Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and create clouds and, under the right conditions, precipitation.

Mount Hua is a mountain located near the city of Huayin in Shaanxi province, about 120 kilometres (75 mi) east of Xi'an. It is the western mountain of the Five Great Mountains of China, and has a long history of religious significance. Originally classified as having three peaks, in modern times the mountain is classified as five main peaks, of which the highest is the South Peak at 2,154.9 metres (7,070 ft).

Robinson is a fell in the English Lake District, its southern slopes descending to Buttermere, while its northern side is set in the Newlands Valley. Paths lead to the summit from the village of Buttermere, from the nearby summit Dale Head and from various locations in the valleys to the north.

Bynack More is a Scottish Mountain that is situated in the Cairngorms range, 16 kilometres east-south-east of the town of Aviemore in the Highland region.

Rusk Mountain is a peak located in the towns of Jewett and Lexington in Greene County, New York, United States. At 3,680 feet in elevation, it is the 20th-highest peak in the Catskill Mountains and considered a member of the Catskill High Peaks. While there is no maintained trail, a bushwhack to the summit is considered relatively easy, and required for membership in the Catskill Mountain 3500 Club.

Long Side is a fell in the English Lake District, it is situated six kilometres north west of Keswick in the northern sector of the national park and is part of the Skiddaw group of fells. Long Side which reaches a height of 734 m (2,408 ft) is located on Skiddaw’s north western ridge, the middle section of which is known as Longside Edge. Strictly speaking the actual summit of the fell is nameless with the name Long Side applying to the south western slope below the summit and is so marked on maps. The fell is often climbed by walkers on their way to the summit of Skiddaw, the route up the north west ridge which passes over Long Side is regarded as being the finest and quietest ascent of that 3,000-foot (910 m) mountain by guide book writers.

Mòruisg is a Scottish mountain situated in the Glencarron and Glenuig Forest, 10 kilometres south west of the village of Achnasheen in the Highland council area.

An Caisteal is a Scottish mountain situated six kilometres south of the village of Crianlarich in the Stirling Council area.

Halcott Mountain is one of the Catskill Mountains of the U.S. state of New York. It is mostly located in Greene County, with some of its lower slopes in Delaware and Ulster counties. Its exact summit elevation has not been officially determined, but the highest contour line on the mountain is 3,520 feet (1,070 m). It is one of the peaks on the divide between the Delaware and Hudson watersheds.

Plateau Mountain is located in the town of Hunter in Greene County, New York, United States. It is part of the Devil's Path range of the Catskill Mountains. Plateau has a two-mile-long (3.2 km) summit ridge above 3,500 feet (1,100 m). The highest point, at least 3,840 feet (1,170 m), is at the southeast end, facing Sugarloaf Mountain to the east across Mink Hollow Notch. It is the 12th-highest peak in the range Devils Tombstone is located west of Plateau Mountain. The northwest end faces Hunter Mountain to the west across 1,400-foot deep (430 m) Stony Clove Notch.

Graham Mountain is the seventh highest of the Catskill High Peaks and the highest privately owned mountain in the range. It is located in the town of Hardenburgh, New York, United States.
Rounds Mountain, 2,257 feet (688 m), is a prominent peak in the Taconic Mountains of western Massachusetts and adjacent New York. The west side of the mountain and summit are located in New York; the east side is located within Massachusetts. The summit a bald; the slopes are wooded with northern hardwood tree species. It is notable for its views of the Hudson River Valley to the west and the Green River and Kinderhook Creek valleys of Hancock, Massachusetts to the east. The 35 mi (56 km) Taconic Crest Trail traverses the mountain. Much of the upper slopes and summit are within protected conservation land.

Alander Mountain, 2,239 feet (682 m) is a prominent peak of the south Taconic Mountains; it is located in southwest Massachusetts and adjacent New York. Part of the summit is grassy and open and part is covered with scrub oak and shrubs; the sides of the mountain are wooded with northern hardwood tree species. Views from the top include the southern Taconic Mountains, the Hudson River Valley including the Catskills. Several trails traverse Alander Mountain, most notably the 15.7 mi (25.3 km) South Taconic Trail, which passes just beneath the summit.

Sgùrr Ghiubhsachain is a mountain in the Lochaber area in the west of Scotland. Its summit is the highest point in a group of mountains that stand south of Glenfinnan, to the south east of the northern part of Loch Shiel. It is considerably lower than the nearby Nevis range, but it is a long way from a public road. Its slopes are steep and rugged on all sides and are devoid of paths. Despite easy access to the trail head from the road from Fort William to Mallaig, an individual or party that climbs this mountain may be alone there, even on a fine day in the summer.

Mount Tremper, officially known as Tremper Mountain and originally called Timothyberg, is one of the Catskill Mountains in the U.S. state of New York. It is located near the hamlet of Phoenicia, in the valley of Esopus Creek.
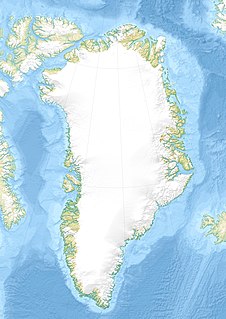
Palasip Qaqqaa is a 544-metre-high (1,785 ft) mountain in the Qeqqata municipality in western Greenland. It is located on the mainland of Greenland on the coast of Davis Strait, immediately to the north of Sisimiut Airport.

Hay Bluff is a prominent hill at the northern tip of the Black Mountains, an extensive upland massif which straddles the border between south-east Wales and England. The mountain sits on an escarpment which faces north and runs roughly east–west, the next peak in the west being the Twmpa. The flat summit of Hay bluff overlooks the middle Wye Valley and the book town of Hay-on-Wye is marked by a triangulation pillar at a height of 677 metres (2,221 ft).

The Petersköpfl is a 1,745m high summit in the Zahmer Kaiser, the northern ridge of the Kaisergebirge mountain range in the Austrian state of Tyrol. To the east the Petersköpfl is linked by a ridge to the Einserkogel, to the west it is separated from the Naunspitze by a wind gap. To the south it falls steeply into the Kaisertal valley and to the north its steep rock faces tower above Ebbs. To the east there is a gently sloping plateau covered with mountain pine that forms the main ridge of the Zahmer Kaiser and runs up to the Pyramidenspitze.