
The Cierva C.30 is an autogyro designed by Juan de la Cierva and built under licence from the Cierva Autogiro Company by A V Roe & Co Ltd (Avro), Lioré-et-Olivier and Focke-Wulf.

A foot-launched powered hang glider (FLPHG), also called powered harness, nanolight, or hangmotor, is a powered hang glider harness with a motor and propeller in pusher configuration. An ordinary hang glider is used for its wing and control frame, and the pilot can foot-launch from a hill or from flat ground, needing a length of about a football field to get airborne, or much less if there is an oncoming breeze and no obstacles.

The Blériot V was an early French aircraft built by Louis Blériot in 1907 and was his first monoplane. Although Blériot only achieved a couple of short flights in it, the second resulting in a crash which damaged the aircraft beyond repair, it was the first of his experimental aircraft to achieve any measure of success.

The Avro Type E, Type 500, and Type 502 made up a family of early British military aircraft, regarded by Alliott Verdon Roe as his firm's first truly successful design. It was a forerunner of the Avro 504, one of the outstanding aircraft of the First World War.

The Siebel Si 202 Hummel ("Bumble-bee") was a German light sportsplane of the late 1930s. It was an angular low-wing monoplane, which could be powered by a variety of small engines.

The Scheibe SF-25 Falke is a German touring motor glider developed from the earlier Bergfalke glider by Scheibe Flugzeugbau. Since May 2006 the business has been run by Scheibe Aircraft GmbH.
The RAE Hurricane was a single-seat, single-engined light monoplane designed and built by the Aero Club of the Royal Aircraft Establishment for the 1923 Lympne Motor Glider Competition. It was underpowered with an unreliable engine. Re-engined, it flew in many races, with first place in the 1926 Grosvenor Challenge Cup its greatest success.
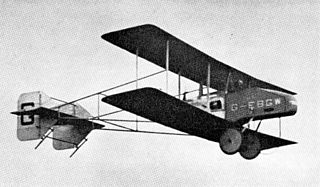
The RAE Zephyr was a single-seat, single-engined light pusher configuration biplane designed and built by the Aero Club of the Royal Aircraft Establishment (RAE) for the 1923 Lympne Motor Glider Competition. At a late stage the Aero Club chose to enter the more promising RAE Hurricane instead, using the Zephyr's engine, and the Zephyr itself was abandoned.

The Farman Moustique is a family of French monoplanes built by the Société des Aéroplanes Henry et Maurice Farman at Billancourt.

The Farman FF 65 Sport was a French built light biplane, with a single engine and tandem seats, intended for sport and touring. First flown in 1919, it achieved modest sales at home and abroad in the early 1920s. Two unusual modifications produced a biplane glider and a low aspect ratio parasol wing machine.

The Gabardini monoplane was a successful early monoplane constructed in Italy which made several notable flights, often carrying passengers, just before World War I. During the war, a number of lower-powered Gabardini monoplanes served as a training aircraft for the military.
The Bonomi BS.19 Alca was a single seat, tractor configuration motor glider, designed and built in Italy shortly before World War II. It had an unusual retractable undercarriage used only for take-offs. Only one was built.
The Bonomi BS.22 Alzavola was a training motor glider, intended to acquaint capable glider pilots with the characteristics of powered aircraft. The sole example was designed and built in Italy in the mid-1930s.
The VFW-Fokker FK-3 is a single seat competition glider, built in Germany in the late 1960s. It had success at the Italian and Austrian national contests of 1968, resulting in a short production run the following year.
The IIL IS-9 was a low powered, experimental pod and boom style motor glider, designed and built in Romania in the late 1950s.

The Daimler L15, sometimes later known as the Daimler-Klemm L15 or the Klemm-Daimler L15 was an early two-seat low-powered light aircraft intended to popularise flying. In mid-career it flew as a glider.

The Potez VIII was a French training aircraft which first flew in 1920. Originally it had a very unusual vertical inline engine and a four-wheeled undercarriage, though the production version was more conventional.
The AMA, named after its designers, was a one-off motor glider built in Poland in the mid-1930s. Its development was abandoned after early tests revealed incurable engine-mounting vibration problems.
The MIP Smyk, MIP from the initials of its Polish designers with Smyk meaning Brat or Kid, was an aerodynamically refined motor glider designed and built at Warsaw Technical University from 1935.

The ITS-8 was a Polish twin-boom motor glider flown in 1936. Two prototypes were completed but production was prevented by the German invasion of Poland in 1939.













