
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and congenital disorders.
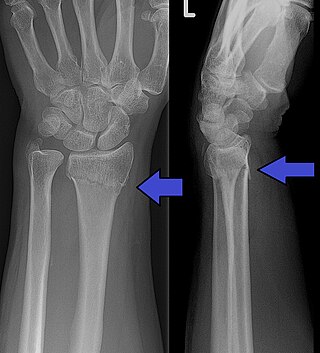
A Colles' fracture is a type of fracture of the distal forearm in which the broken end of the radius is bent backwards. Symptoms may include pain, swelling, deformity, and bruising. Complications may include damage to the median nerve.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a comminuted fracture. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.

A distal radius fracture, also known as wrist fracture, is a break of the part of the radius bone which is close to the wrist. Symptoms include pain, bruising, and rapid-onset swelling. The ulna bone may also be broken.

A Smith's fracture, is a fracture of the distal radius.
Hand surgery deals with both surgical and non-surgical treatment of conditions and problems that may take place in the hand or upper extremity including injury and infection. Hand surgery may be practiced by post graduates of orthopedic surgery and plastic surgery.

A scaphoid fracture is a break of the scaphoid bone in the wrist. Symptoms generally includes pain at the base of the thumb which is worse with use of the hand. The anatomic snuffbox is generally tender and swelling may occur. Complications may include nonunion of the fracture, avascular necrosis of the proximal part of the bone, and arthritis.
Anterior interosseous syndrome is an idiopathic medical condition of the anterior interosseous nerve (AIN), a distal motor and sensory branch of the median nerve. The findings are weakness in bending (flexion) the tips of the thumb and index finger.

A supracondylar humerus fracture is a fracture of the distal humerus just above the elbow joint. The fracture is usually transverse or oblique and above the medial and lateral condyles and epicondyles. This fracture pattern is relatively rare in adults, but is the most common type of elbow fracture in children. In children, many of these fractures are non-displaced and can be treated with casting. Some are angulated or displaced and are best treated with surgery. In children, most of these fractures can be treated effectively with expectation for full recovery. Some of these injuries can be complicated by poor healing or by associated blood vessel or nerve injuries with serious complications.

Sean Patrick Francis Hughes is emeritus professor of orthopaedic surgery at Imperial College London where he was previously professor of orthopaedic surgery and head of the department of surgery, anaesthetics and intensive care. Earlier in his career he had been professor of orthopaedic surgery at the University of Edinburgh.

Sir Robert Jones, 1st Baronet, was a Welsh orthopaedic surgeon who helped to establish the modern specialty of orthopaedic surgery in Britain.

Kantilal H. Sancheti is an orthopaedic physician who invented India's first indigenous knee implant, the Indus Knee, and founder of Maharashtra's first orthopaedic dedicated specialty hospital.

Carpal tunnel surgery, also called carpal tunnel release (CTR) and carpal tunnel decompression surgery, is a nerve decompression in which the transverse carpal ligament is divided. It is a surgical treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) and recommended when there is constant (not just intermittent) numbness, muscle weakness, or atrophy, and when night-splinting no longer controls intermittent symptoms of pain in the carpal tunnel. In general, milder cases can be controlled for months to years, but severe cases are unrelenting symptomatically and are likely to result in surgical treatment. Approximately 500,000 surgical procedures are performed each year, and the economic impact of this condition is estimated to exceed $2 billion annually.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trauma and orthopaedics:
The American Society of Maxillofacial Surgeons (ASMS) is a professional organization focused on the science and practice of surgery of the facial region and craniofacial skeleton. The organization is involved in education, research, and advocacy on behalf of patients and maxillofacial surgeons.
The National Hip Fracture Database (NHFD) is a nationwide audit within the NHS concerning the management and outcomes of patients with hip fractures.
Patrick Wensley Clarkson,, was a plastic surgeon at Guy's Hospital in London, best known for surgery of the hand and the description of "Poland Syndactyly", later termed Poland syndrome.
Hugh Graham Stack FRCS was a British orthopaedic surgeon with a specialism in surgery of the hand. He was secretary of the Second Hand Club and was instrumental in the merger of the British hand surgery organisations to become the British Society for Surgery of the Hand.

Raju Vaishya is an Indian researcher with contributions in the field of orthopaedics. He is former President and founder member of Indian Cartilage Society (2018–19) and Founder President of Arthritis Care Foundation. He has established a center for Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation (ACI) at Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, New Delhi, India. Instrumental (PSI) in starting the first cartilage club in Delhi, to enhance the awareness about the cartilage science and regenerative treatments used in Orthopaedics. He has the credit of doing the first preplan patient specific instruments (PSI) total knee arthroplasty, in Northern India in May 2013.

Christopher Lewis Colton is an English orthopaedic surgeon and Professor Emeritus in Orthopaedic and Accident Surgery at the University of Nottingham. He is a past president of both the British Orthopaedic Association and of the AO Foundation.












