
The government budget balance, also referred to as the general government balance, public budget balance, or public fiscal balance, is the difference between government revenues and spending. For a government that uses accrual accounting the budget balance is calculated using only spending on current operations, with expenditure on new capital assets excluded. A positive balance is called a government budget surplus, and a negative balance is a government budget deficit. A government budget presents the government's proposed revenues and spending for a financial year.

A budget is a calculation plan, usually but not always financial, for a defined period, often one year or a month. A budget may include anticipated sales volumes and revenues, resource quantities including time, costs and expenses, environmental impacts such as greenhouse gas emissions, other impacts, assets, liabilities and cash flows. Companies, governments, families, and other organizations use budgets to express strategic plans of activities in measurable terms.

The Stability and Growth Pact (SGP) is an agreement, among all the 27 member states of the European Union (EU), to facilitate and maintain the stability of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). Based primarily on Articles 121 and 126 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, it consists of fiscal monitoring of member states by the European Commission and the Council of the European Union, and the issuing of a yearly Country-Specific Recommendation for fiscal policy actions to ensure a full compliance with the SGP also in the medium-term. If a member state breaches the SGP's outlined maximum limit for government deficit and debt, the surveillance and request for corrective action will intensify through the declaration of an Excessive Deficit Procedure (EDP); and if these corrective actions continue to remain absent after multiple warnings, a member state of the eurozone can ultimately also be issued economic sanctions. The pact was outlined by a European Council resolution in June 1997, and two Council regulations in July 1997. The first regulation "on the strengthening of the surveillance of budgetary positions and the surveillance and coordination of economic policies", known as the "preventive arm", entered into force 1 July 1998. The second regulation "on speeding up and clarifying the implementation of the excessive deficit procedure", sometimes referred to as the "dissuasive arm" but commonly known as the "corrective arm", entered into force 1 January 1999.
The public sector budget of Germany is divided among the administrative divisions of the country.

The Union Budget of India, also referred to as the Annual Financial Statement in Article 112 of the Constitution of India. It is the annual budget of the Republic of India set by Ministry of Finance for the following financial year, with the revenues to be gathered by Department of Revenue to identify planned government spending and expected government revenue and the expenditures gathered by Department of Expenditure of the public sector, to forecast economic conditions in compliance with government policy.

The budget of the European Union is used to finance EU funding programmes and other expenditure at the European level.

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. CBO estimated in February 2024 that Federal debt held by the public is projected to rise from 99 percent of GDP in 2024 to 116 percent in 2034 and would continue to grow if current laws generally remained unchanged. Over that period, the growth of interest costs and mandatory spending outpaces the growth of revenues and the economy, driving up debt. Those factors persist beyond 2034, pushing federal debt higher still, to 172 percent of GDP in 2054.
A government policy statement is a declaration of a government's political activities, plans and intentions relating to a concrete cause or, at the assumption of office, an entire legislative session. In certain countries they are announced by the head of government or a minister of the parliament. In constitutional monarchies, this function may be fulfilled by the Speech from the Throne.
A government budget or a budget is a projection of the government's revenues and expenditure for a particular period of time often referred to as a financial or fiscal year, which may or may not correspond with the calendar year. Government revenues mostly include taxes while expenditures consist of government spending. A government budget is prepared by the Central government or other political entity. In most parliamentary systems, the budget is presented to the legislature and often requires approval of the legislature. Through this budget, the government implements economic policy and realizes its program priorities. Once the budget is approved, the use of funds from individual chapters is in the hands of government ministries and other institutions. Revenues of the state budget consist mainly of taxes, customs duties, fees and other revenues. State budget expenditures cover the activities of the state, which are either given by law or the constitution. The budget in itself does not appropriate funds for government programs, hence need for additional legislative measures. The word budget comes from the Old French bougette.

Prinsjesdag is the day on which the reigning monarch of the Netherlands addresses a joint session of the States-General of the Netherlands to give the Speech from the Throne, similar to the annual State of the Union in the United States or the British State Opening of Parliament. This speech sets out the main features of government policy for the coming parliamentary session.

Canadian public debt, or general government debt, is the liabilities of the government sector. Government gross debt consists of liabilities that are a financial claim that requires payment of interest and/or principal in future. They consist mainly of Treasury bonds, but also include public service employee pension liabilities. Changes in debt arise primarily from new borrowing, due to government expenditures exceeding revenues.
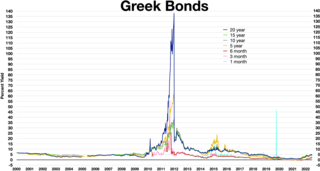
Greece faced a sovereign debt crisis in the aftermath of the financial crisis of 2007–2008. Widely known in the country as The Crisis, it reached the populace as a series of sudden reforms and austerity measures that led to impoverishment and loss of income and property, as well as a humanitarian crisis. In all, the Greek economy suffered the longest recession of any advanced mixed economy to date and became the first developed country whose stock market was downgraded to that of an emerging market in 2013. As a result, the Greek political system was upended, social exclusion increased, and hundreds of thousands of well-educated Greeks left the country.

The Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) is a non-departmental public body funded by the UK Treasury, that the UK government established to provide independent economic forecasts and independent analysis of the public finances. It was formally created in May 2010 following the general election and was placed on a statutory footing by the Budget Responsibility and National Audit Act 2011. It is one of a growing number of official independent fiscal watchdogs around the world.

The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003 (FRBMA) is an Act of the Parliament of India to institutionalize financial discipline, reduce India's fiscal deficit, improve macroeconomic management and the overall management of the public funds by moving towards a balanced budget and strengthen fiscal prudence. The main purpose was to eliminate revenue deficit of the country and bring down the fiscal deficit to a manageable 3% of the GDP by March 2008. However, due to the 2007 international financial crisis, the deadlines for the implementation of the targets in the act was initially postponed and subsequently suspended in 2009. In 2011, given the process of ongoing recovery, Economic Advisory Council publicly advised the Government of India to reconsider reinstating the provisions of the FRBMA. N. K. Singh is currently the Chairman of the review committee for Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003, under the Ministry of Finance (India), Government of India.

Roelof Johannes Nelissen was a Dutch politician of the defunct Catholic People's Party (KVP) now merged into the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA) party and businessman.
Government spending in the United Kingdom, also referred to as public spending, is the total spent by Central Government departments and certain other bodies as authorised by Parliament through the Estimates process. It includes net spending by the three devolved governments: the Scottish Government, the Welsh Government and the Northern Ireland Executive.

The federal budget of Russia is the leading element of the budget system of Russia. The federal budget is a major state financial plan for the fiscal year, which has the force of law after its approval by the Russian parliament and signed into law by the President of Russia. That the federal budget is the primary means of redistribution of national income and gross domestic product through it mobilized the financial resources necessary to regulate the country's economic development, social policy and the strengthening of the national defense. The share of federal budget accounts for a significant portion of the distribution process, which is the allocation of funds between sectors of the economy, manufacturing and industrial areas, regions of the country.

Paul Johannes George (Paul) Tang is a Dutch economist and politician on behalf of the Dutch Labour Party.

Accountability Day ) is the day in the Netherlands when the national government and ministries present their annual reports to the House of Representatives. On the same day, the Court of Audit publishes its report on the inspections of those annual reports. Accountability Day is held every year on the third Wednesday in May. The annual reports not only account for how much money has been spent and on what; the specific goals that were envisioned, and to what degree they have been achieved in the past year, are also discussed.
The Canadian federal budget for fiscal year 1988–1989 was presented to the House of Commons of Canada by finance minister Michael Wilson on 10 February 1988. It was the fourth budget after the 1984 Canadian federal election and would be the last before the 1988 Canadian federal election.













