
The University of Sussex is a public research university located in Falmer, East Sussex, England. It lies mostly within the city boundaries of Brighton and Hove. Its large campus site is surrounded by the South Downs National Park, and provides convenient access to central Brighton 5.5 kilometres (3.4 mi) away. The university received its royal charter in August 1961, the first of the plate glass university generation.

Brighton is a seaside resort and one of the two main areas of the city of Brighton and Hove in the county of East Sussex, England. It is located 47 miles (76 km) south of London. Archaeological evidence of settlement in the area dates back to the Bronze Age, Roman and Anglo-Saxon periods. The ancient settlement of "Brighthelmstone" was documented in the Domesday Book (1086). The town's importance grew in the Middle Ages as the Old Town developed, but it languished in the early modern period, affected by foreign attacks, storms, a suffering economy and a declining population. Brighton began to attract more visitors following improved road transport to London and becoming a boarding point for boats travelling to France. The town also developed in popularity as a health resort for sea bathing as a purported cure for illnesses.

Brighton and Hove is a unitary authority with city status in East Sussex, England. There are multiple villages alongside the seaside resorts of Brighton and Hove in the district. It is administered by Brighton and Hove City Council, which is currently under Labour majority control.

Falmer Stadium, known for sponsorship purposes as the American Express Stadium and more commonly referred to as the Amex, is a football stadium in Falmer, Brighton and Hove, East Sussex. With a capacity of 31,876, it is the second largest stadium in all of South East England, and the 31st largest stadium in the United Kingdom. The largest in South East England is St. Mary's Stadium (Southampton) with about 800 seats more.

Whitehawk is a suburb in the east of Brighton, England, south of Bevendean and north of Brighton Marina. The area is a large, modern housing estate built in a downland dry valley historically known as Whitehawk Bottom. The estate was originally developed by the local council between 1933 and 1937 and included nearly 1,200 residences. Subsequently, the Swanborough flats were built in 1967, and in the 1970s and 1980s much of the estate was rebuilt by altering the road layouts and increasing the number of houses. Whitehawk is part of the East Brighton ward of Brighton and Hove City Council.

The Royal Alexandra Children's Hospital is a children's hospital located within the grounds of the Royal Sussex County Hospital in Brighton on the south coast of England. It provides outpatient services, inpatient facilities, intensive care and a 24-hour emergency care service for children referred by GPs and other specialists. It is managed by University Hospitals Sussex NHS Foundation Trust.

The Royal Sussex County Hospital is an acute teaching hospital in Brighton, England. Together with the Princess Royal Hospital, it is administered by the University Hospitals Sussex NHS Foundation Trust. The services provided at the hospital include an emergency department, cancer services at the Sussex Cancer Centre, cardiac surgery, maternity services, and both adult and neonatal intensive care units. The hospital is served by Brighton & Hove bus routes 1, 7, 14B, 14C, 23, 27C, 71, 73 and 94A.

The LGBT community of Brighton and Hove is one of the largest in the United Kingdom. Brighton, a seaside resort on the south coast of England, has been described in some media as a "gay capital" of the UK, with records pertaining to LGBT history dating back to the early 19th century.

Brighton Fringe is an open-access arts festival held annually in Brighton, England. It is the largest annual arts festival in England and one of the largest fringe festivals in the world. The programme of 2018 included 1008 events at over 166 venues across 4 weeks, in May and June.

Hollingdean is a district in the city of Brighton & Hove. The Ward is called Hollingdean and Stanmer with a population of 15,681 at the 2011 Census. Hollingdean is in effect the older part of Hollingbury. It is bounded by Ditchling Road to the west, the Round Hill area to the south, and Lewes Road and Moulsecoomb to the east. It is a mainly residential area, with many council houses to the east and low-rise flats in the central part, with late 19th and early 20th-century terraced houses towards Fiveways, and some railway land, light industry, and warehousing.
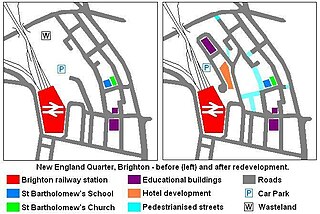
The New England Quarter is a mixed-use development in the city of Brighton and Hove, England. It was built between 2004 and 2008 on the largest brownfield site in the city, adjacent to Brighton railway station. Most parts of the scheme have been finished, but other sections are still being built and one major aspect of the original plan was refused planning permission.

Brighton Toy and Model Museum is an independent toy museum situated in Brighton, East Sussex. Its collection focuses on toys and models produced in the UK and Europe up until the mid-Twentieth Century, and occupies four thousand square feet of floor space within four of the early Victorian arches supporting the forecourt of Brighton railway station. Founded in 1991, the museum holds over ten thousand toys and models, including model train collections, puppets, Corgi, Dinky, Budgie Toys, construction toys and radio-controlled aircraft.
The Sussex Partnership NHS Foundation Trust provides mental health and learning disability services to the people of Brighton & Hove, East Sussex and West Sussex. The trust also provide some community services in Hampshire for children and young people with mental health problem. They work in partnership with those who use their services, with their staff, with NHS and social care agencies and with the voluntary sector.

75 Holland Road in Hove, part of the English coastal city of Brighton and Hove, is now in residential use as loft-style apartments called Palmeira Yard, but was originally a repository belonging to the Brighton & Hove Co-operative Supply Association, the main cooperative business organisation in the area. Elaborately designed in 1893 in the French Second Empire style by local architect Thomas Lainson of the firm Lainson & Sons, the storage building had built-in stables and was lavishly decorated with terracotta. After a period of ownership by haulage and removals company Pickfords, who used the building for furniture storage, a local architecture firm carried out the conversion into mixed-use live-work units between 2004 and 2006. English Heritage has listed the building at Grade II for its architectural and historical importance.

Brighton Hippodrome is an entertainment venue in Brighton, England. It was built in 1897 and closed in 2007.

The Jubilee Library is the largest running public library in the English city of Brighton and Hove. The Jubilee Library forms part of the Jubilee Square development in central Brighton, as a £50 million endeavour to regenerate a 40-year-old brownfield site. Opened in 2005 by the Princess Royal, the library has won several architectural design awards, and on one occasion dubbed, "A triumph" by the Pevsner Architectural Guides. In terms of the number of daily visitors, the library is one of the busiest in England. The library brought together facilities previously housed in separate sites.

The Keep is a purpose-built archive and historical resource centre which stores, conserves and gives the public access to the records of its three managing partners: The East Sussex Record Office, The University of Sussex Special Collections, and Brighton & Hove Museums Local History Collections. The Keep also houses the library and office of the Sussex Family History Group, functions as headquarters of Friends of The Keep Archives, and holds the Historic Environment Record database for East Sussex. From November 2018, it has also functioned as the South East Hub for the Unlocking Our Sound Heritage project for The British Library. It was funded by East Sussex County Council, the City Council of neighbouring Brighton and Hove and the University of Sussex, and was built on land close to the university in the Moulsecoomb area of Brighton and Hove. The building, constructed with a budget of £19 million, opened on 31 October 2013, superseding the former East Sussex Record Office in the county town of Lewes.

The Astoria Theatre was a former cinema in Brighton, part of the English coastal city of Brighton and Hove. Built in 1933 in the Art Deco style for a local entertainment magnate who opened one of Brighton's first cinemas many years earlier, it was the first and most important expansion of the Astoria brand outside London. It initially struggled against the town's other "super-cinemas", but enjoyed a period of success in the 1950s and 1960s before rapid decline set in, culminating in its closure in 1977.
Thomas Simpson (1825–1908) was a British architect associated with the seaside town of Brighton. As architect to the Brighton and Preston School Board and the equivalent institution in neighbouring Hove, he designed "a distinguished group of board schools" during the late 19th century, when the provision of mass education was greatly extended. Many of these schools survive and some have listed status. He also worked on five Nonconformist chapels for various Christian denominations, using a wide variety of materials and architectural styles. He was the father of Sir John William Simpson and Gilbert Murray Simpson, who both became architects.
Brighton Photo Biennial (BPB), now known as Photoworks Festival, is a month-long festival of photography in Brighton, England, produced by Photoworks. The festival began in 2003 and is often held in October. It plays host to curated exhibitions across the city of Brighton and Hove in gallery and public spaces. Previous editions have been curated by Jeremy Millar (2003), Gilane Tawadros (2006), Julian Stallabrass (2008), Martin Parr (2010) and Photoworks (2012). Brighton Photo Biennial announced its merger with Photoworks in 2006 and in 2020 its name was changed to Photoworks Festival.
















