combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing field defenses, and road and airfield construction and repair.

A beachhead is a temporary line created when a military unit reaches a landing beach by sea and begins to defend the area as other reinforcements arrive. Once a large enough unit is assembled, the invading force can begin advancing inland. The term is sometimes used interchangeably with bridgehead and lodgement. Beachheads were important in many military actions; examples include operations such as Operation Neptune during World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War.

Operation Badr, also known as Plan Badr, was an Egyptian military offensive and operation across the Suez Canal that destroyed the Bar-Lev Line, a chain of Israeli fortifications along the frontline of the Israeli-occupied Sinai Peninsula, on 6 October 1973. It was launched in conjunction with a Syrian military offensive against the Israeli-occupied Golan Heights, triggering the Yom Kippur War. During the War of Attrition, which preceded Operation Badr, both Egypt and Syria had been seeking to recover the territories that Israel had captured from them during the 1967 Arab–Israeli War.
An airhead is a designated area in a hostile or threatened territory which, when seized and held, allows the air landing of further teams and materiel via an airbridge, and provides the maneuver and preparation space necessary for projected operations. Normally, it is the area seized in the assault phase of an airborne operation. It may also be used as a staging or refueling point for less permanent operations.

Modlin Fortress is one of the largest 19th-century fortresses in Poland. It is located in the town of Nowy Dwór Mazowiecki in district Modlin on the Narew river, approximately 50 kilometers north of Warsaw. It was originally constructed by the French from 1806 to 1812.

Coastal artillery is the branch of the armed forces concerned with operating anti-ship artillery or fixed gun batteries in coastal fortifications. In modern times, coastal artillery has generally been replaced with anti-ship missiles, such as the Ukrainian R-360 Neptune.

The Ludendorff Bridge was a bridge across the river Rhine in Germany which was captured by United States Army forces in early March 1945 during the Battle of Remagen, in the closing weeks of World War II, when it was one of the few remaining bridges in the region and therefore a critical strategic point. Built during World War I to help deliver reinforcements and supplies to German troops on the Western Front, it connected Remagen on the west bank and the village of Erpel on the east bank between two hills flanking the river.

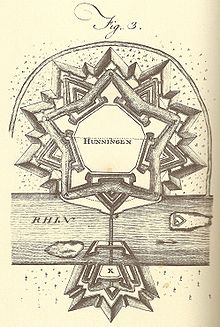
A bastion fort or trace italienne is a fortification in a style that evolved during the early modern period of gunpowder when the cannon came to dominate the battlefield. It was first seen in the mid-fifteenth century in Italy. Some types, especially when combined with ravelins and other outworks, resembled the related star fort of the same era.

A landing operation is a military operation during which a landing force, usually utilizing landing craft, is transferred to land with the purpose of power projection ashore. With the proliferation of aircraft, a landing may refer to amphibious forces, airborne forces, or a combination of both.

Operation Lumberjack was a military operation with the goal of capturing the west bank of the Rhine River and seizing key German cities, near the end of World War II in Europe. The First United States Army launched the operation in March 1945 to capture strategic cities in Nazi Germany and to give the Allies a foothold along the Rhine.

The Battle of the Dnieper was a military campaign that took place in 1943 on the Eastern Front of World War II. Being one of the largest operations of the war, it involved almost four million troops at one point and stretched over a 1,400 kilometres (870 mi) front. Over four months, the eastern bank of the Dnieper was recovered from German forces by five of the Red Army's fronts, which conducted several assault river crossings to establish several lodgements on the western bank. Kiev was later liberated in the Battle of Kiev. 2,438 Red Army soldiers were awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union for their involvement.

The Western Allied invasion of Germany was coordinated by the Western Allies during the final months of hostilities in the European theatre of World War II. In preparation for the Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine, a series of offensive operations were designed to seize and capture its east and west banks: Operation Veritable and Operation Grenade in February 1945, and Operation Lumberjack and Operation Undertone in March 1945; these are considered separate from the main invasion operation. The Allied invasion of Germany east of the Rhine started with the Western Allies crossing the river on 22 March 1945 before fanning out and overrunning all of western Germany from the Baltic in the north to the Alpine passes in the south, where they linked up with troops of the U.S. Fifth Army in Italy. Combined with the capture of Berchtesgaden, any hope of Nazi leadership continuing to wage war from a so-called "national redoubt" or escape through the Alps was crushed, shortly followed by unconditional German surrender on 8 May 1945. This is known as the Central Europe Campaign in United States military histories.

The Battle of Remagen was an 18-day battle during the Allied invasion of Germany in World War II. It lasted from 7 to 25 March 1945 when American forces unexpectedly captured the Ludendorff Bridge over the Rhine intact. They were able to hold it against German opposition and build additional temporary crossings. The presence of a bridgehead across the Rhine advanced by three weeks the Western Allies' planned crossing of the Rhine into the German interior.

Sapping is a term used in siege operations to describe the digging of a covered trench to approach a besieged place without danger from the enemy's fire. The purpose of the sap is usually to advance a besieging army's position towards an attacked fortification. It is excavated by specialised military units, whose members are often called sappers.

The Battle of Oltenița was fought on 4 November 1853 and was the first engagement of the Crimean War. In this battle an Ottoman army under the command of Omar Pasha was defending its fortified positions from the Russian forces led by General Peter Dannenberg, until the Russians were ordered to withdraw. The Russian attack was called off just when they reached the Ottoman fortifications, and they retreated in good order, but suffered heavy losses. The Ottomans held their positions, but did not pursue the enemy, and later retreated to the other side of Danube.

The siege of Kehl lasted from 26 October 1796 to 9 January 1797. Habsburg and Württemberg regulars numbering 40,000, under the command of Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour, besieged and captured the French-controlled fortifications at the village of Kehl in the German state of Baden-Durlach. The fortifications at Kehl represented an important bridgehead crossing the Rhine to Strasbourg, an Alsatian city, a French Revolutionary stronghold. This battle was part of the Rhine Campaign of 1796, in the French Revolutionary War of the First Coalition.
The 110th Guards Rifle Division was formed as an elite infantry division of the Red Army from July into September 1943, based on the 5th Guards Rifle Brigade and the 7th Guards Rifle Brigade and was the third of a small series of Guards divisions formed on a similar basis. It would follow a very similar combat path to the 108th and 109th Guards Rifle Divisions and would serve well into the postwar era.
The Battle of Cibakháza was one of the several battles for the bridge over the Tisza river from Cibakháza in the Hungarian war of Independence of 1848-1849, fought on 24 February 1849 between the Hungarian troops defending the bridge led by Major Károly Leiningen-Westerburg and the troops of the Austrian Empire, led by Major General Ferenc Ottinger, who were trying to capture and destroy it, in order to prevent the Hungarian incursions on the right bank of the river. The Hungarians defeated the Austrians, forcing Ottinger to retreat. The Hungarians managed to keep the bridge, which continued to remain a danger for the Austrian possessions on the right baank of the Tisza. One of the consequences of this thing was the Hungarian victory in the Second Battle of Szolnok in which, after crossing the bridge of Cibakháza, the Hungarian army surprised the Austrian garrison from Szolnok.