Definition
According to the US Army, the definition of overmatch is "the concept where my (insert lethality system here) can willfully and without prejudice or luck defeat your (insert your protective system here)." [4]
According to Raytheon, overmatch is a verb which means "to defeat threats at every level – strategic, tactical and technological." [5]
According to Ben Barry, "overmatch is a very polite, clinical way of saying could be defeated.” [6]
Example — AI versus human pilots
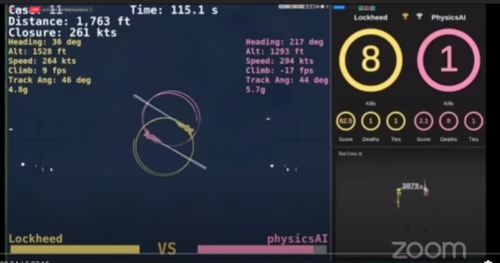
AI agents are not subject to the physiological constraints of a human pilot, such as the danger of flying at low altitude, or the g-forces of the aircraft accelerations. Human pilots noted that the AI agents flew with fine motor control. In the 2020 AlphaDogfight Trials (see image to the right), the AI agents battled for the chance to dogfight an expert human pilot. The winning AI agent consistently defeated an expert human pilot. [7] The technology will be installed in actual aircraft by 2024. [8] [9] [10]
Note: DoD's Joint AI Center (JAIC) has convened 100 online participants from 13 countries to discuss how to use AI in a way that is consonant with their national ethical principles, termed the 'AI Partnership for Defense' in 2020. [11] [9] [12]
One possible application is to elevate the role of human pilots to mission commanders, leaving AIs as wingmen to perform as high-skill operators of low-cost robotic craft. [10] [7] [13]
History
From 2017, after the Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, and the dismissal of the need for counter-insurgency for a second time, the US Army emphasized overmatch in their modernization effort. [14]
In 2017 a task force was formed to modernize the Army. Its recommendation was to form the Army Futures Command, to engage in systematic development of capabilities to overmatch its adversaries. [15]
In 2021 the 40th Chief of Staff of the Army identified [16]
"Overmatch will belong to the side that can make decisions faster. To meet emerging challenges, the Army is transforming to provide the joint force with speed, range, and convergence of cutting edge technologies that will generate the decision dominance and overmatch required to win the next fight.”
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.